diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore
index f2f3f468f..1332a6de3 100644
--- a/.gitignore
+++ b/.gitignore
@@ -22,4 +22,4 @@ npm-debug.log*
yarn-debug.log*
yarn-error.log*
-checkEmptyOrHeadingFiles.mjs
+checkEmptyOrHeadingFiles.mjsgit
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/README.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/README.md
index c038a9d21..097c47a00 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/README.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/README.md
@@ -6,8 +6,6 @@ hide_table_of_contents: true
Access can be granted to a user via:
-* [SSO Login Services](../sso-login.md)
-
* [User Permissions](user-access.md)
* [Permission Groups](permission-groups.md)
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens.md
index 401f81de7..cf9432b2f 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/api-tokens.md
@@ -6,21 +6,21 @@ API tokens are the access tokens for authentication. Instead of using username a
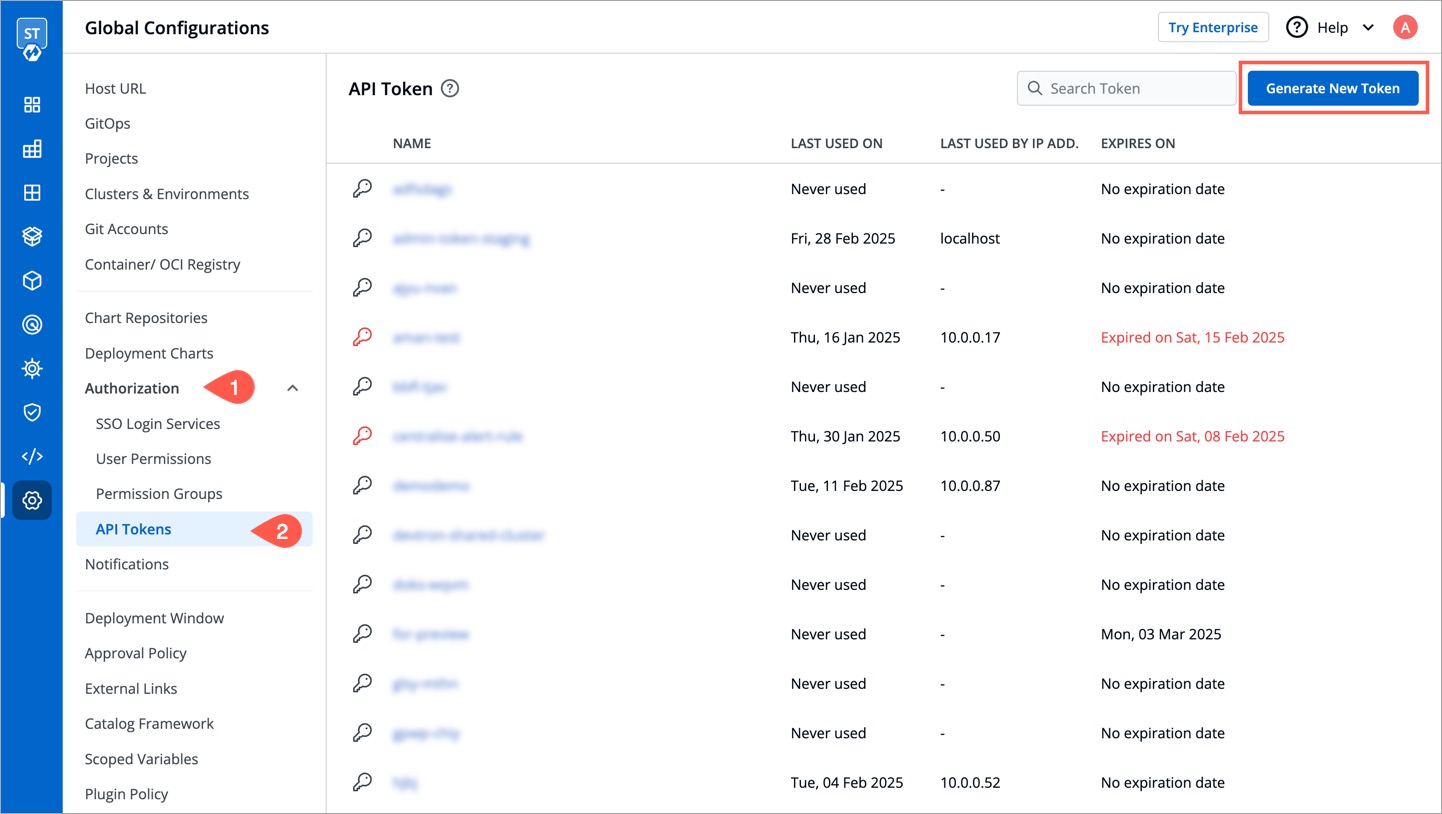
To generate API tokens, go to `Global Configurations -> Authorization -> API tokens` and click `Generate New Token`.
-
-
* Enter a name for the token.
* Add Description.
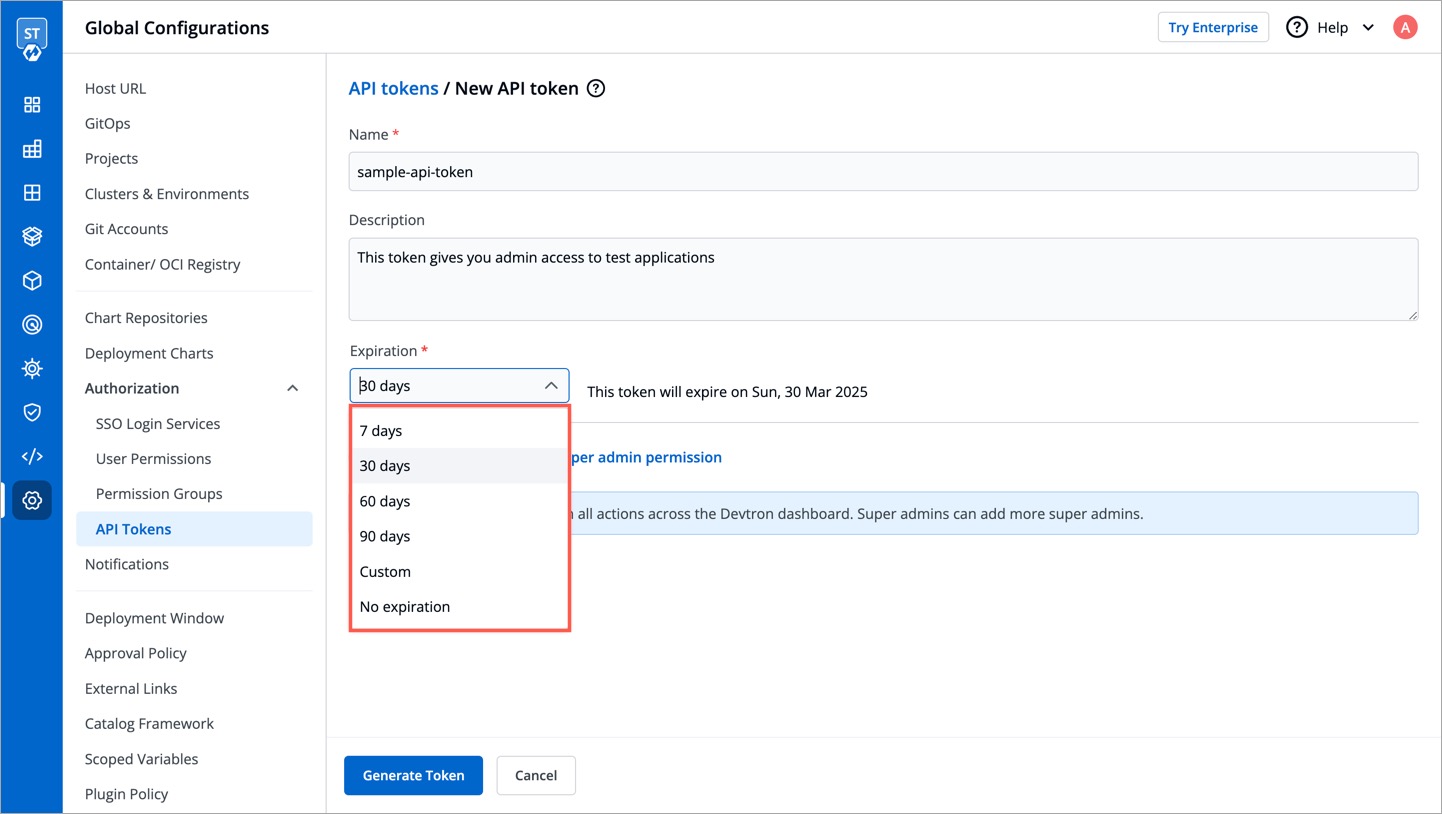
* Select an expiration date for the token (7 days, 30 days, 60 days, 90 days, custom and no expiration).
-
-
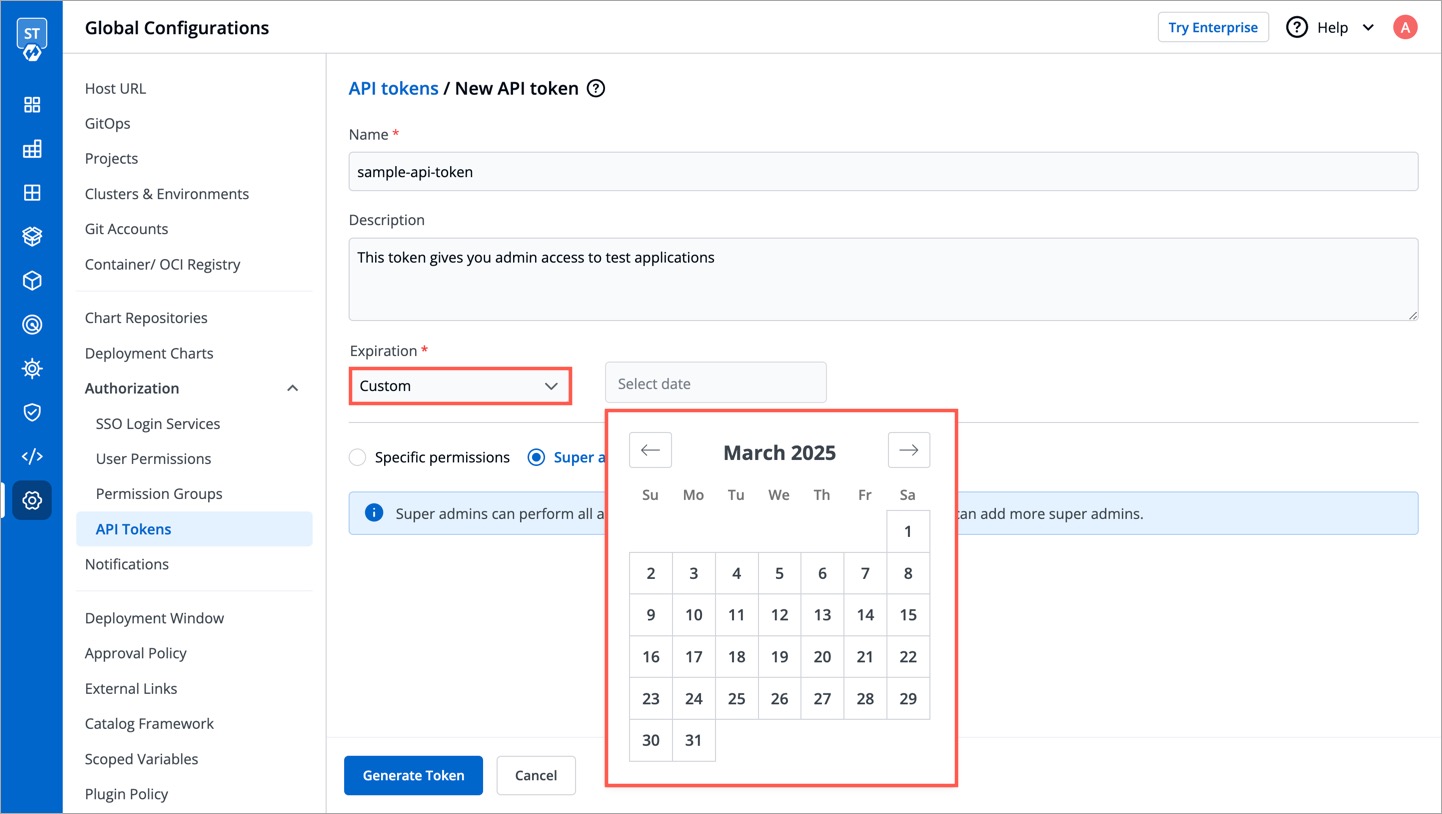
* To select a custom expiration date, select `Custom` from the drop-down list. In the adjacent field, you can select your custom expiration date for the API token.
-
-
* You can assign permission to the token either with:
@@ -30,16 +30,16 @@ To generate API tokens, go to `Global Configurations -> Authorization -> API tok
* **Specific permissions**: Selecting `Specific permissions` option allows you to generate a token with a specific role for:
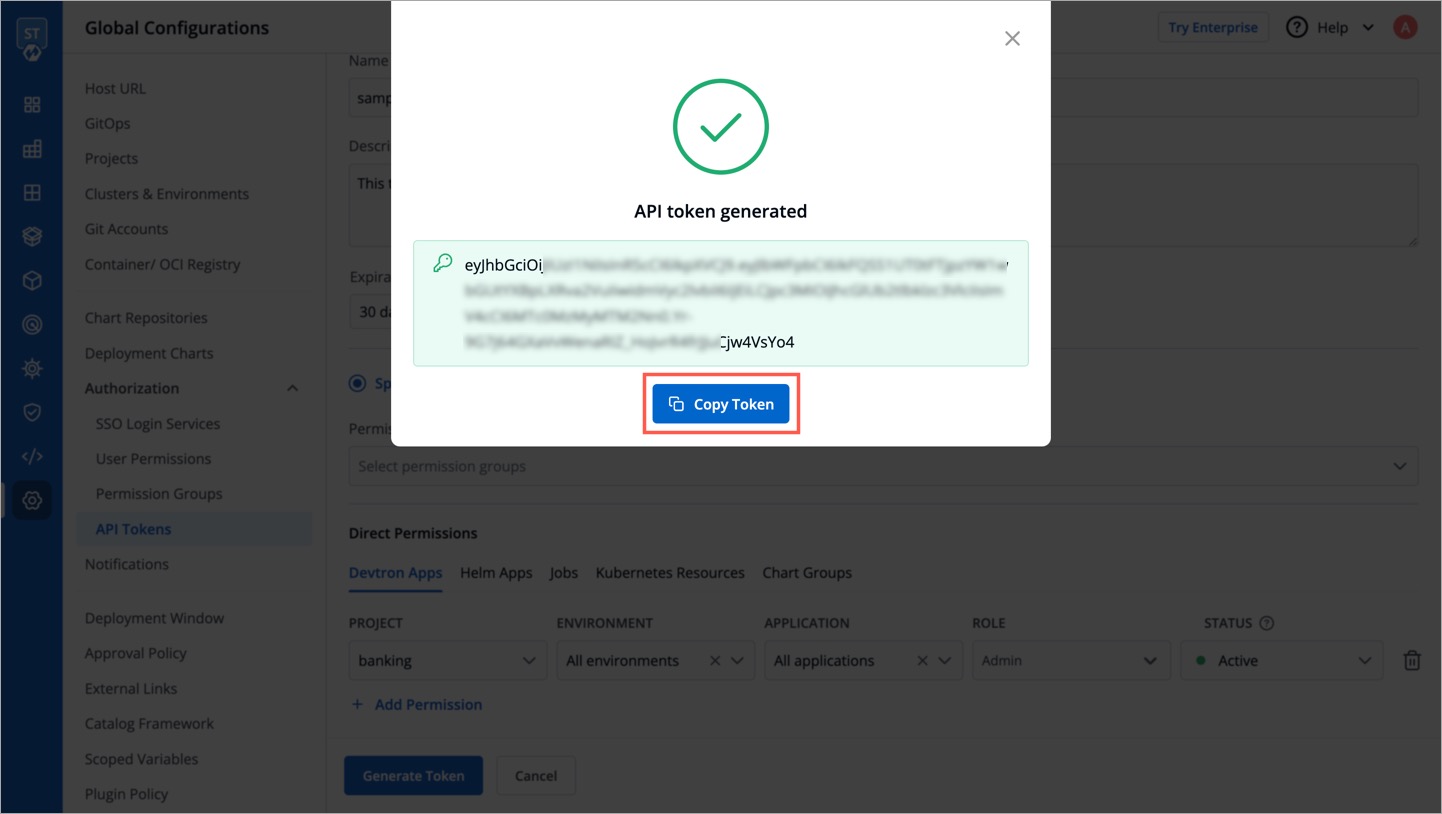
* Click `Generate Token`.
A pop-up window will appear on the screen from where you can copy the API token.
-
-
## Use API Token
@@ -47,19 +47,19 @@ Once Devtron API token has been generated, you can use this token to request Dev
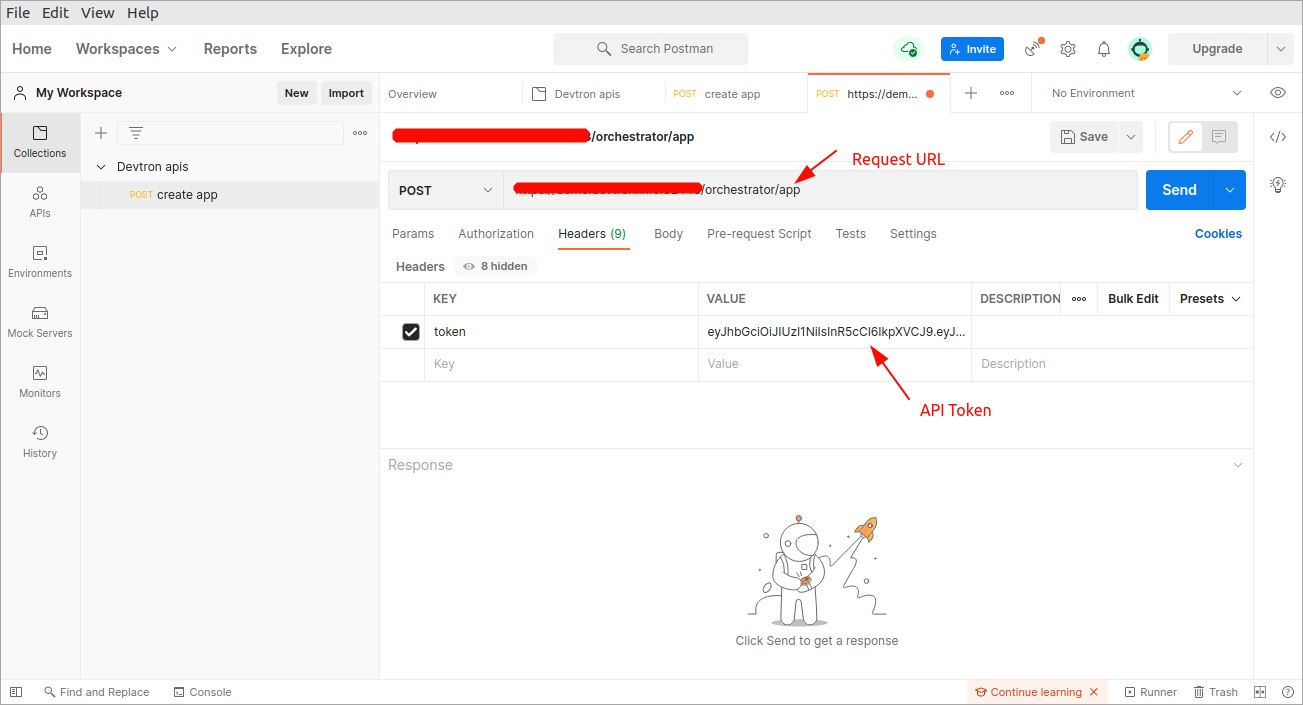
Open Postman. Enter the request URL with `POST` method and under HEADERS, enter the API token as shown in the image below.
-
-
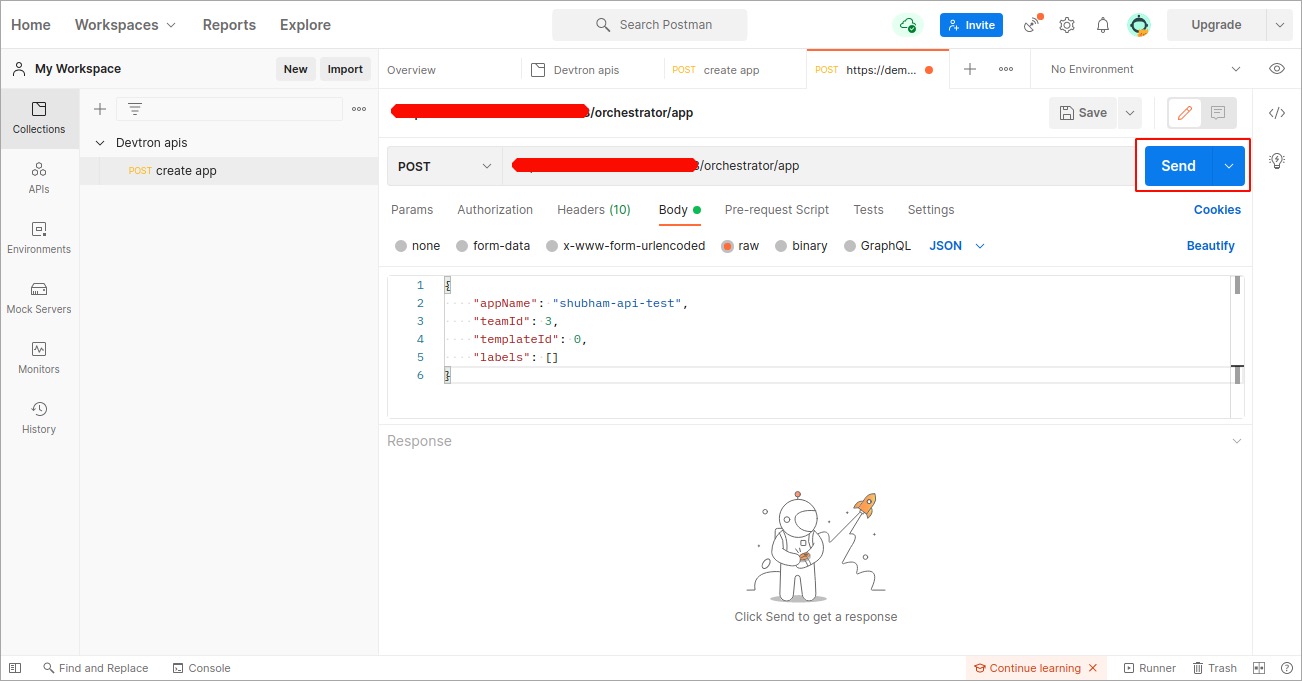
In the `Body` section, provide the API payload as shown below and click `Send`.
-
-
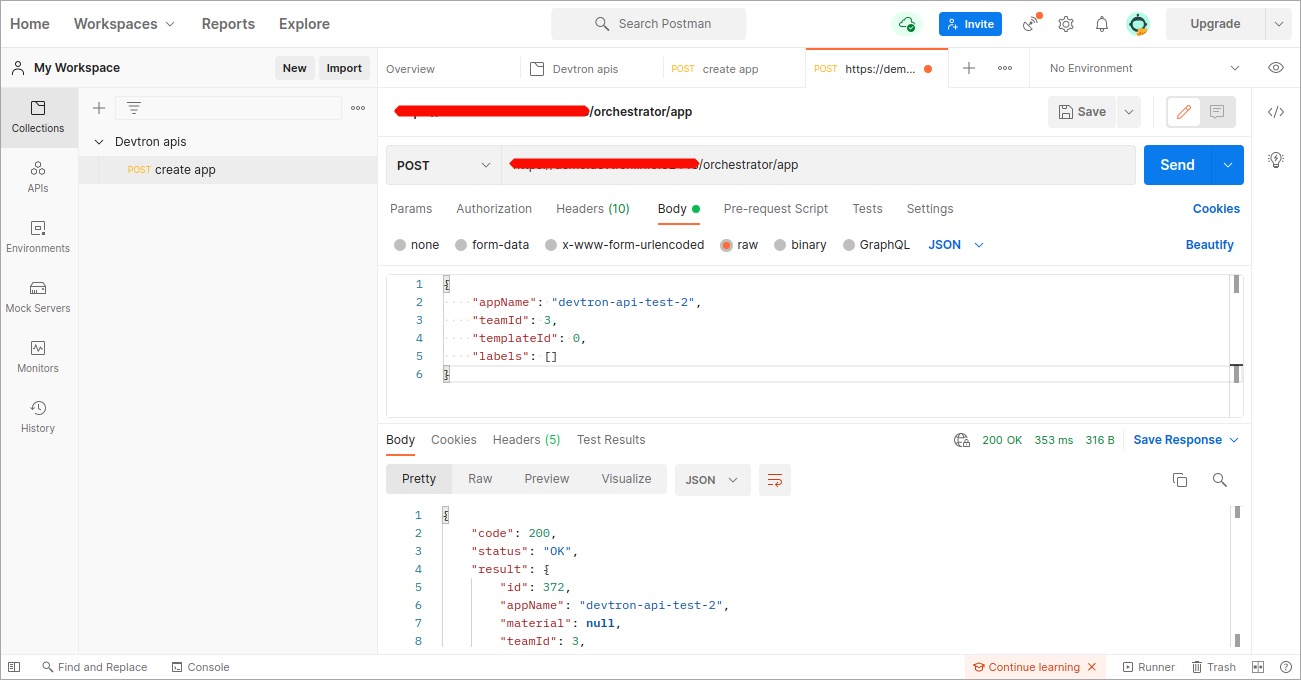
As soon as you click `Send`, the created application API will be triggered and a new Devtron app will be created as provided in the payload.
-
-
## Update API Token
@@ -67,27 +67,27 @@ As soon as you click `Send`, the created application API will be triggered and a
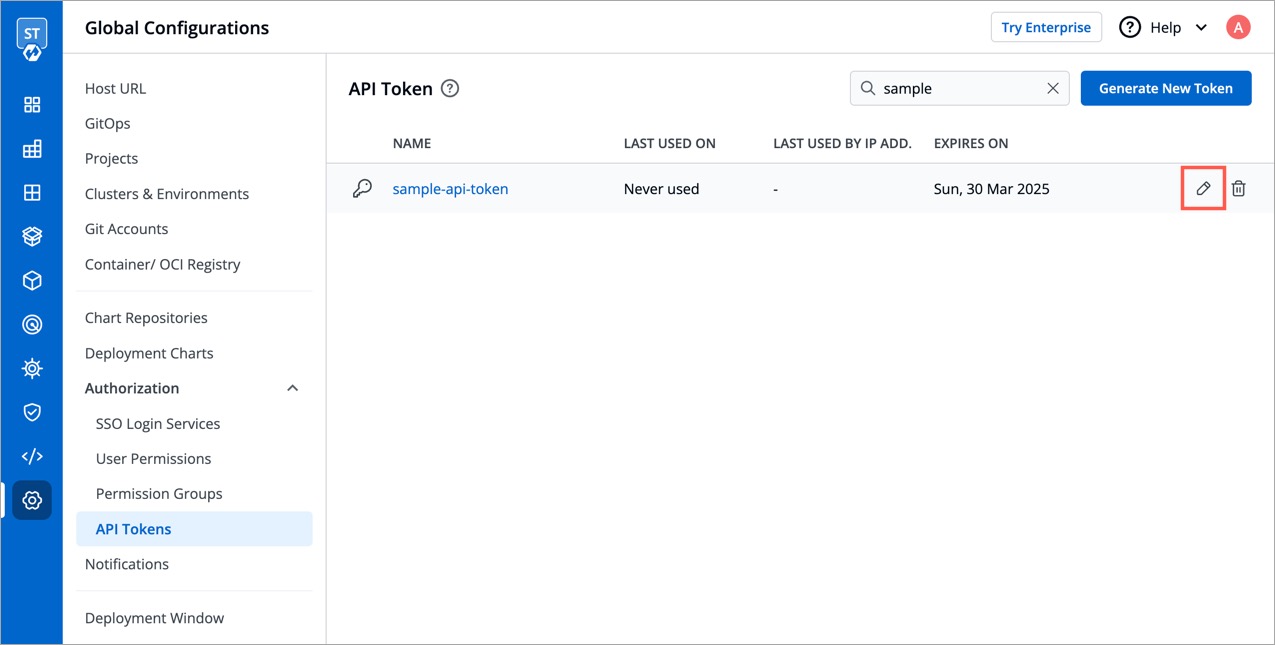
To set a new expiration date or to make changes in permissions assigned to the token, we need to update the API token in Devtron.
To update the API token, click the token name or click on the edit icon.
-
-
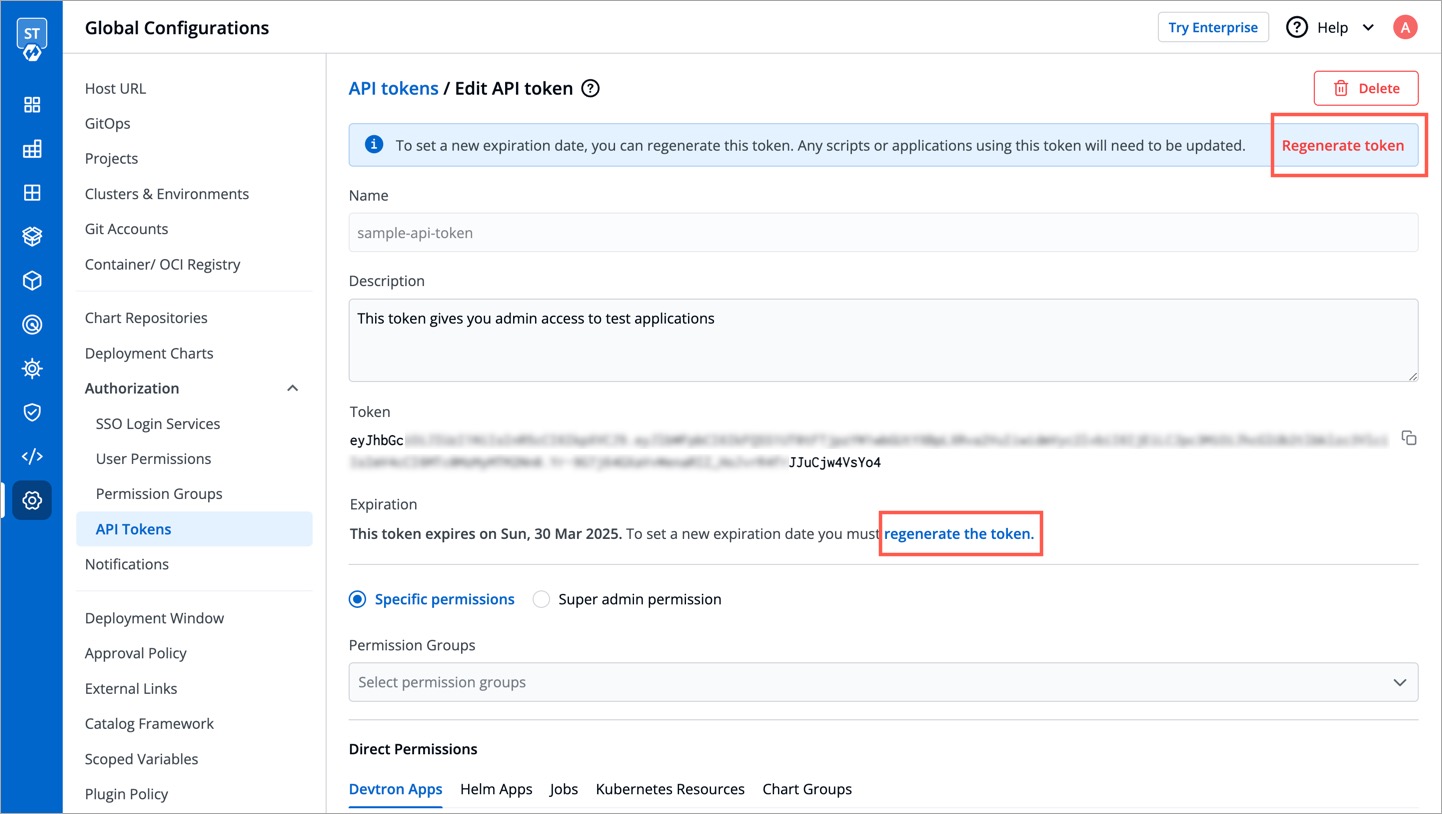
To set a new expiration date, you can regenerate the API token. Any scripts or applications using this token must be updated. To regenerate a token, click `Regenerate token`.
A pop-up window will appear on the screen from where you can select a new expiration date.
-
-
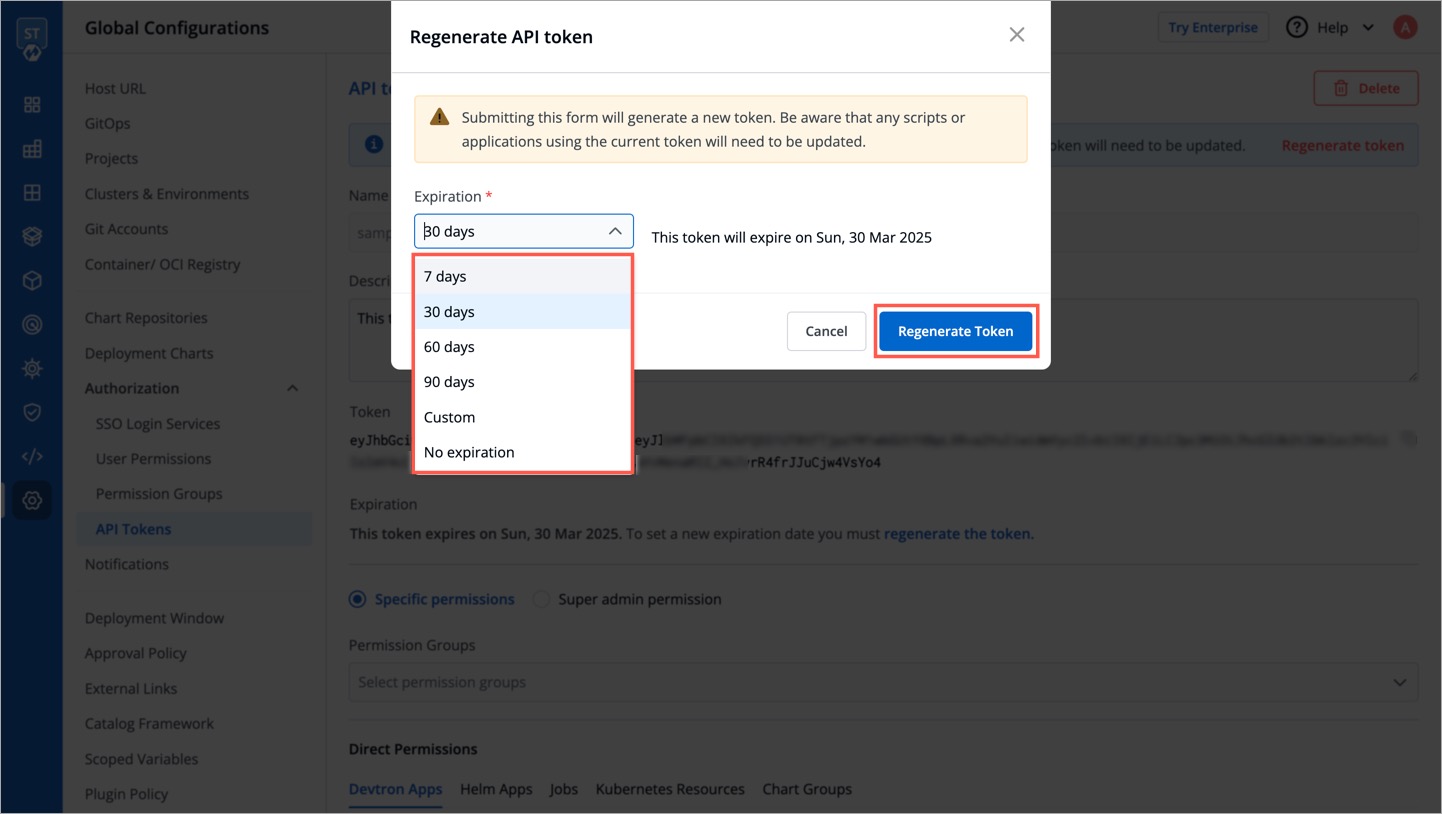
Select a new expiration date and click `Regenerate token`.
-
-
Figure 11: Configuring Expiry for Regenerating the Token
This will generate a new token with a new expiration date.
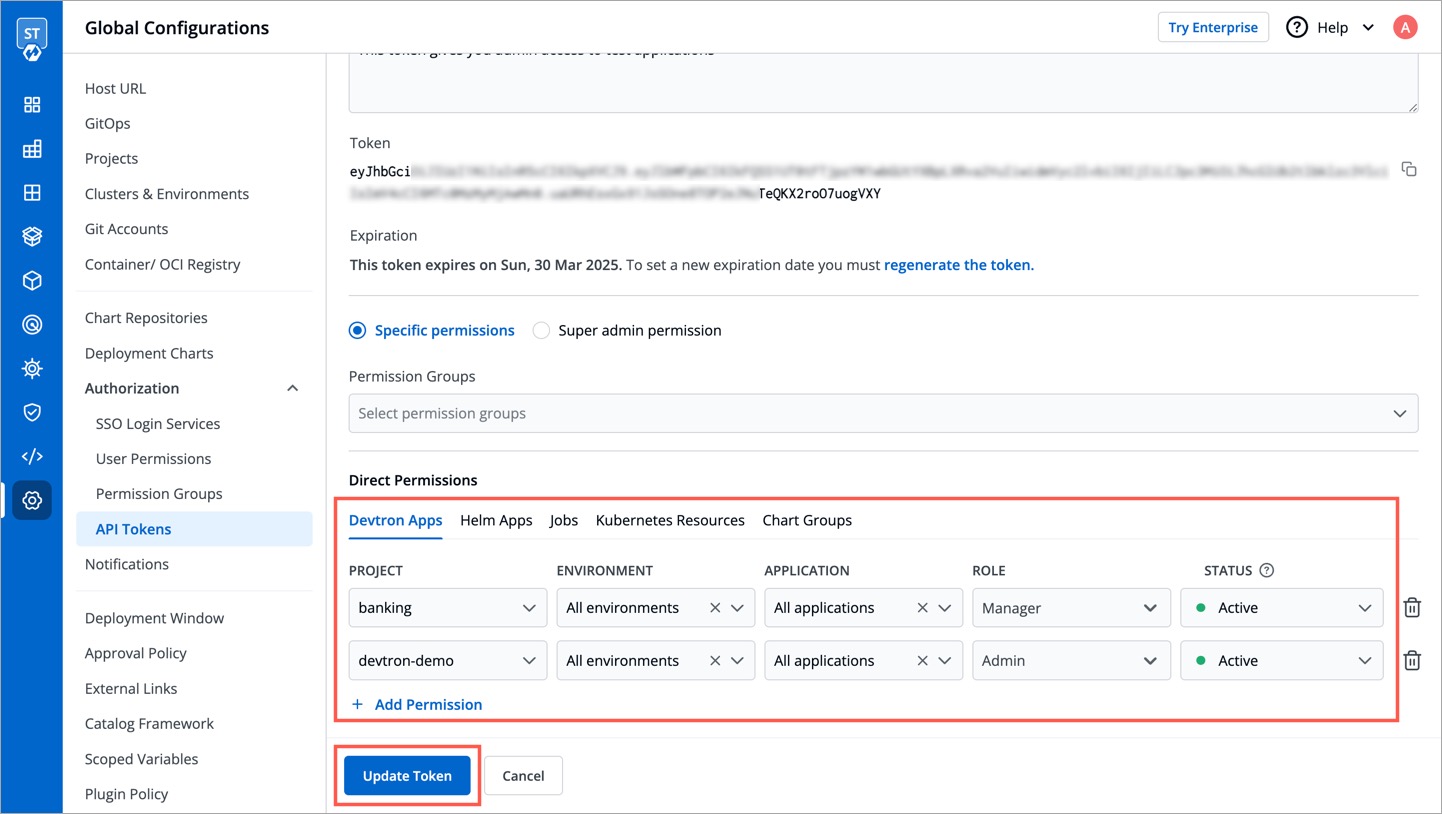
-To update API token permissions, give the permissions as you want to and click `Update Token`.
+To update API token permissions, give the permissions as you want to and click `Update Token`.
-
-
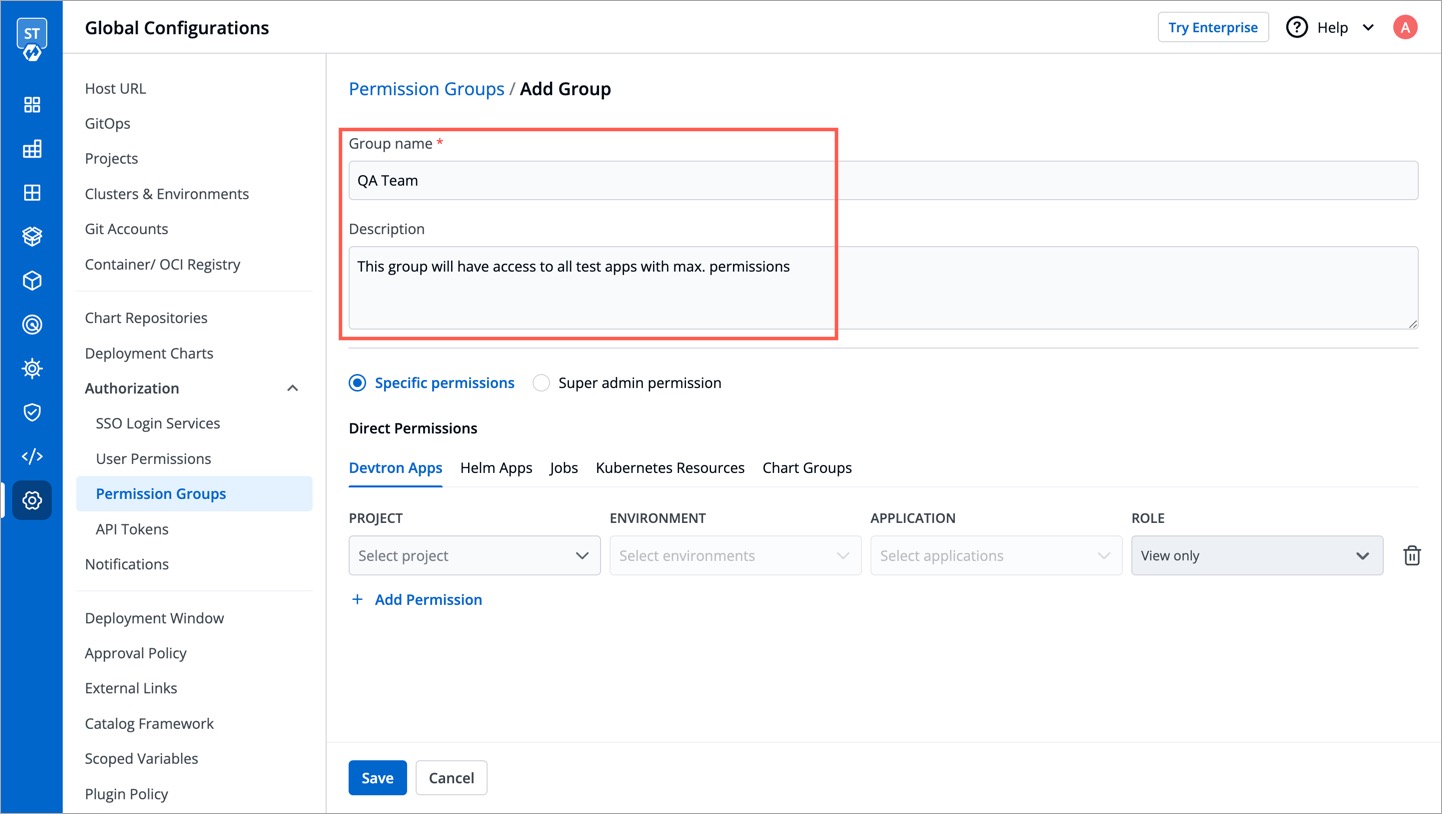
Enter the `Group Name` and `Description`.
-
-
You can either grant [super-admin](../../global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md#grant-super-admin-permission) permission to a user group or specific permissions to manage access for:
@@ -38,8 +38,8 @@ The `Devtron Apps` option will be available only if you install [CI/CD integrati
Provide the information in the following fields:
-
-
Figure 3: Configuring Permissions for Devtron Apps
| Dropdown | Description |
@@ -59,8 +59,8 @@ In `Helm Apps` option, you can provide access to a group to manage permission fo
Provide the information in the following fields:
-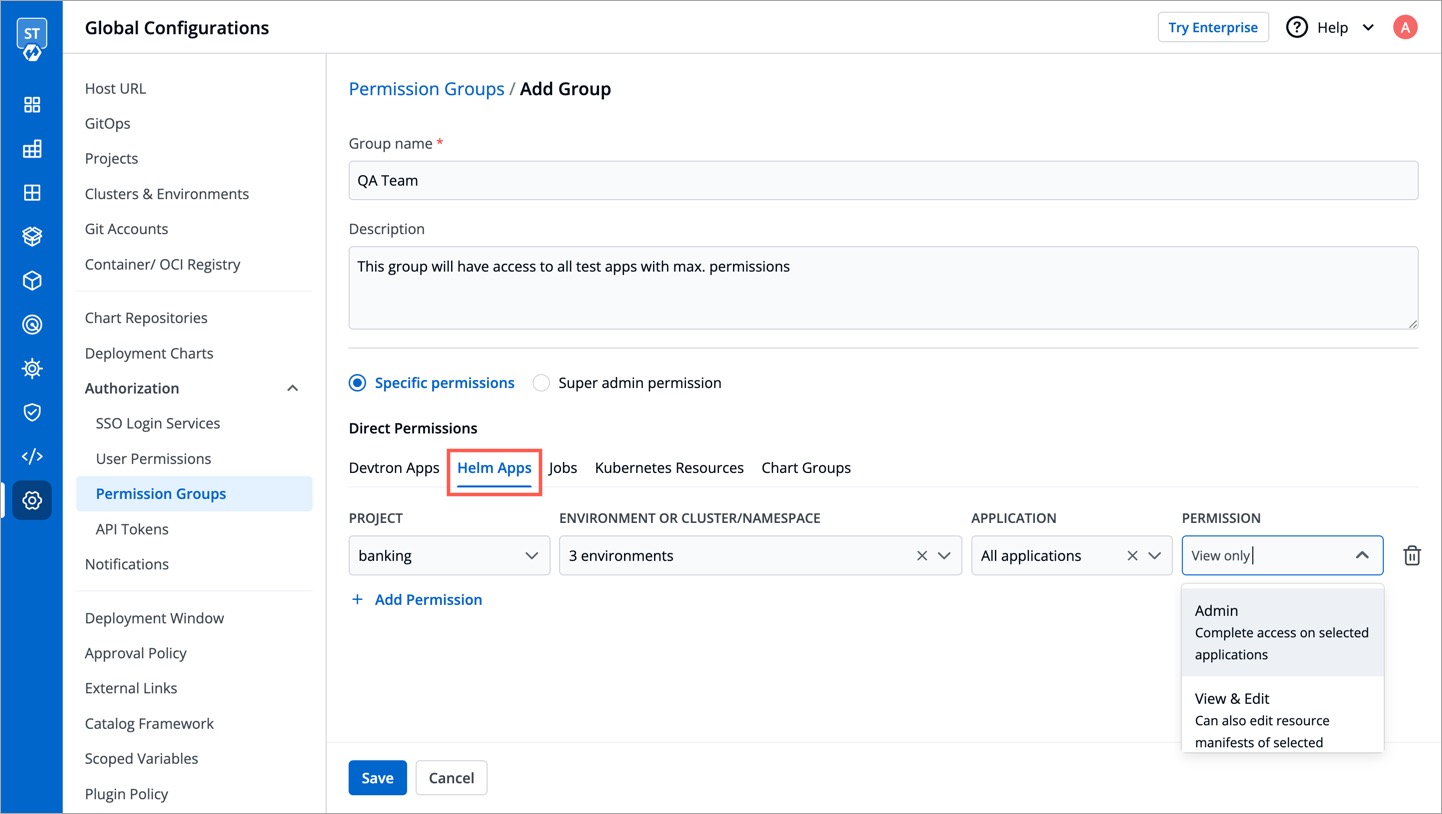
-
| Dropdown | Description |
| --- | --- |
@@ -79,8 +79,8 @@ In `Jobs` option, you can provide access to a group to manage permission for job
Provide the information in the following fields:
-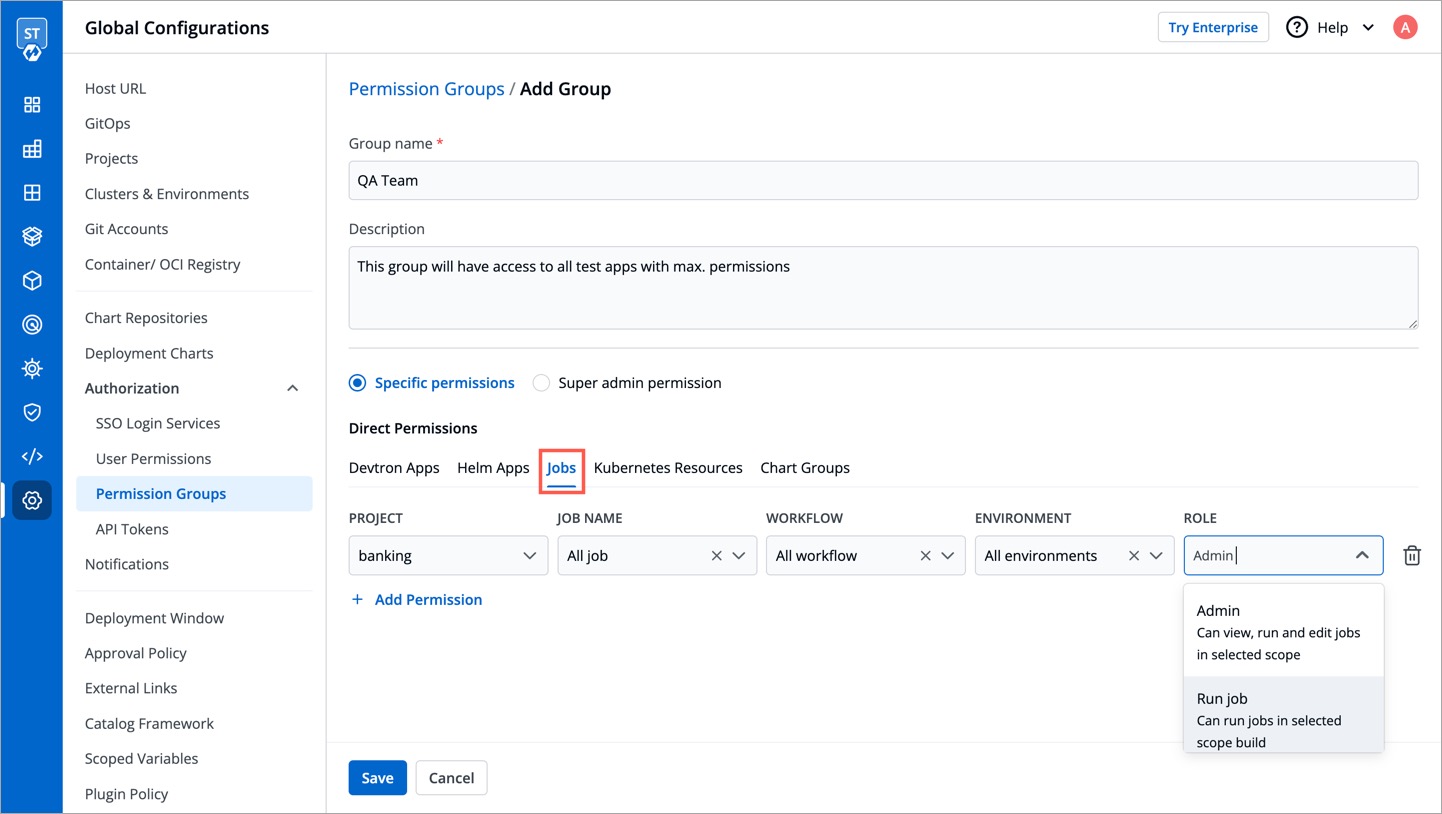
-
| Dropdown | Description |
| --- | --- |
@@ -105,14 +105,14 @@ Only super admin users will be able to see `Kubernetes Resources` tab and provid
To provide Kubernetes resource permission, click `Add permission`.
-
-
Figure 6: Configuring Permissions for Kubernetes Resources
On the `Kubernetes resource permission`, provide the information in the following fields:
-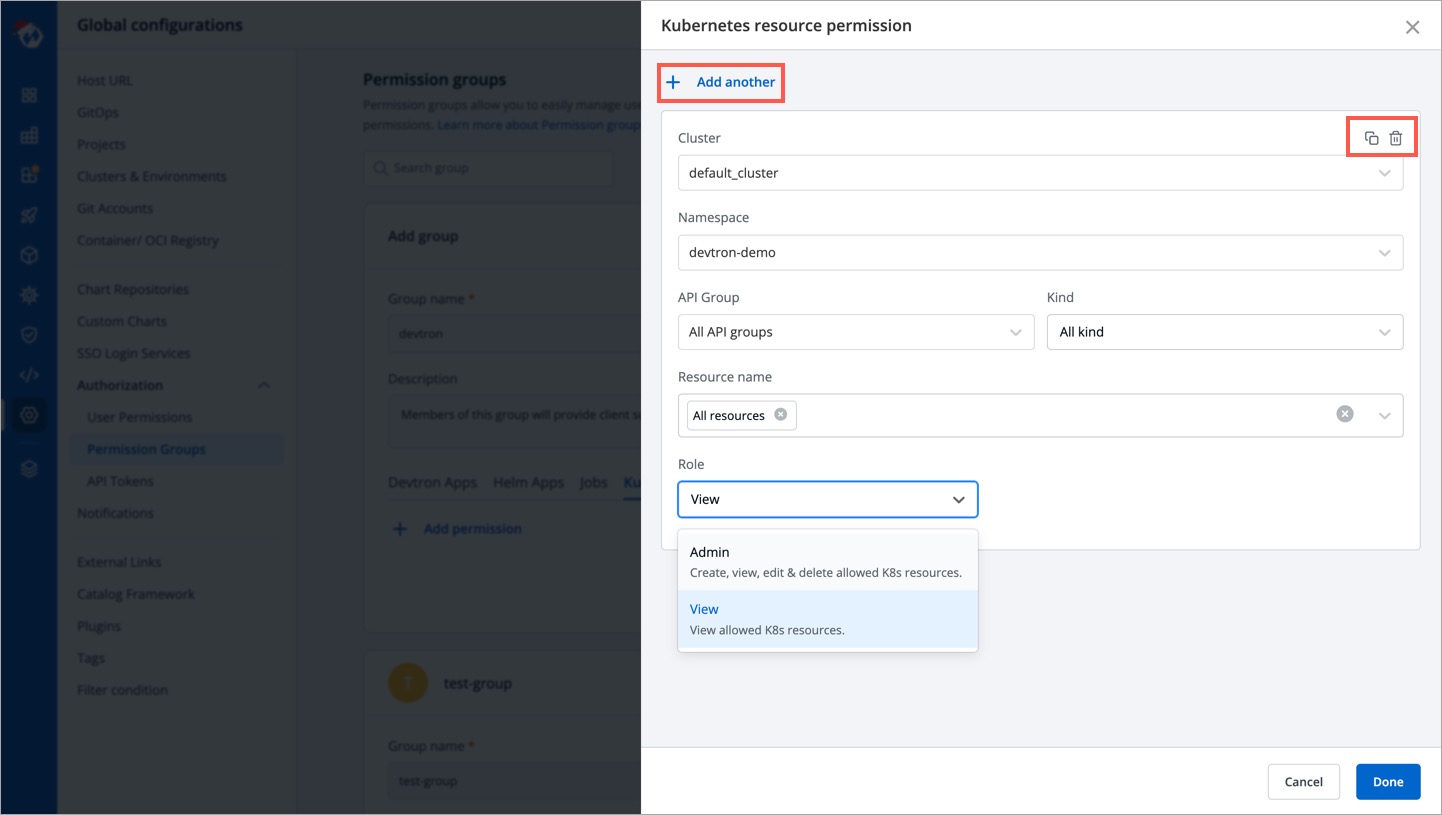
-
| Dropdown | Description |
| --- | --- |
@@ -135,8 +135,8 @@ In `Chart group permission` option, you can manage the access of groups for Char
The `Chart group permission` option will be available only if you install [CI/CD integration](../../integrations/build-and-deploy-ci-cd.md).
:::
-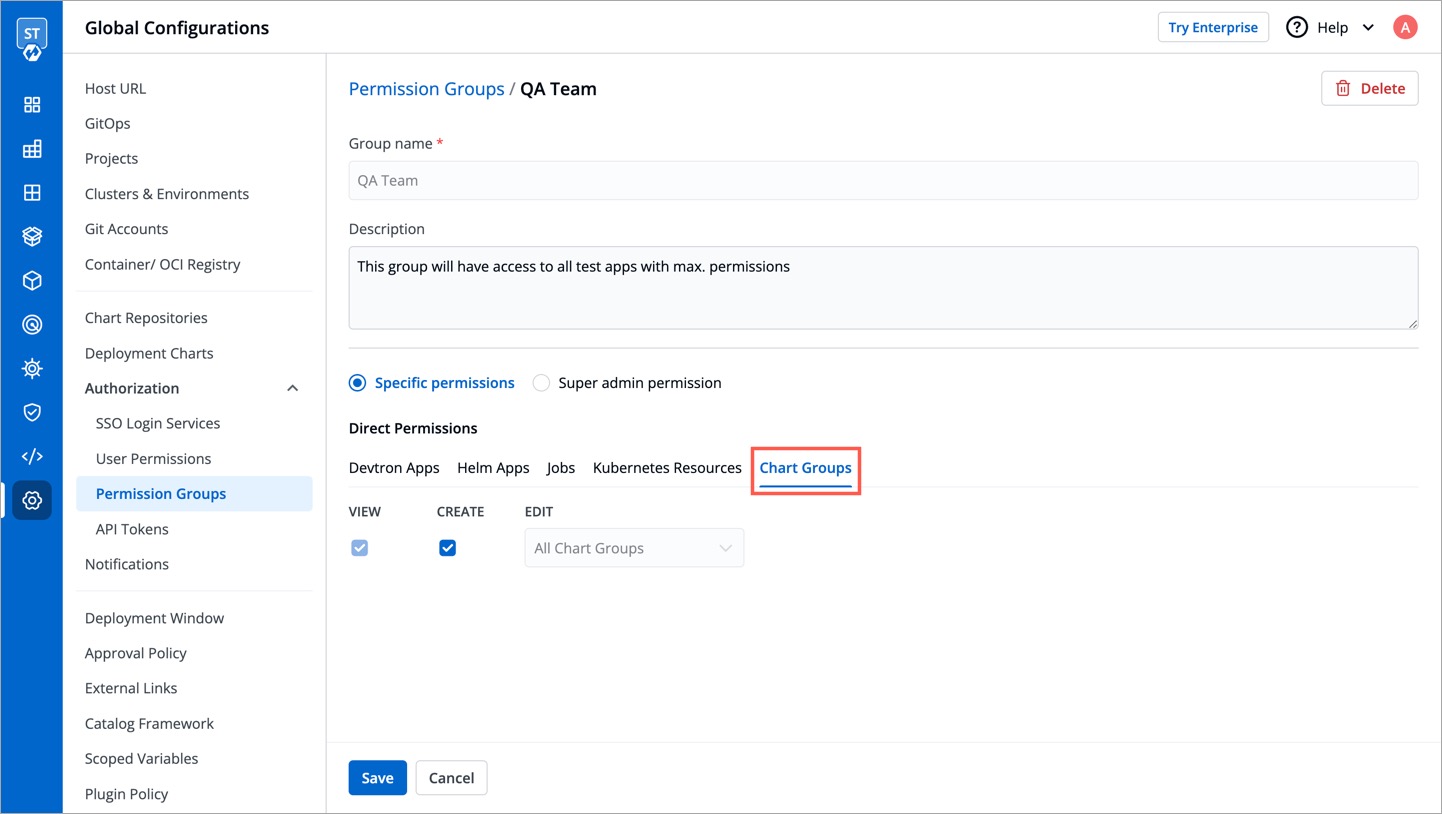
-
Figure 8: Configuring Permissions for Chart Groups
:::info
You can only give users the ability to `create` or `edit`, not both.
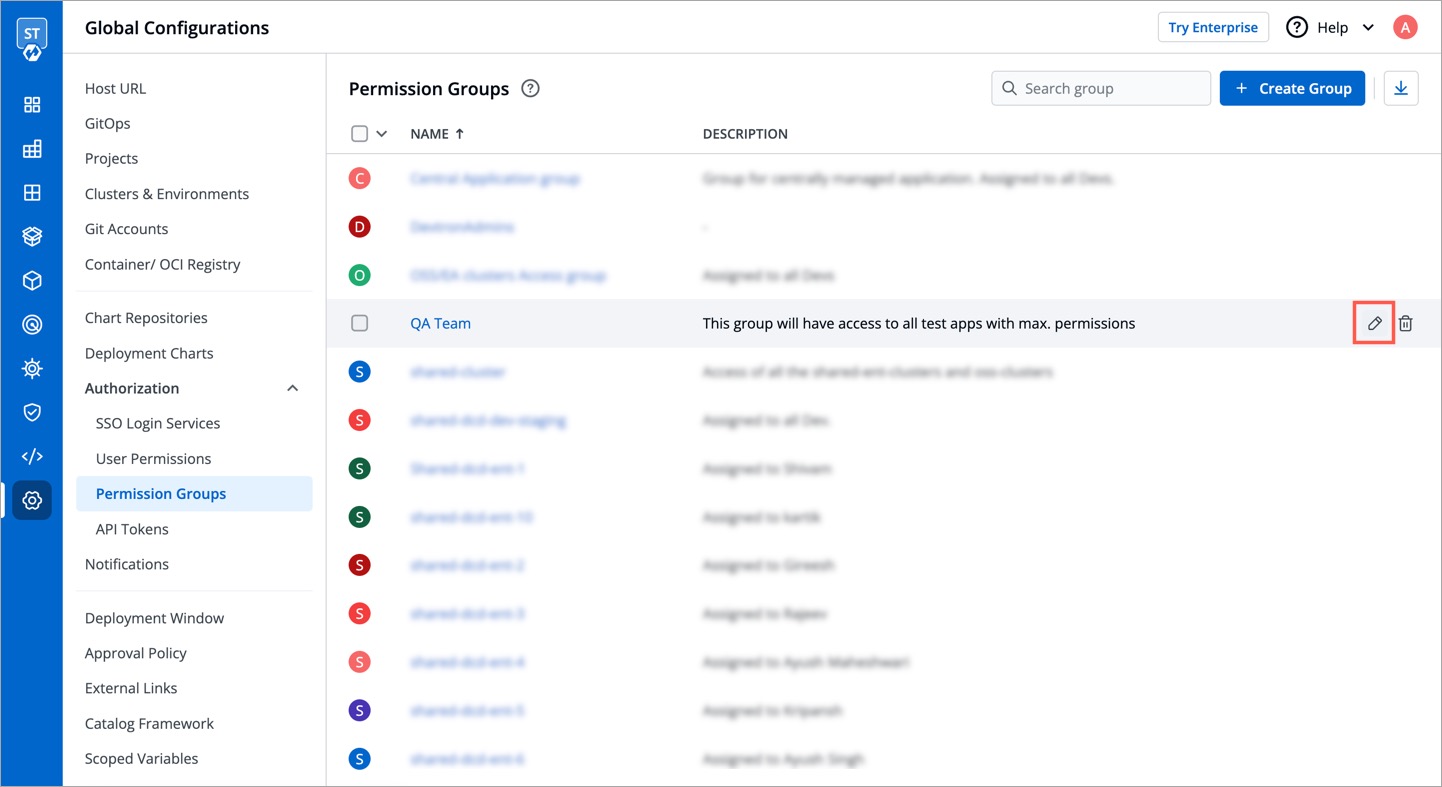
@@ -155,13 +155,13 @@ Click **Save** once you have configured all the required permissions for the gro
You can edit the permission groups by clicking the `downward arrow.`
-
-
Once you are done editing the permission group, click **Save**.
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/github.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/github.md
index 72595b3ee..375f5072c 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/github.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/github.md
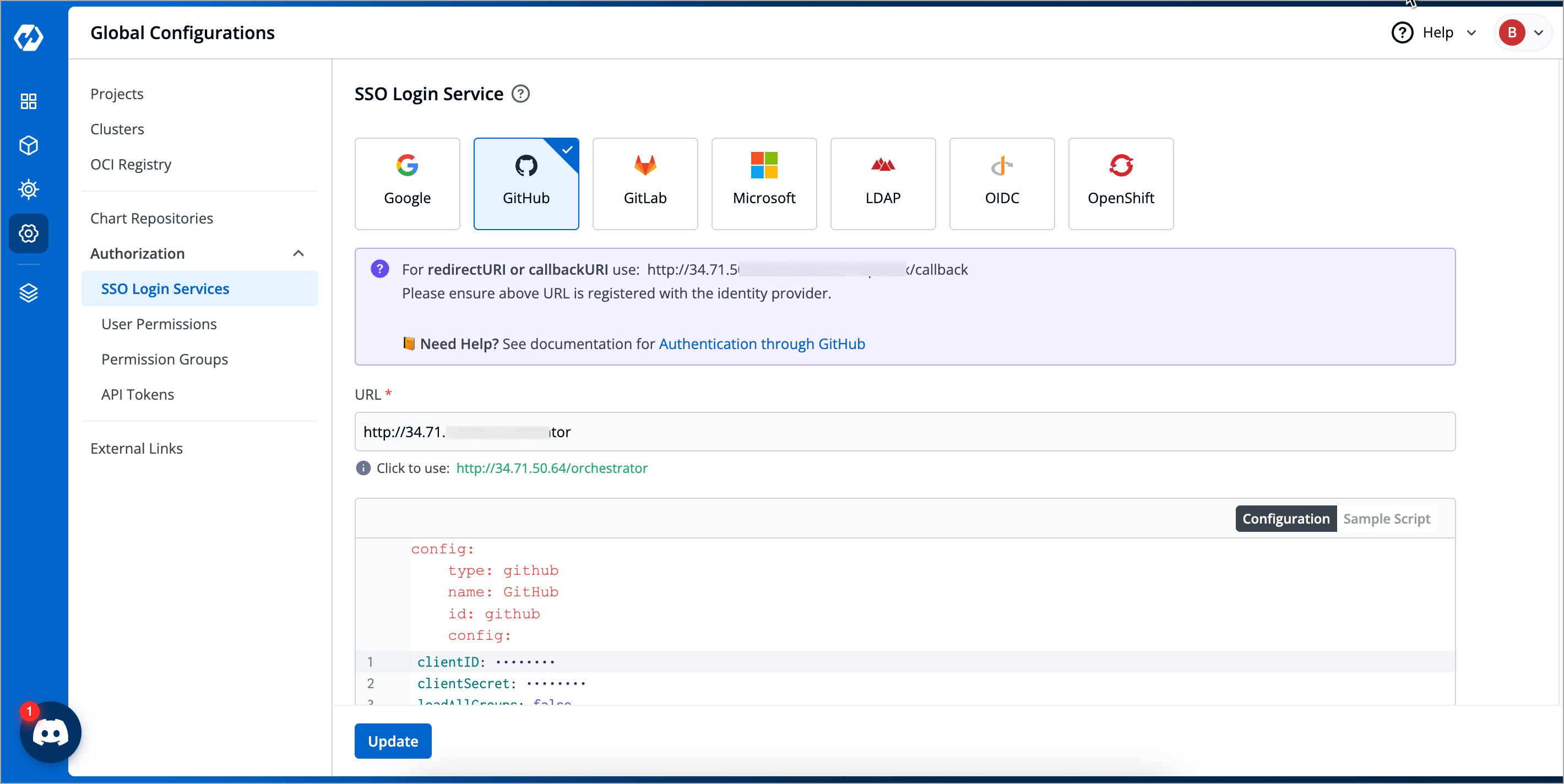
@@ -23,16 +23,20 @@ Getting the redirectURI from Devtron is a crucial component of the authenticatio
1. Navigate to **Global Configurations** → **Authorization** → **SSO Login Services**. The SSO Login Service page is displayed.
- 
-
2. Select **GitHub** from the list of available SSO login services.
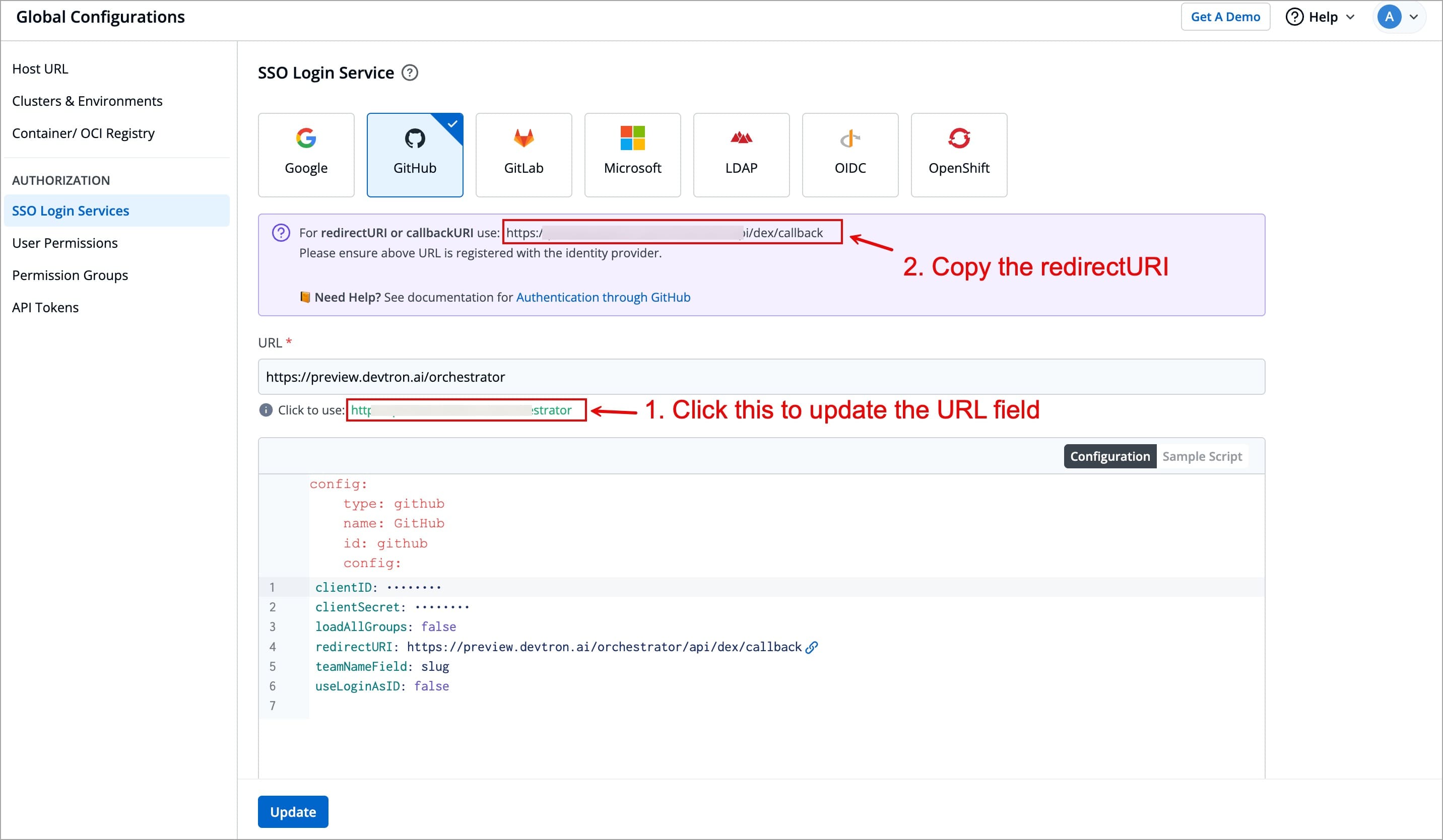
-3. Click the URL suggested in green color next to the **Click to use** label to update the **URL** field. Update the **URL** field only if the host URL displayed in the **URL** field is incorrect.
+3. Click the URL suggested in green color next to the **Click to use** label to update the **URL** field.
-4. Click the **Update** button.
+ When you populate **URL** field, the redirectURI (or callbackURI) is updated automatically in the purple block displayed at the top of the SSO Login Service screen. This redirectURI is essential, as it is required while setting up the OAuth credentials in GitHub.
+
+4. Copy the redirectURI from the purple block.
+
+ 
+
Figure 2: Copy Redirect URI
-When you populate the Host URL in the **URL** field, the redirectURI (or callbackURI) is updated automatically in the purple block displayed at the top of the SSO Login Service screen. This redirectURI is essential, as it is required while setting up the OAuth credentials in GitHub.
---
@@ -46,8 +50,8 @@ Open Authentication (OAuth) allows you to authorize one application to sign in t
2. Select your preferred OAuth app and click **Edit**.
- 
-
3. Click the **Generate a new client secret** button to create a new client secret. The client secret is created and displayed in the **Client Secrets** section. The Client ID is created by default and can be found in the **Client ID** field.
@@ -67,8 +71,8 @@ To configure the GitHub SSO in Devtron, follow the below steps of instructions:
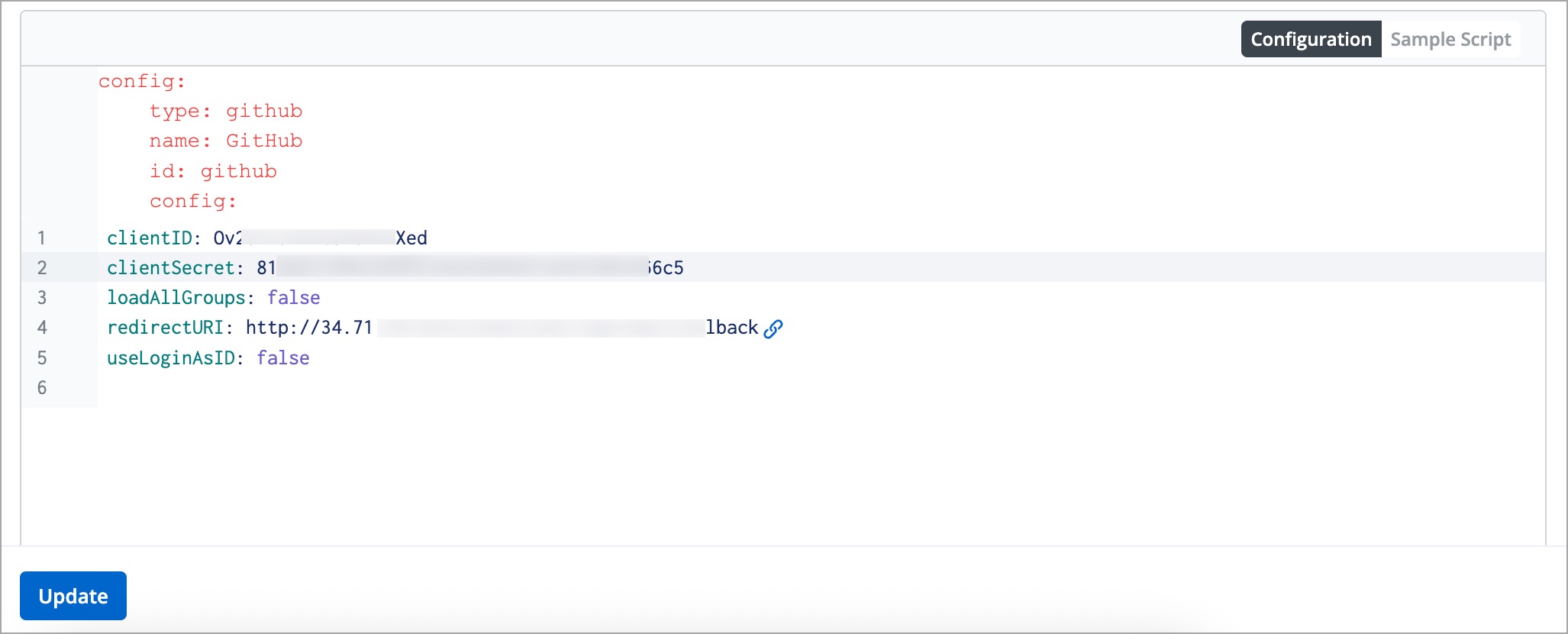
2. Select the **Configuration** section available below the **URL** field.
- 
-
3. Update the `clientID` attribute with the Client ID generated in the OAuth application on GitHub.
@@ -78,8 +82,8 @@ To configure the GitHub SSO in Devtron, follow the below steps of instructions:
6. Click **Update** to save the configuration. GitHub SSO is now successfully configured.
-
-
---
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/gitlab.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/gitlab.md
index 361b55637..65e98e86d 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/gitlab.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/gitlab.md
@@ -25,16 +25,19 @@ Getting the redirectURI from Devtron is a crucial component of the authenticatio
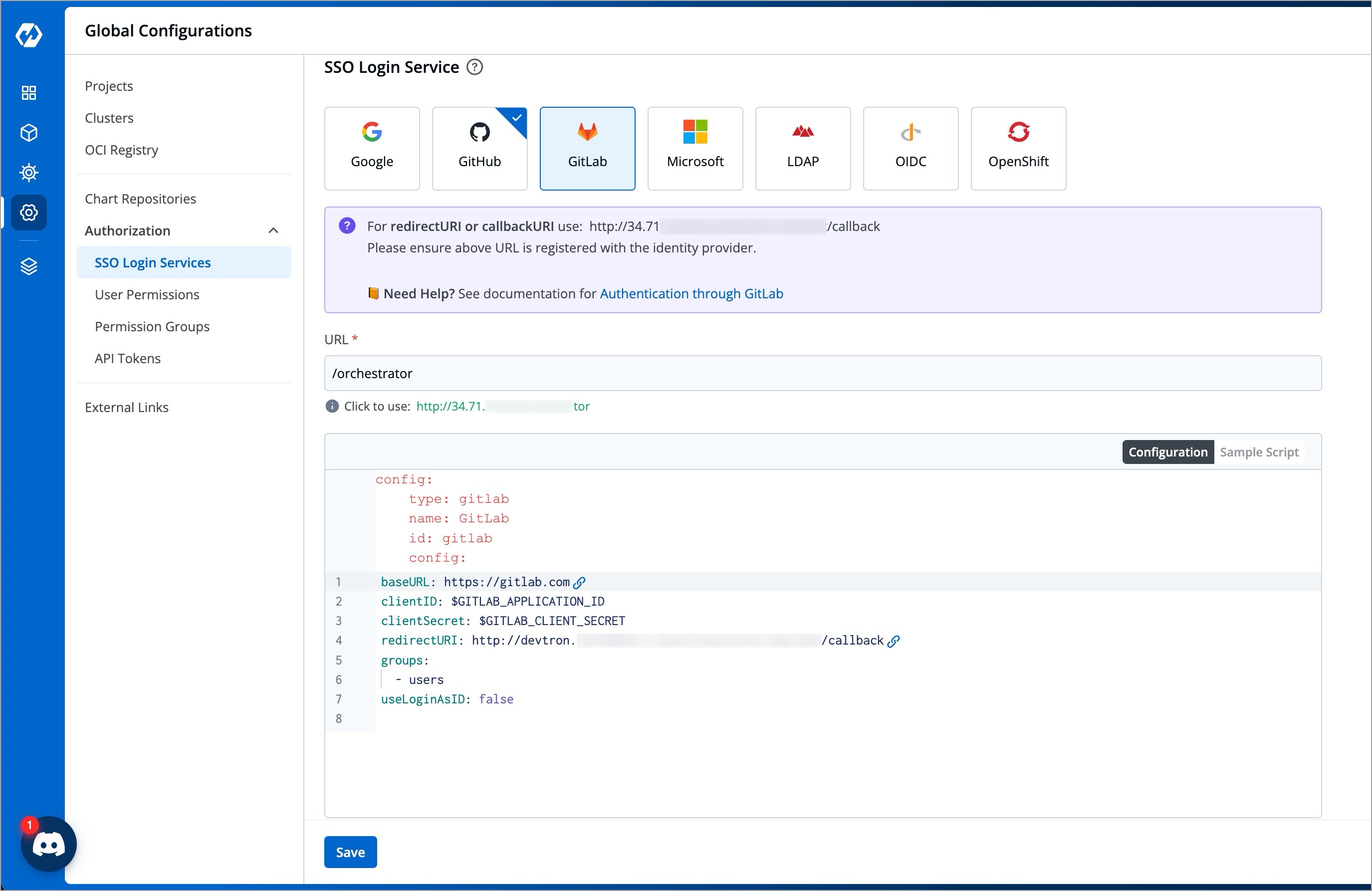
1. Navigate to **Global Configurations** → **Authorization** → **SSO Login Services**. The SSO Login Service page is displayed.
- 
-
2. Select **GitLab** from the list of available SSO login services.
-3. Click the URL suggested in green color next to the **Click to use** label to update the **URL** field. Update the **URL** field only if the host URL displayed in the **URL** field is incorrect.
+3. Click the URL suggested in green color next to the **Click to use** label to update the **URL** field.
-4. Click the **Save** button.
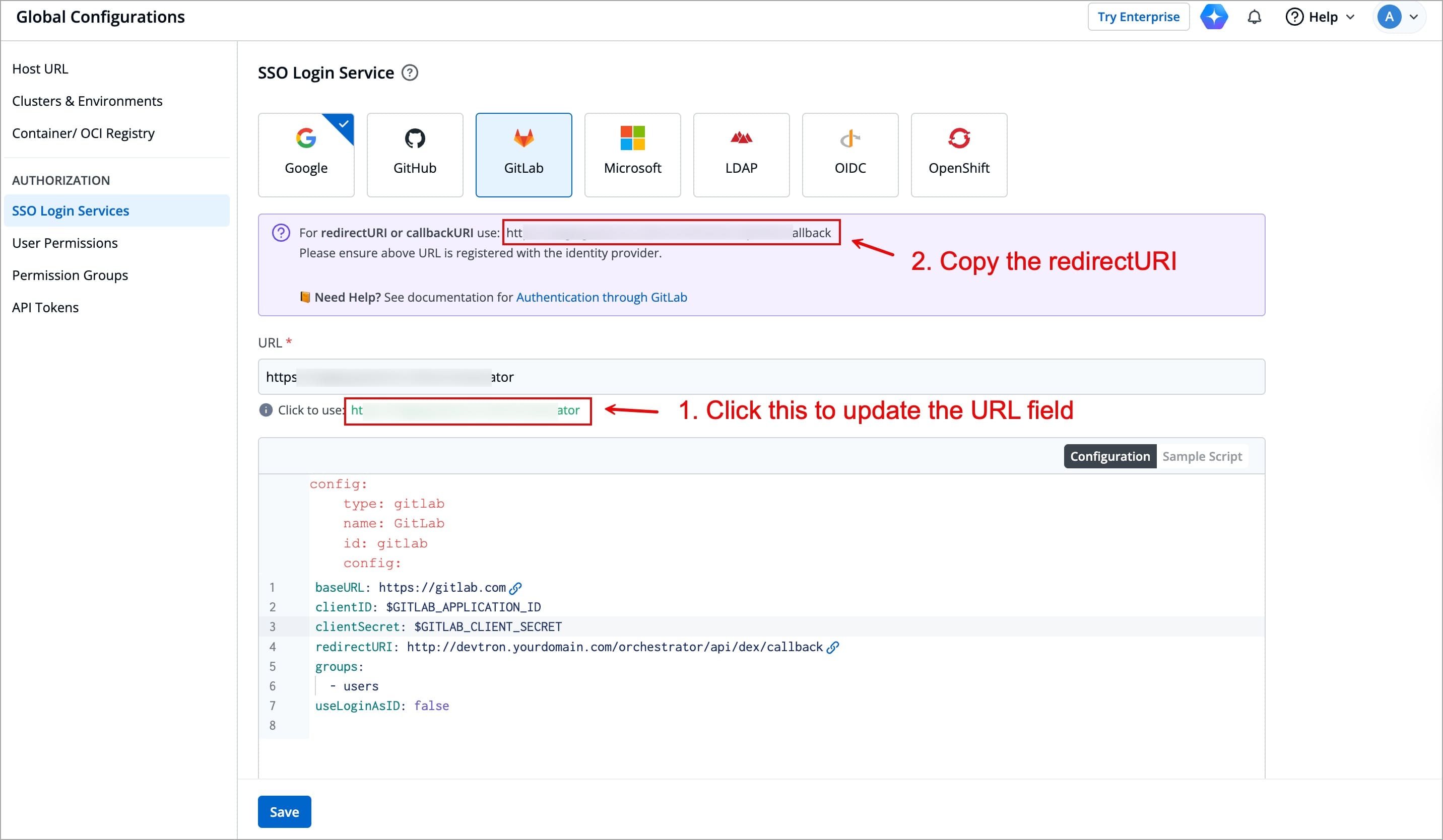
+ When you populate **URL** field, the redirectURI (or callbackURI) is updated automatically in the purple block displayed at the top of the SSO Login Service screen. This redirectURI is essential, as it is required while setting up the OAuth credentials in GitHub.
-When you populate the Host URL in the **URL** text box, the redirectURI (or callbackURI) is updated automatically in the purple block at the top of the SSO Login Service screen. This redirectURI is essential, as it is required while setting up the OAuth credentials in GitLab.
+4. Copy the redirectURI from the purple block.
+
+ 
+
Figure 2: Copy Redirect URI
---
@@ -48,8 +51,8 @@ Open Authentication (OAuth) allows you to authorize one application to sign in t
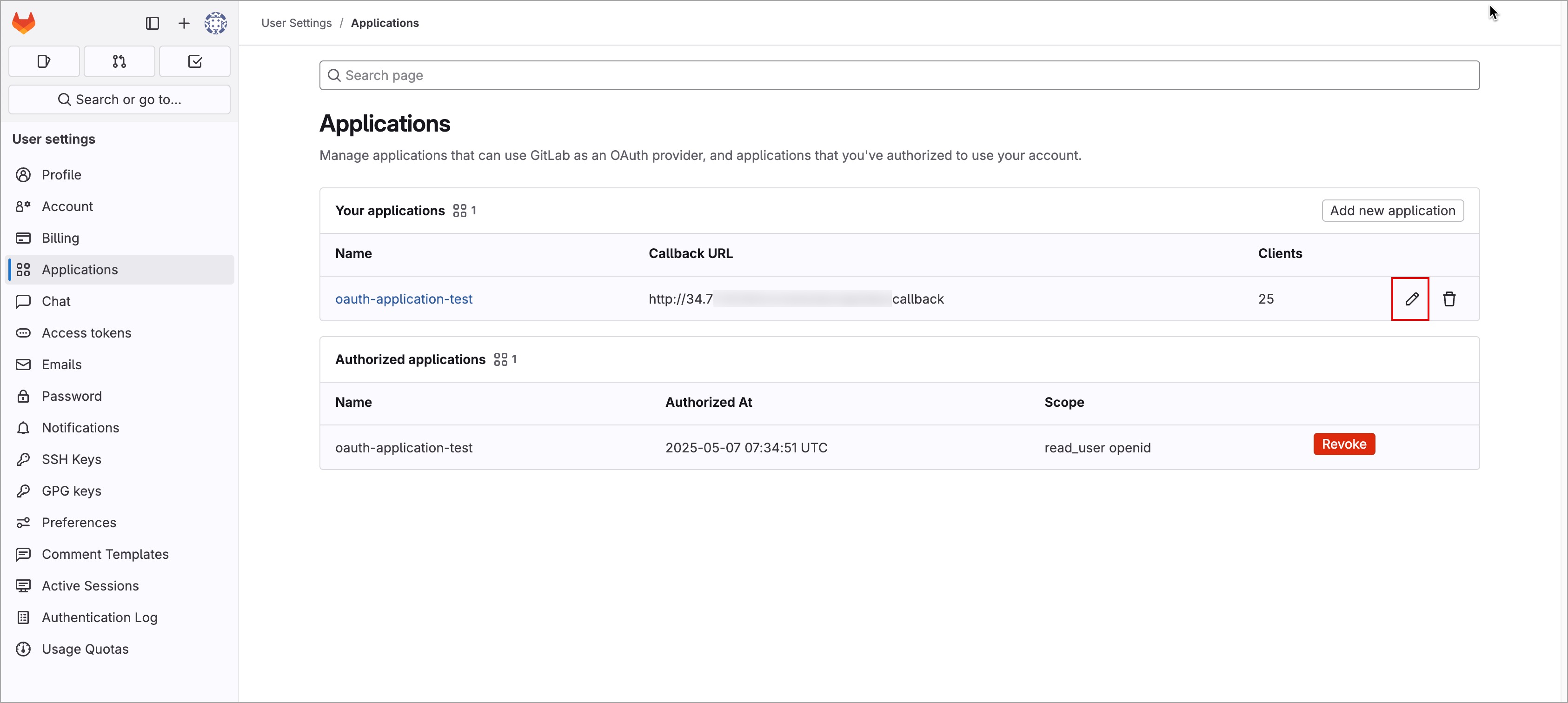
2. Select your preferred OAuth app and click **Edit**.
- 
-
3. Update the **Redirect URI** field with the redirectURI created in Devtron.
@@ -57,8 +60,8 @@ Open Authentication (OAuth) allows you to authorize one application to sign in t
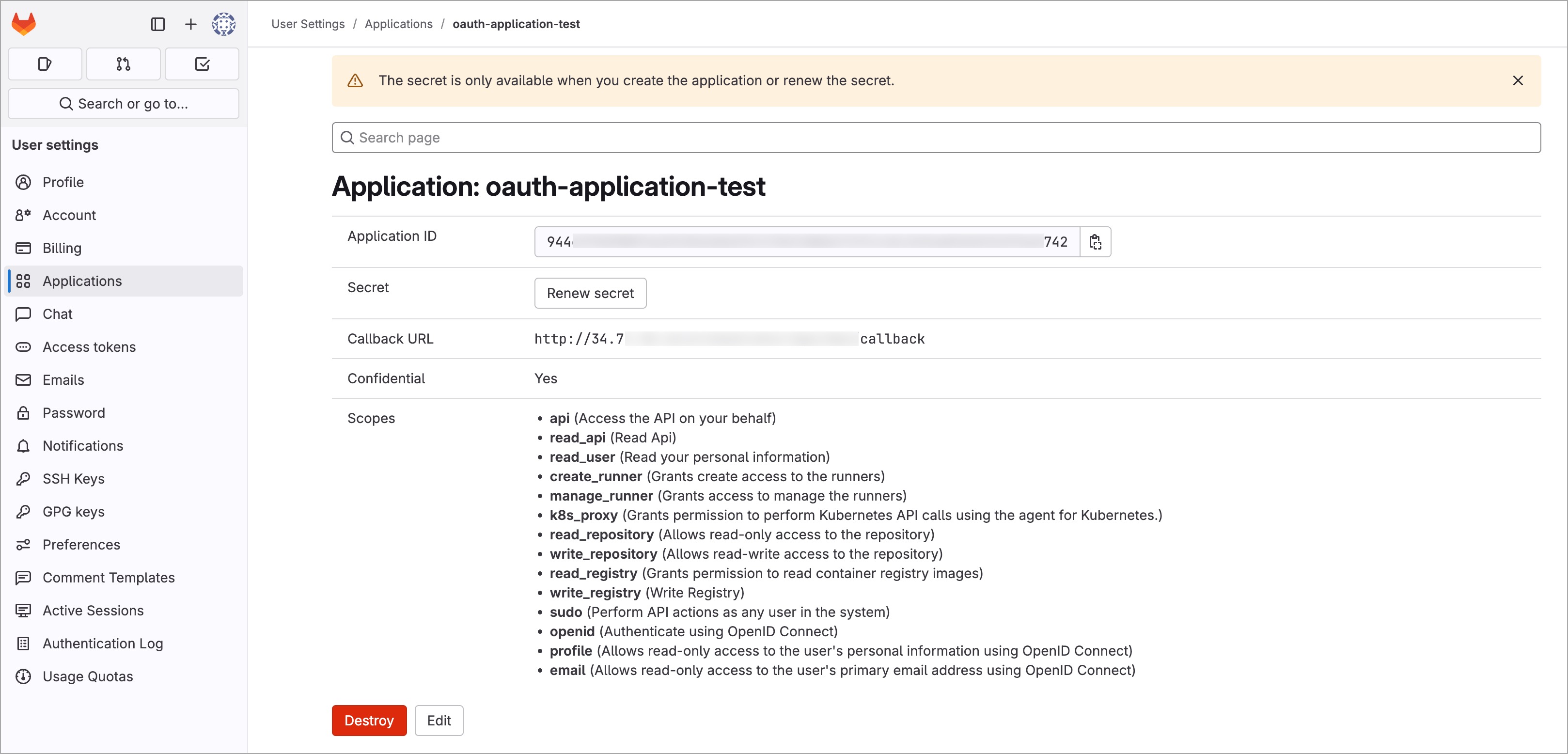
5. Click the **Save Application** button. The following page is displayed.
- 
-
The client ID is displayed in the **Application ID** field.
@@ -74,8 +77,8 @@ To configure the GitLab SSO in Devtron, follow the below steps of instructions:
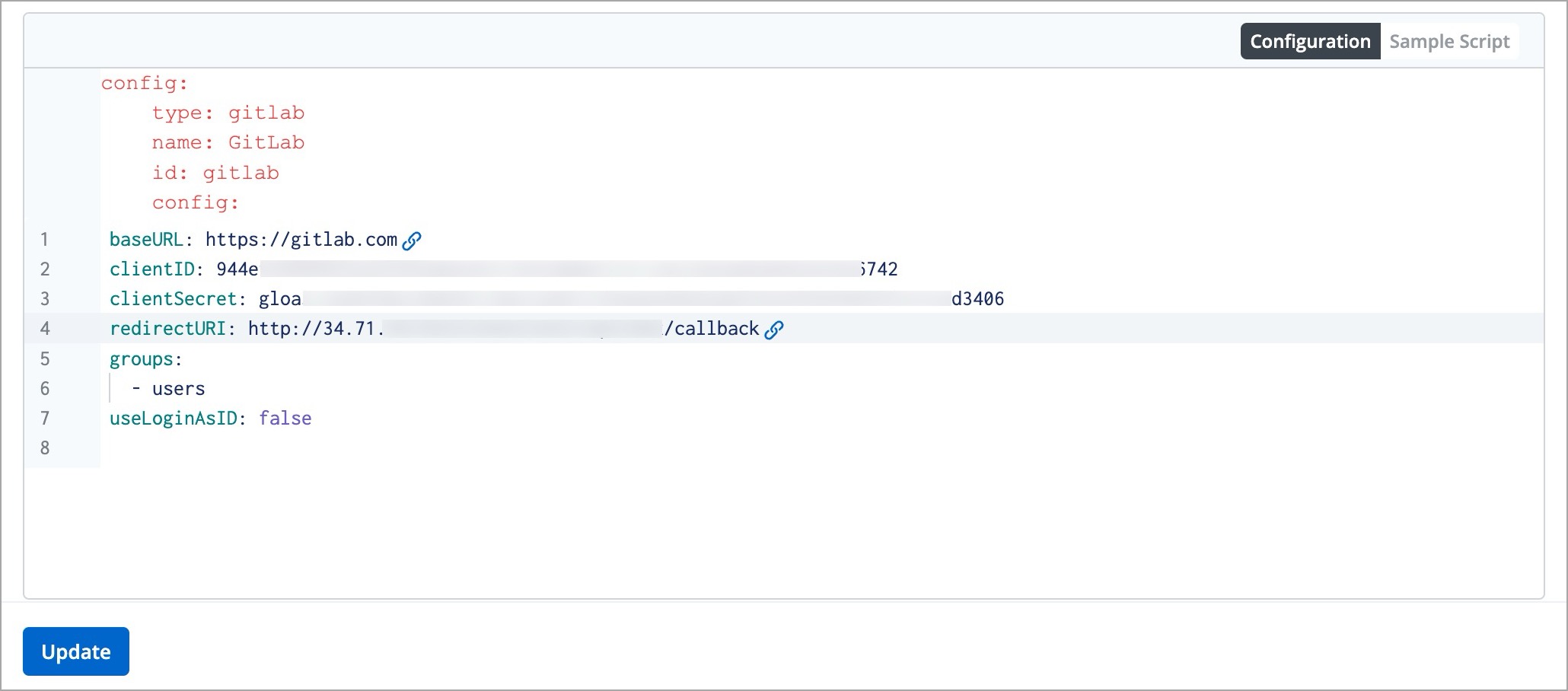
2. Select the **Configuration** section available next to the **URL** field.
- 
-
3. Update the `clientID` attribute with the Client ID generated in the OAuth application on GitLab.
@@ -85,8 +88,8 @@ To configure the GitLab SSO in Devtron, follow the below steps of instructions:
6. Click **Update** button to save the configuration. GitLab SSO is now successfully configured.
-
-
:::caution Important Note
Although GitLab SSO is now configured, you will not be able to sign in with GitLab unless you add yourself as a user with the necessary permissions and manage other user permissions as well in Devtron. It is highly recommended to create [User Permissions](../user-access.md).
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/google.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/google.md
index ed063f436..d88af150f 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/google.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/google.md
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ Before configuring Google as an SSO provider,
* Click the URL next to **Click to use** in green color. The URL field will be automatically populated with the URL next to **Click to use**; this is essential to generate the correct **Redirect URI**.
* Copy the **Redirect URI** displayed in this section. You will need to enter this in Google Cloud.
-
+
## Configure OAuth in Google Cloud Console
@@ -60,17 +60,17 @@ Examples of invalid URIs:
❌ `http://192.168.1.10/callback`
:::
-
+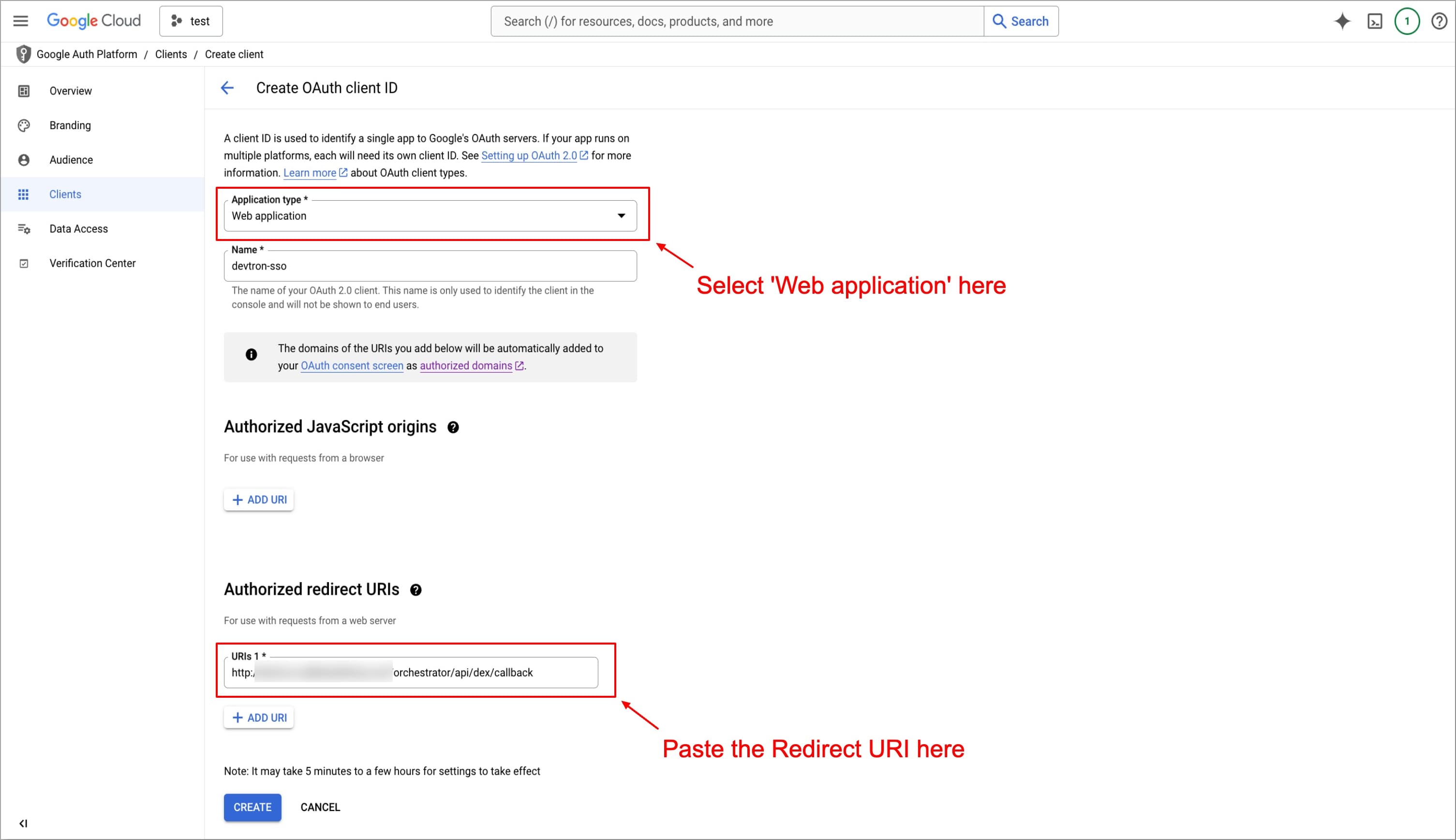
Figure 1: Creating OAuth Client
You can see a new client ID is created in the **APIs & Services** → **Credentials**, under **OAuth 2.0 Client IDs** section. To obtain Client ID and Client Secret, click on the name (devtron-sso in our case) of the **OAuth 2.0 Client IDs**
-
+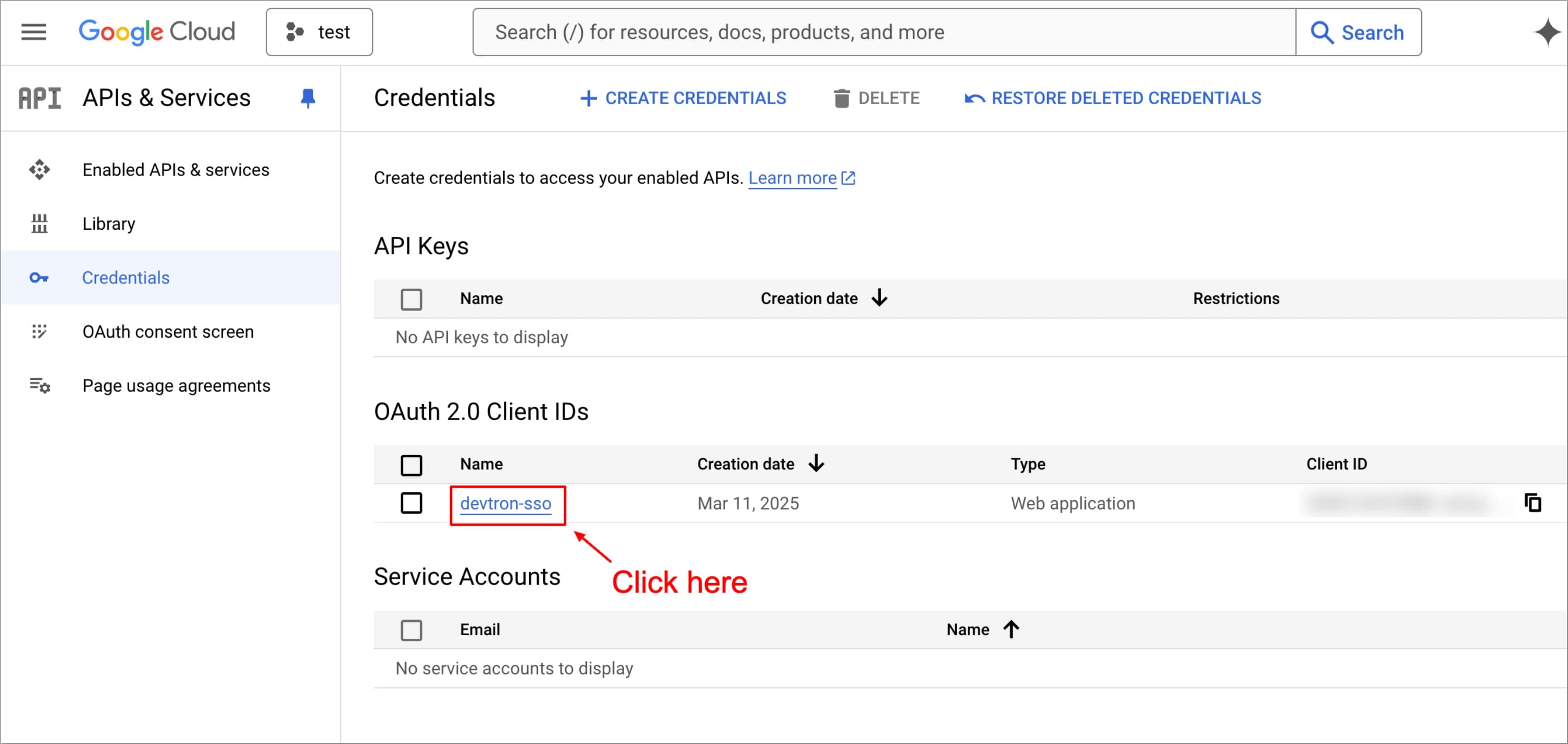
Figure 2: Client ID Created
Copy the Client ID and Client Secret, as they will be required in Devtron’s SSO configuration.
-
+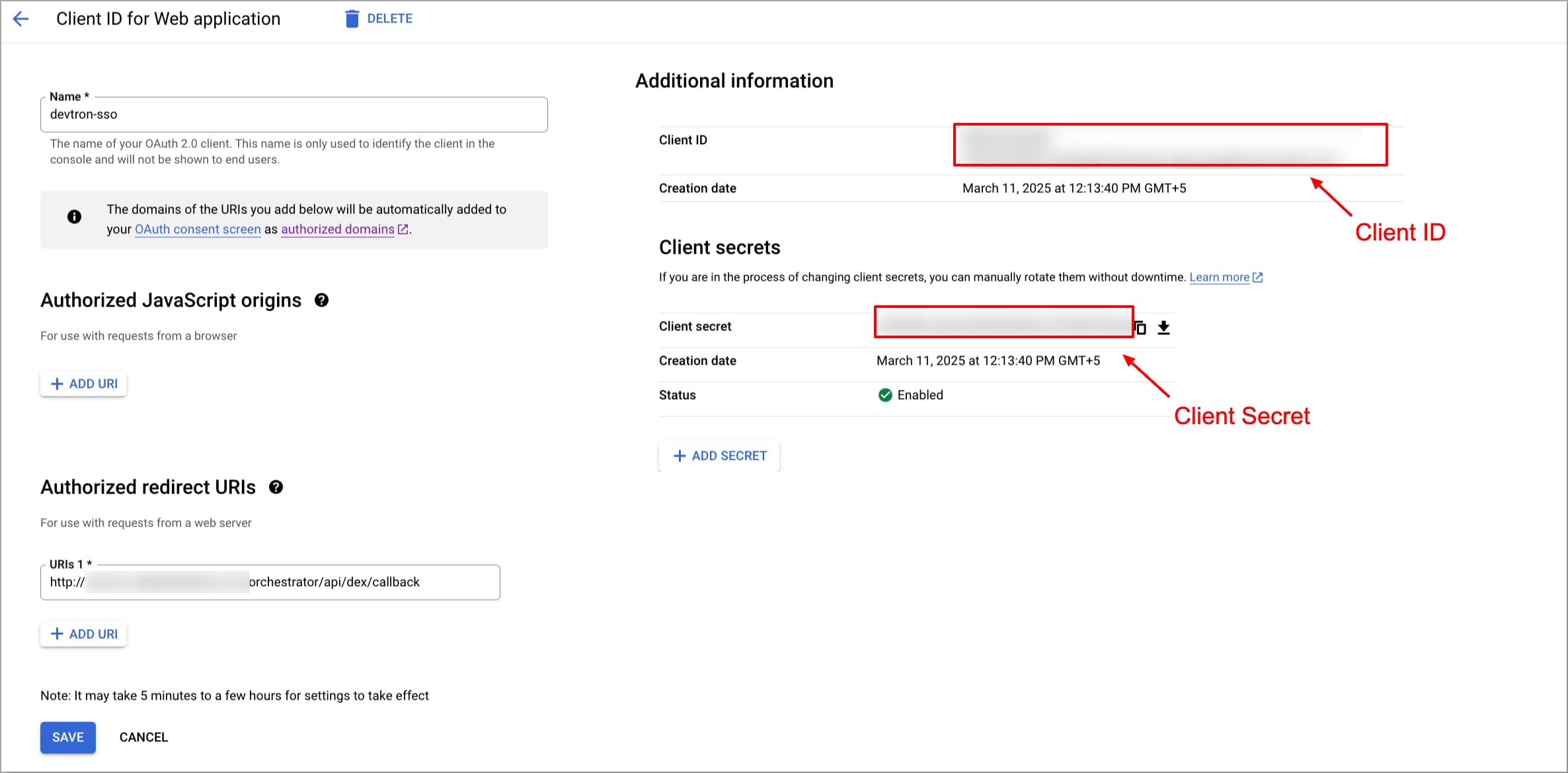
Figure 3: Get the Client ID and Client Secret
For a detailed step-by-step guide, refer to Google’s official documentation: [Get Google API Client ID](https://developers.google.com/identity/gsi/web/guides/get-google-api-clientid).
@@ -79,10 +79,13 @@ For a detailed step-by-step guide, refer to Google’s official documentation: [
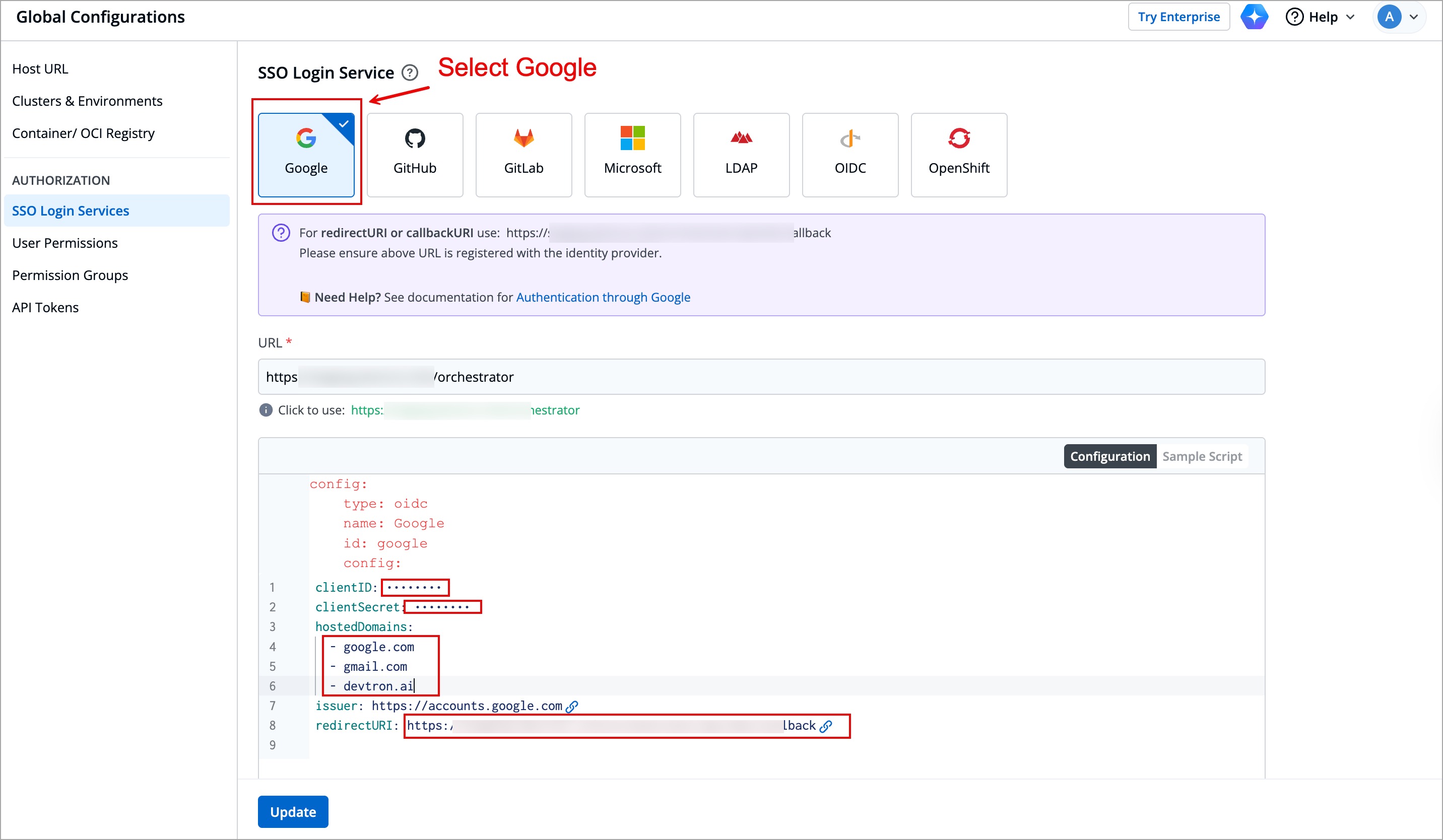
The next step is to configure Devtron to use these credentials for authentication. For this, navigate back to **Global Configurations → SSO Login Services**, here you can already find a configuration template.
+
+
In the configuration,
@@ -107,15 +110,16 @@ To ensure users can log in:
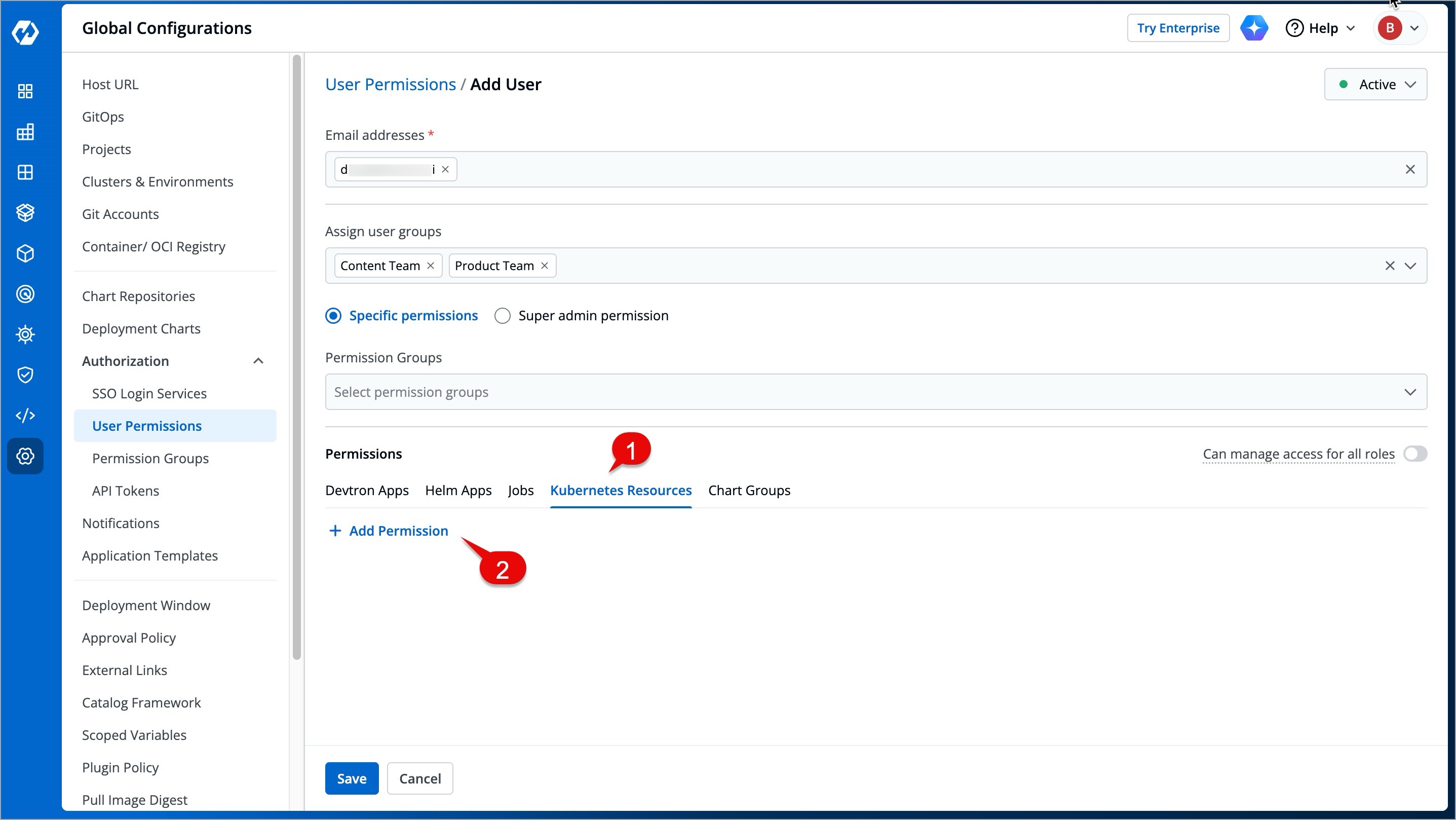
* Go to **Global Configurations** → **Authorization** → **User Permissions**.
* Click **Add User**.
-
-
* Enter their email (matching their Google account).
* Assign the required role.
* Click **Save** to complete the setup.
-
-
Once saved, Devtron will use Google OAuth for authentication, allowing users to log in using their Google accounts.
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/keycloak.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/keycloak.md
index caddb1482..17cacc699 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/keycloak.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/keycloak.md
@@ -7,6 +7,26 @@
---
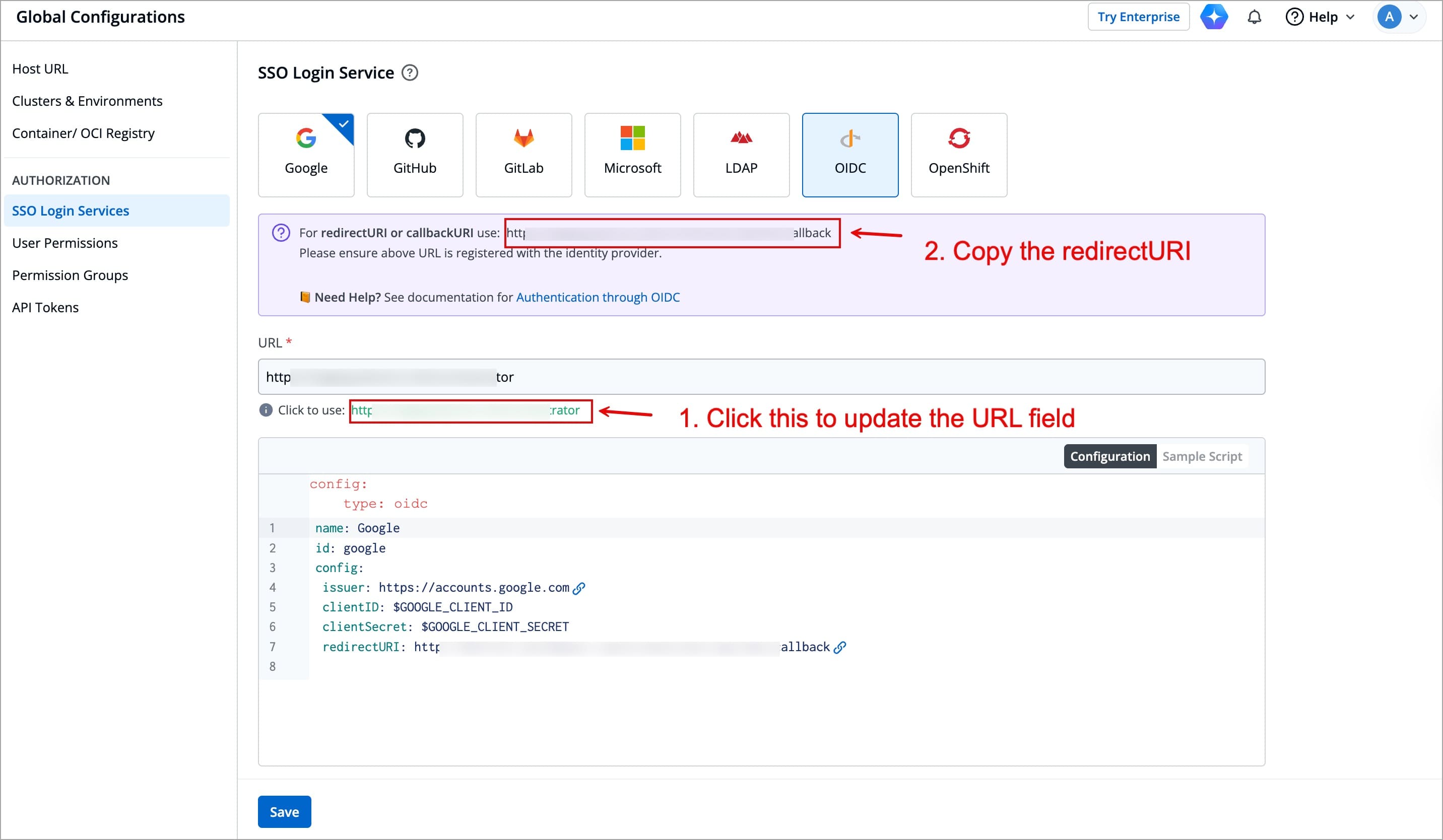
+## Get the redirectURI from Devtron
+
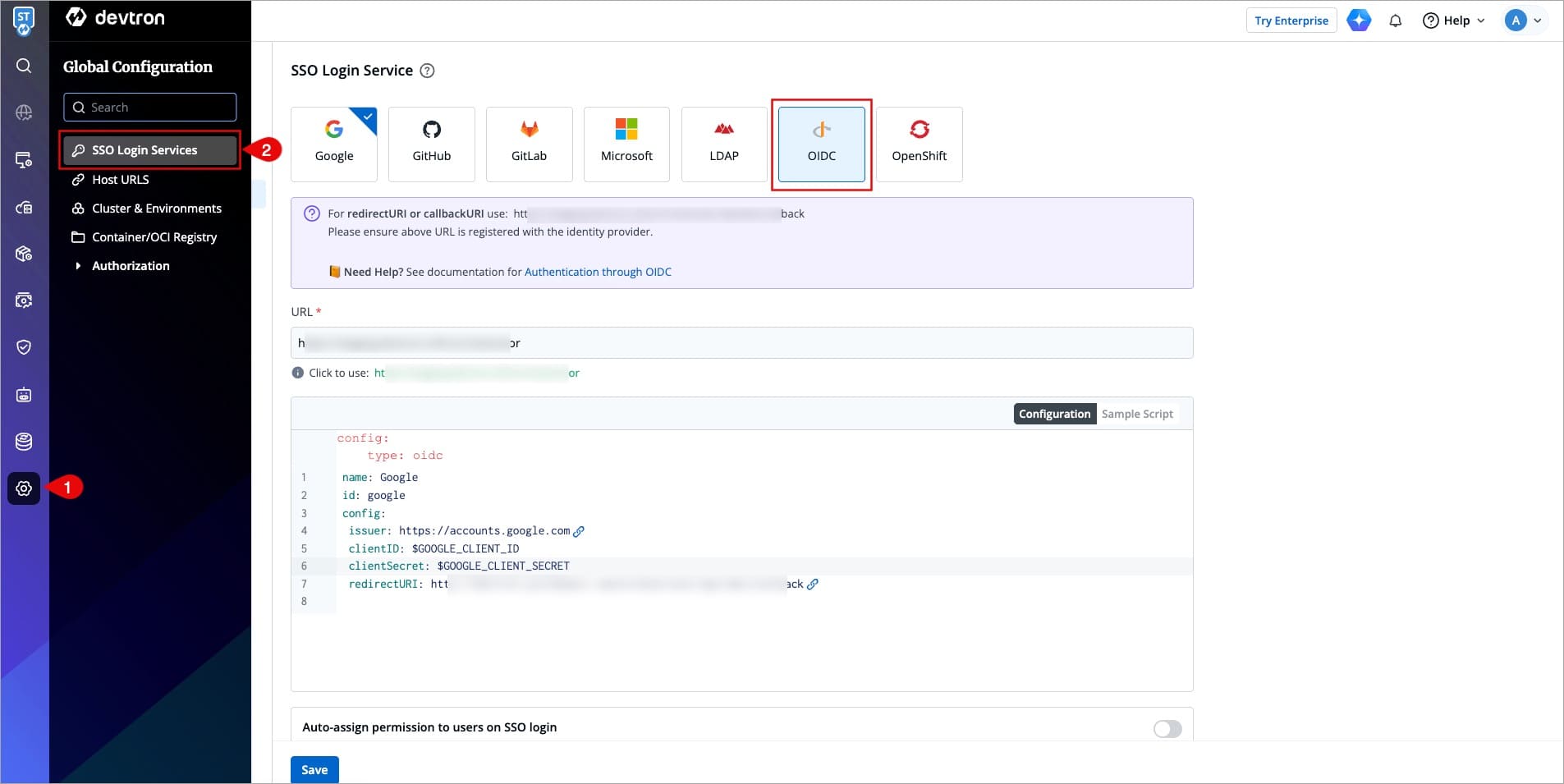
+1. Navigate to **Global Configurations** → **Authorization** → **SSO Login Services**. The SSO Login Service page is displayed.
+
+ 
+
Figure 1: Select OIDC
+
+2. Select **OIDC** from the list of available SSO login services.
+
+3. Click the URL suggested in green color next to the **Click to use** label to update the **URL** field.
+
+ When you populate **URL** field, the redirectURI (or callbackURI) is updated automatically in the purple block displayed at the top of the SSO Login Service screen. This redirectURI is essential, as it is required while setting up the OAuth credentials in GitHub.
+
+4. Copy the redirectURI from the purple block.
+
+ 
+
Figure 2: Copy Redirect URI
+
+---
+
## Steps on Keycloak Admin Console
### Creating a Client
@@ -15,31 +35,29 @@ Here, we will add Devtron as a client for using Keycloak SSO.
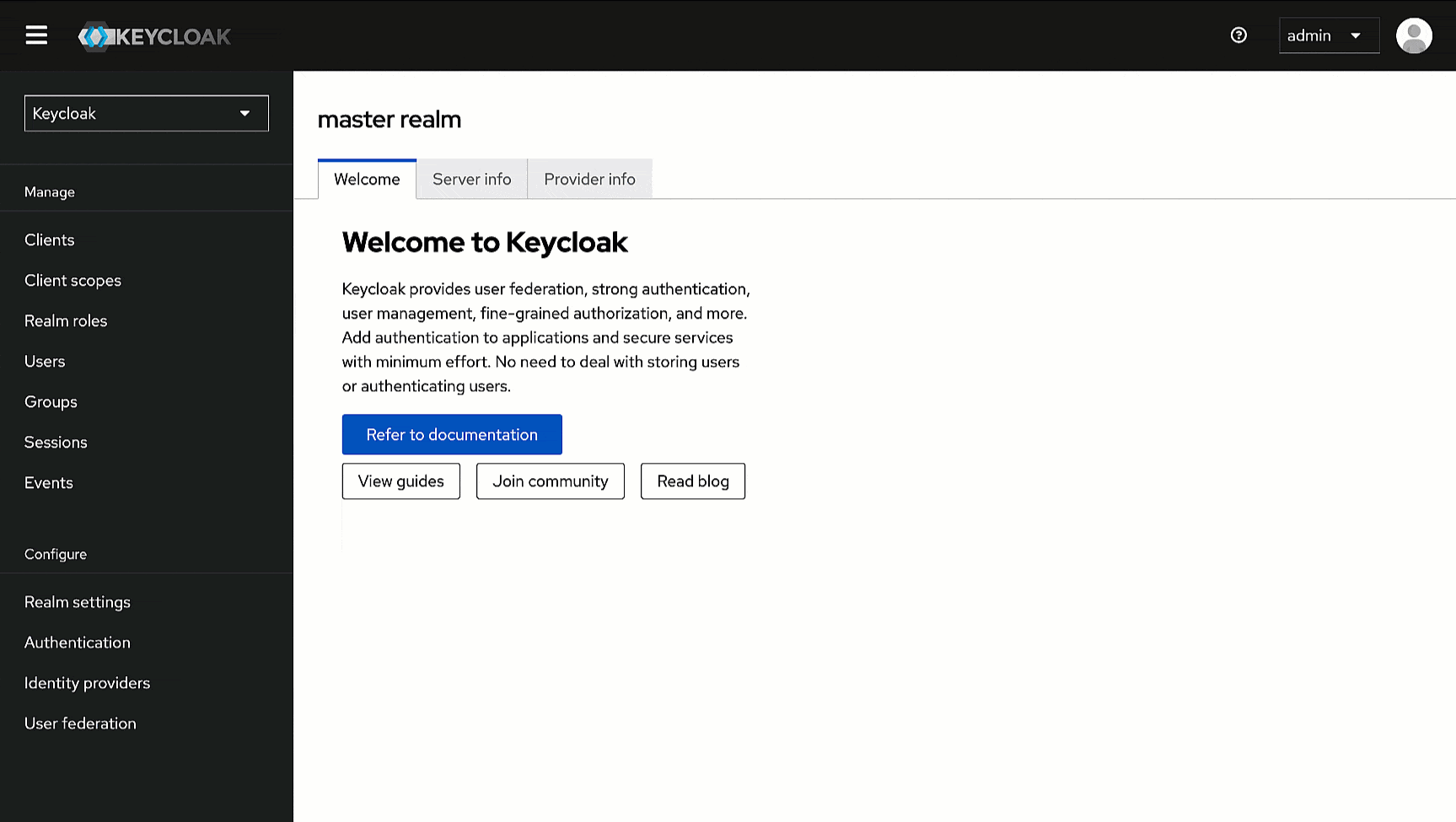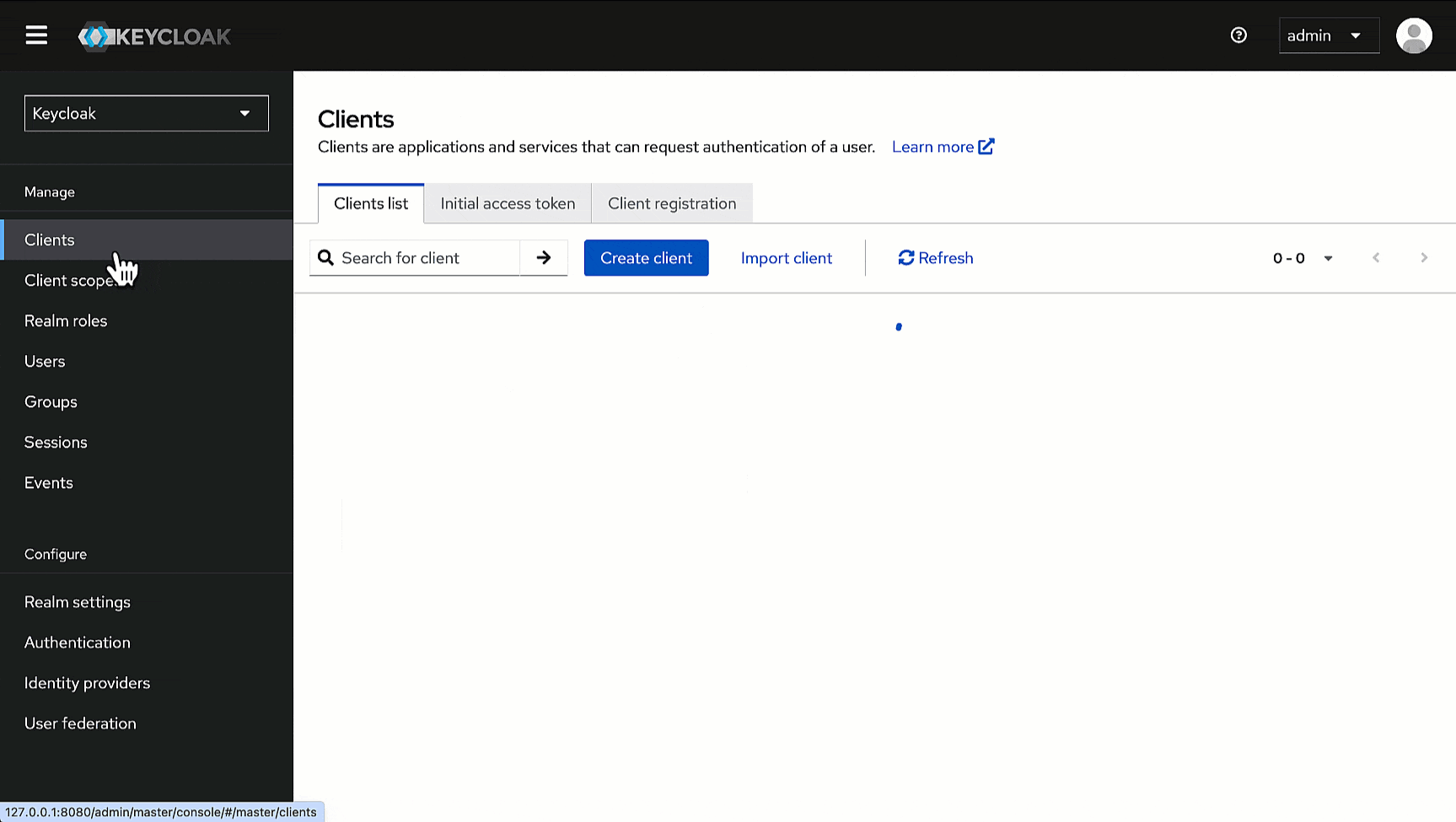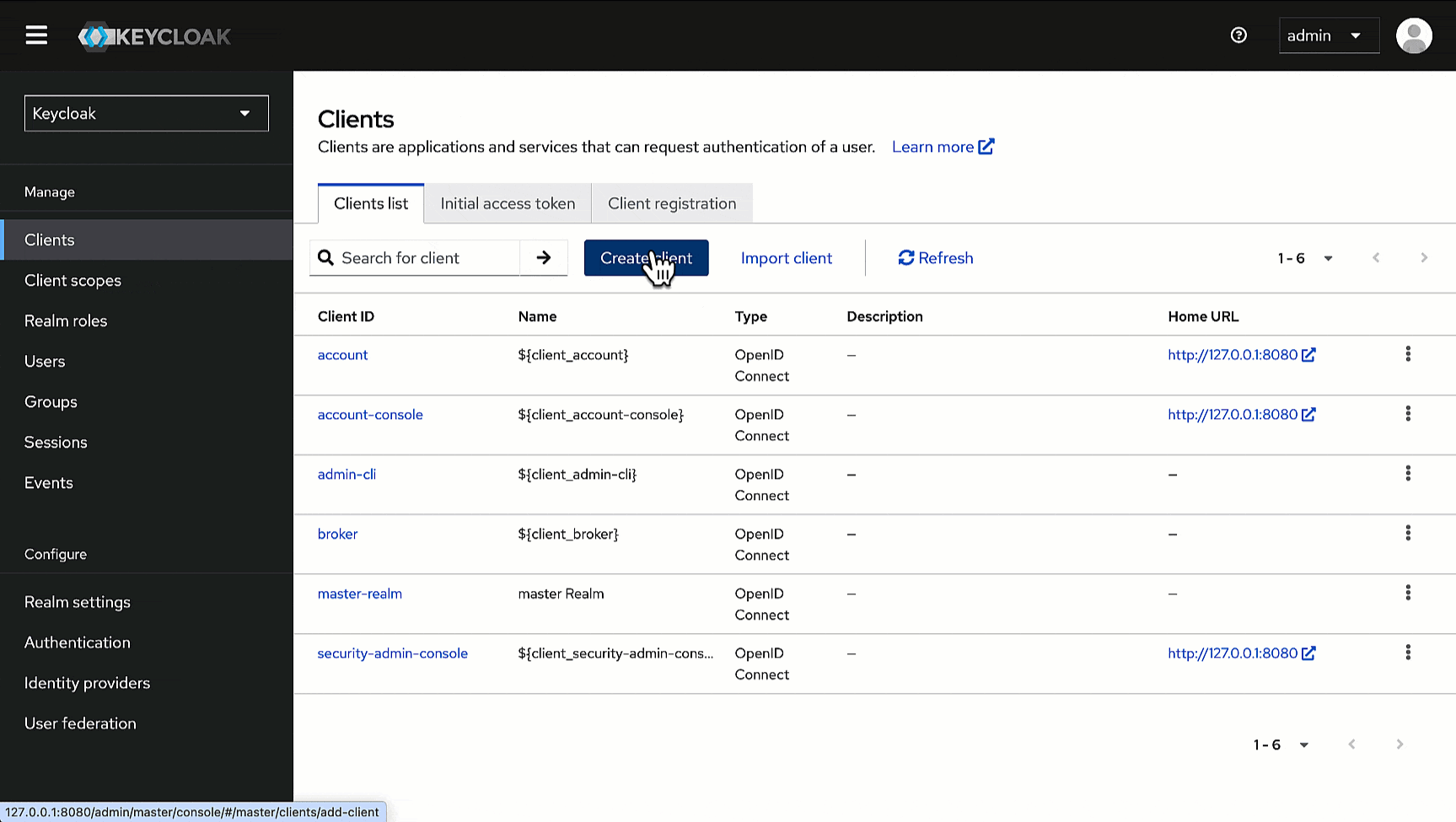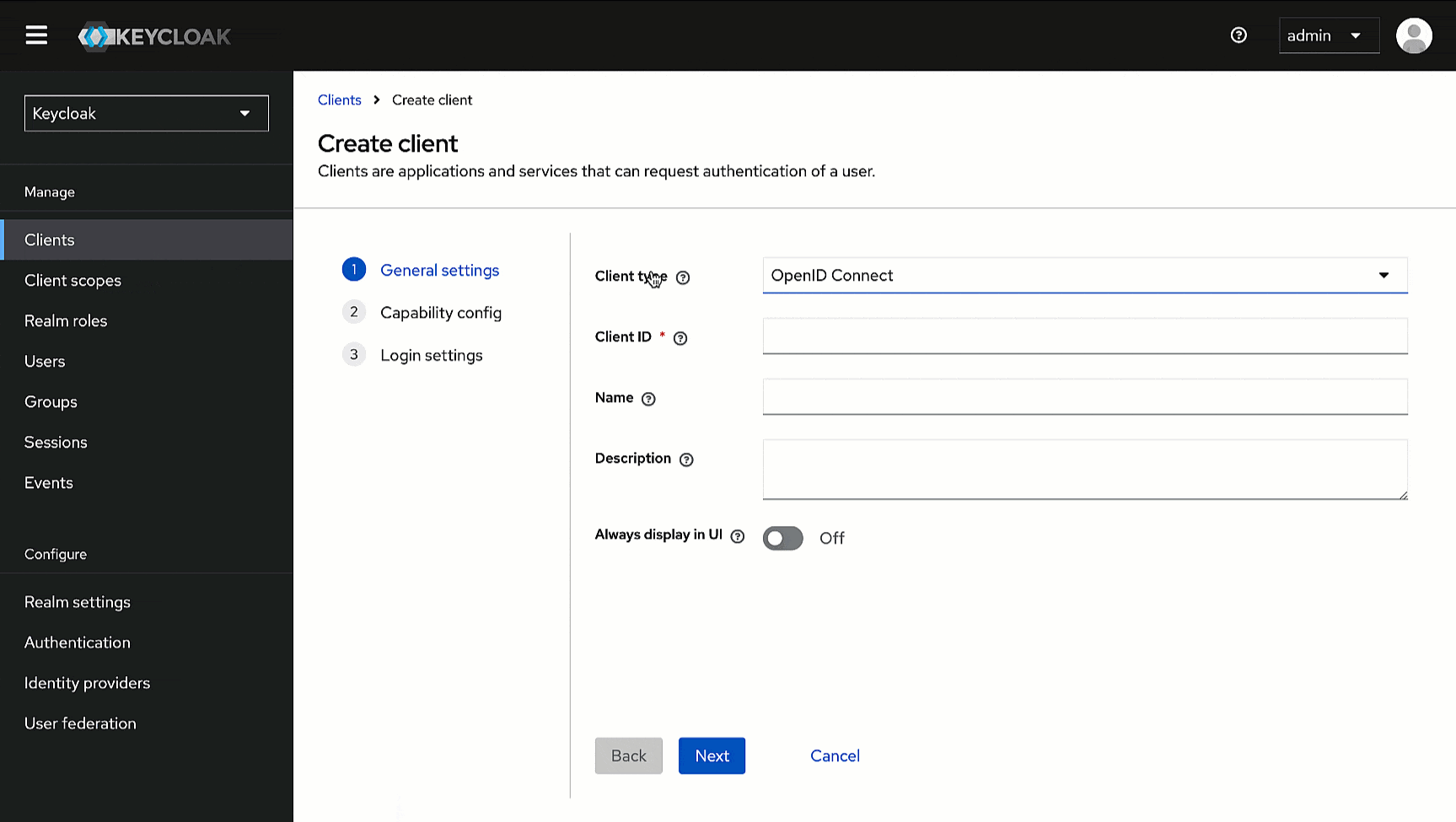
1. In the Admin Console, go to **Clients** and click **Create client**.
- 
-
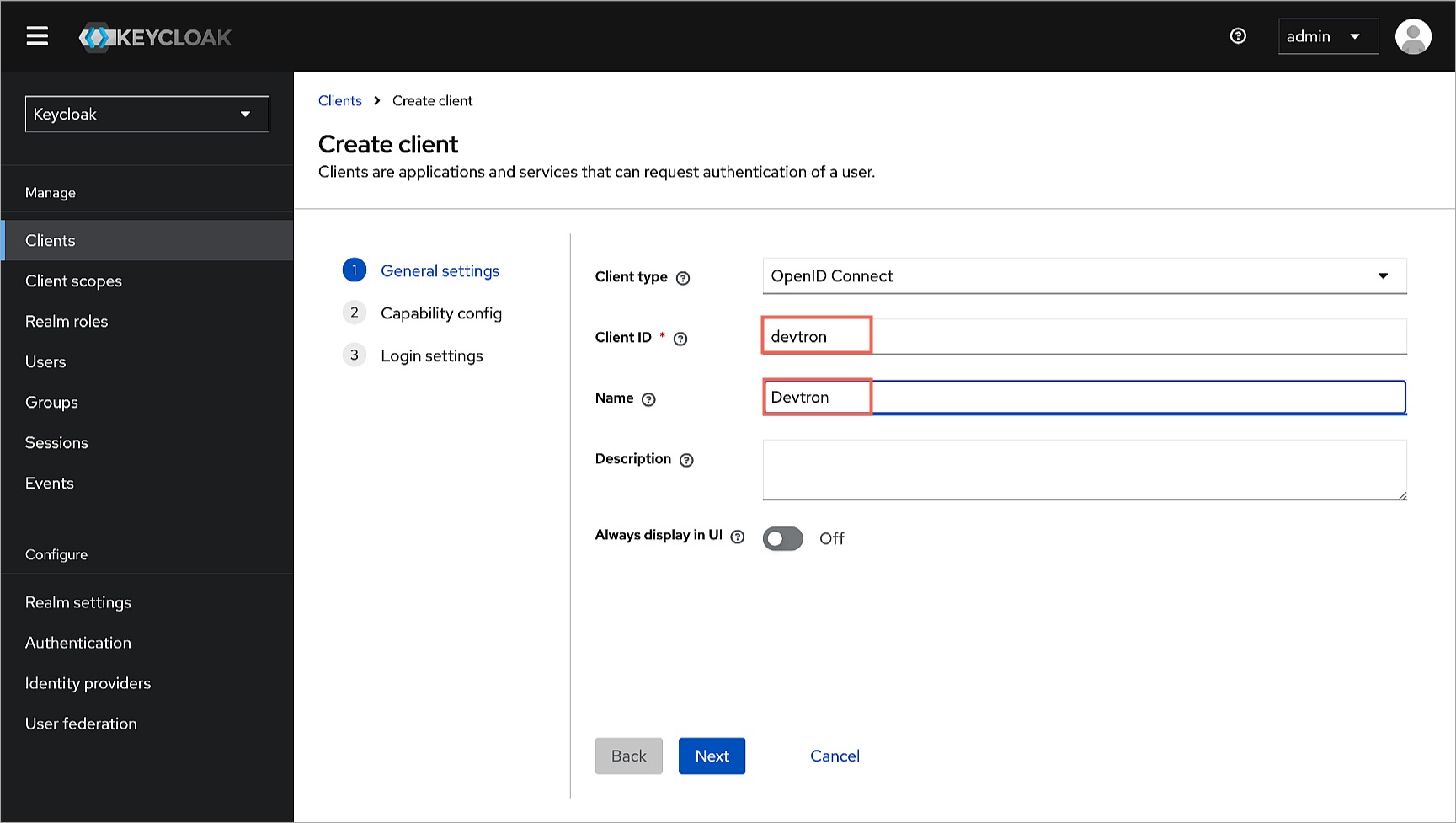
2. Within **General Settings**:
* Enter `devtron` in the **Client ID** field. We will use this ID while configuring SSO later in Devtron.
* Enter `Devtron` in the **Name** field.
- 
-
-4. Within **Login settings**, enter `https:///orchestrator/api/dex/callback` in the following fields.
+4. Within **Login settings**, enter the `redirectURI` you have copied earlier in the following fields.
* **Valid redirect URIs**
* **Valid post logout redirect URIs**
* **Web origins**
- [Click here](https://devtron-public-asset.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/images/global-configurations/sso-login-service/keycloak/base-url.jpg) to know where to find `DEVTRON_BASE_URL`.
-
- 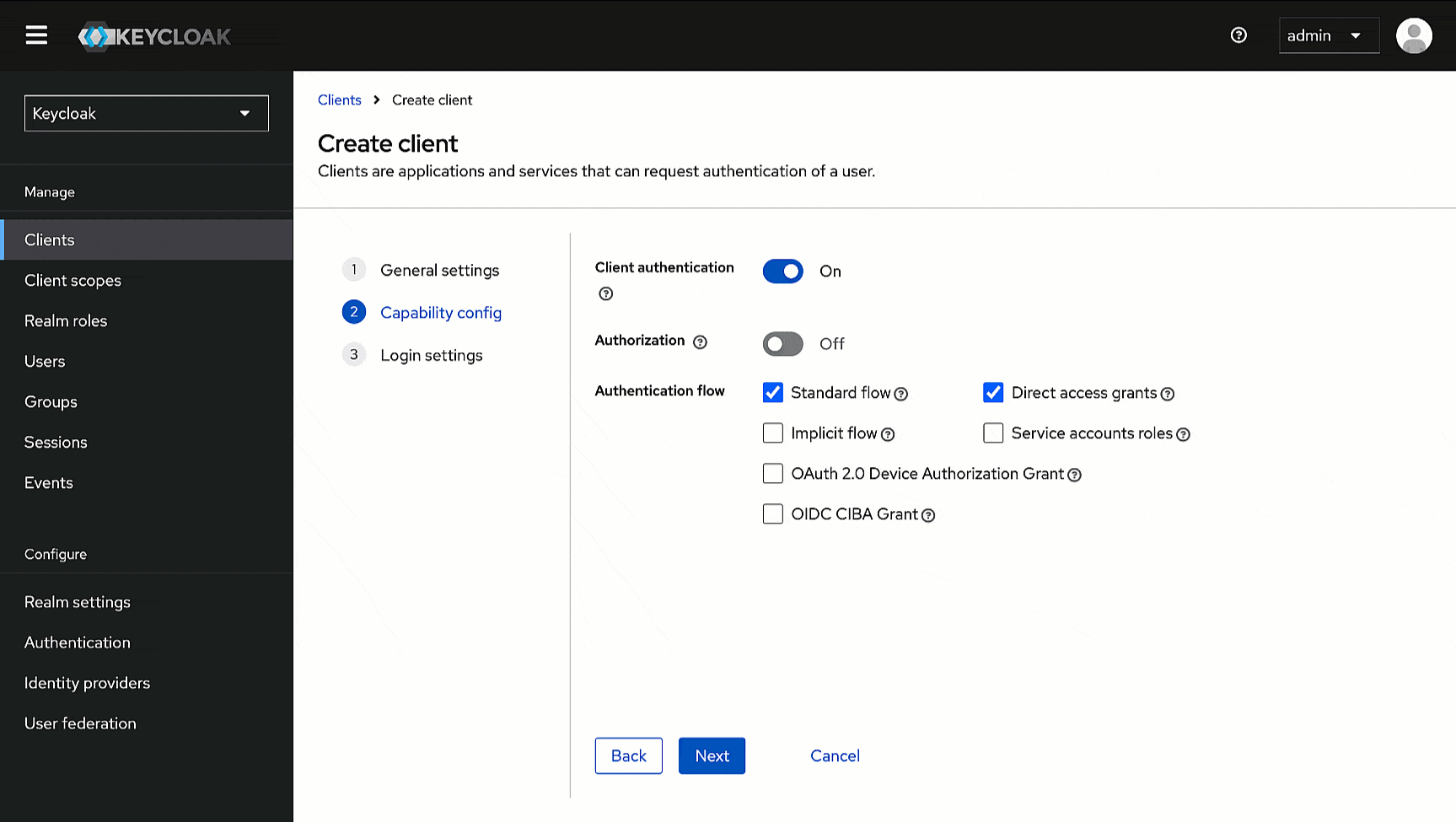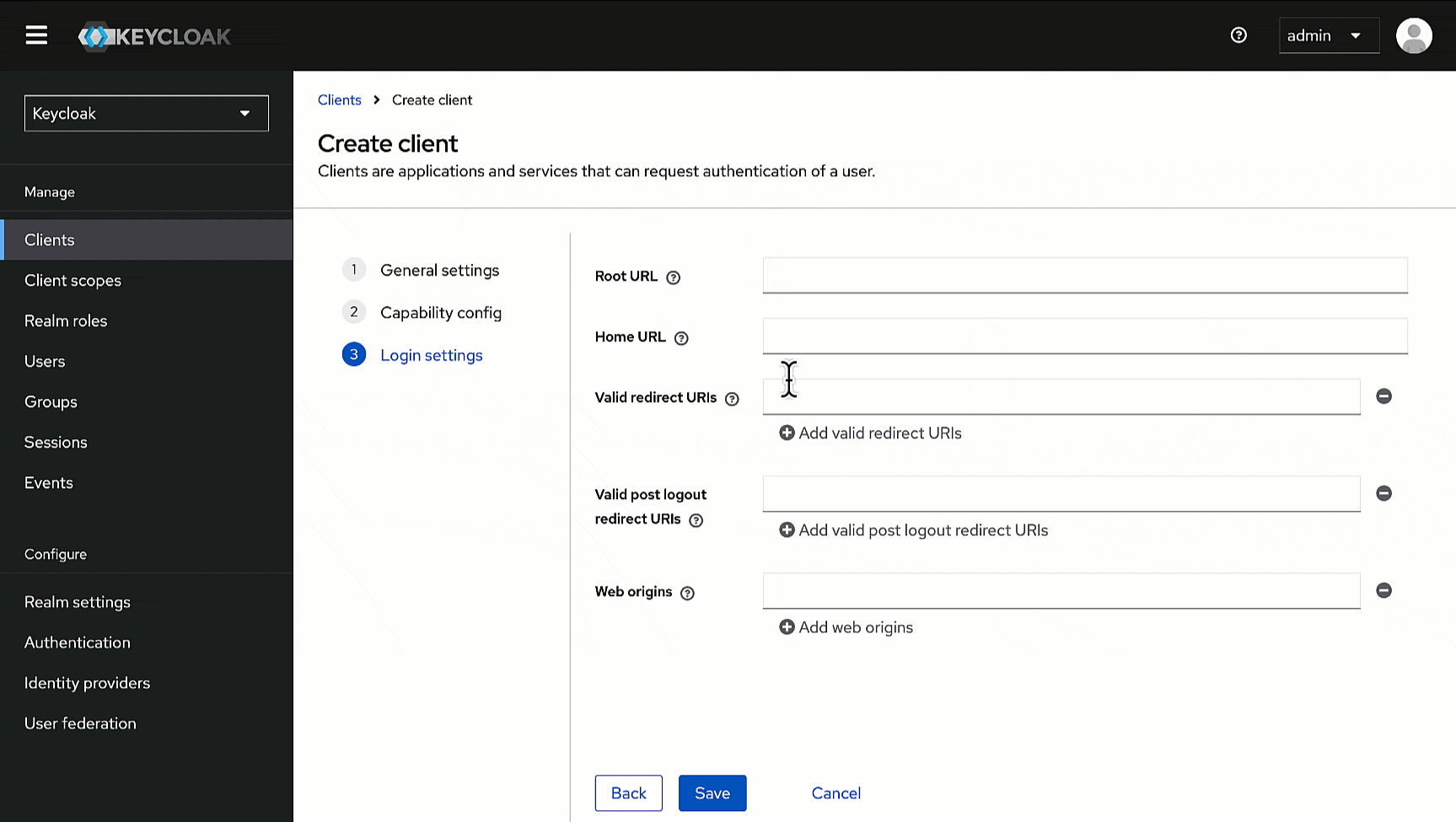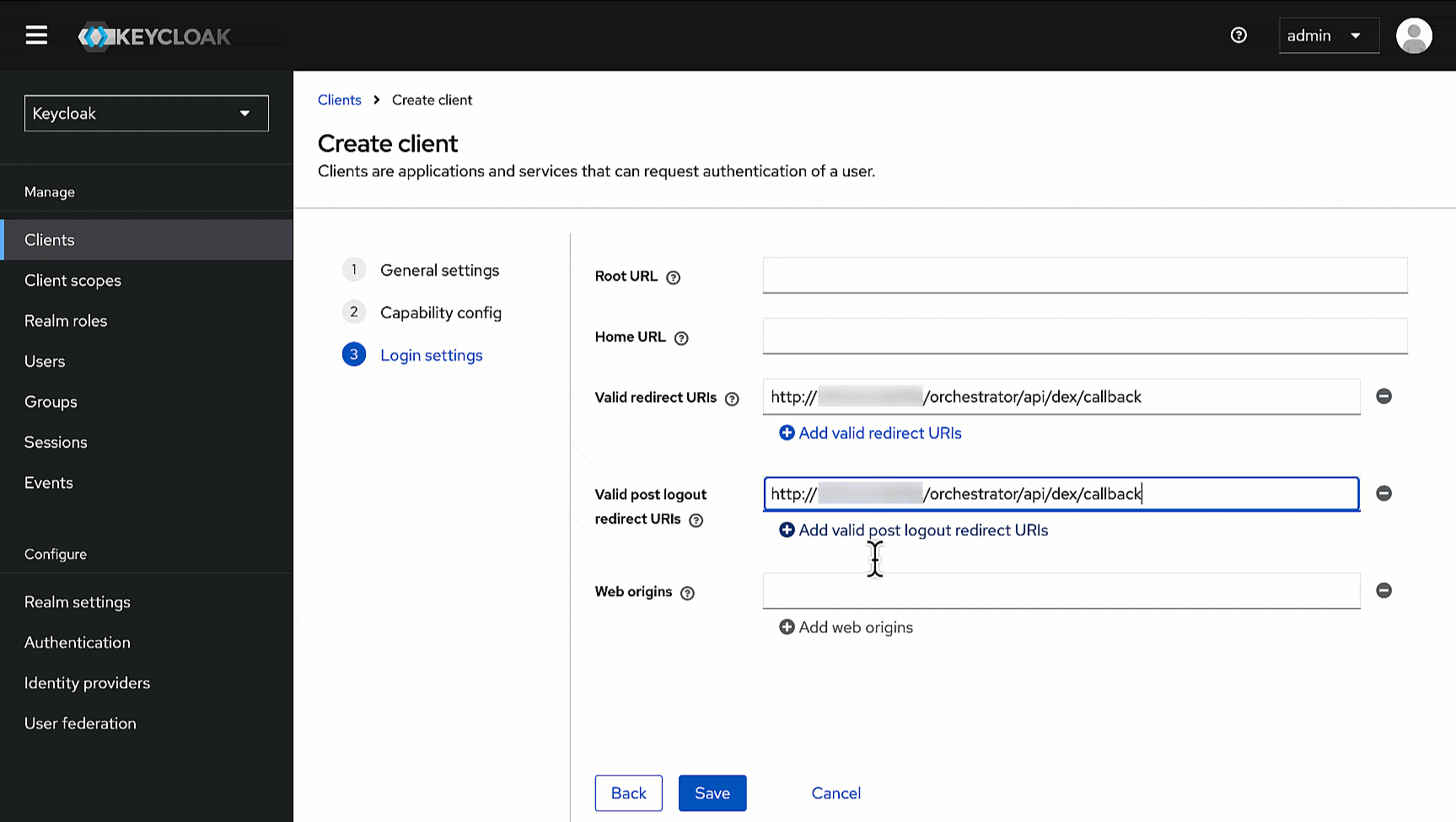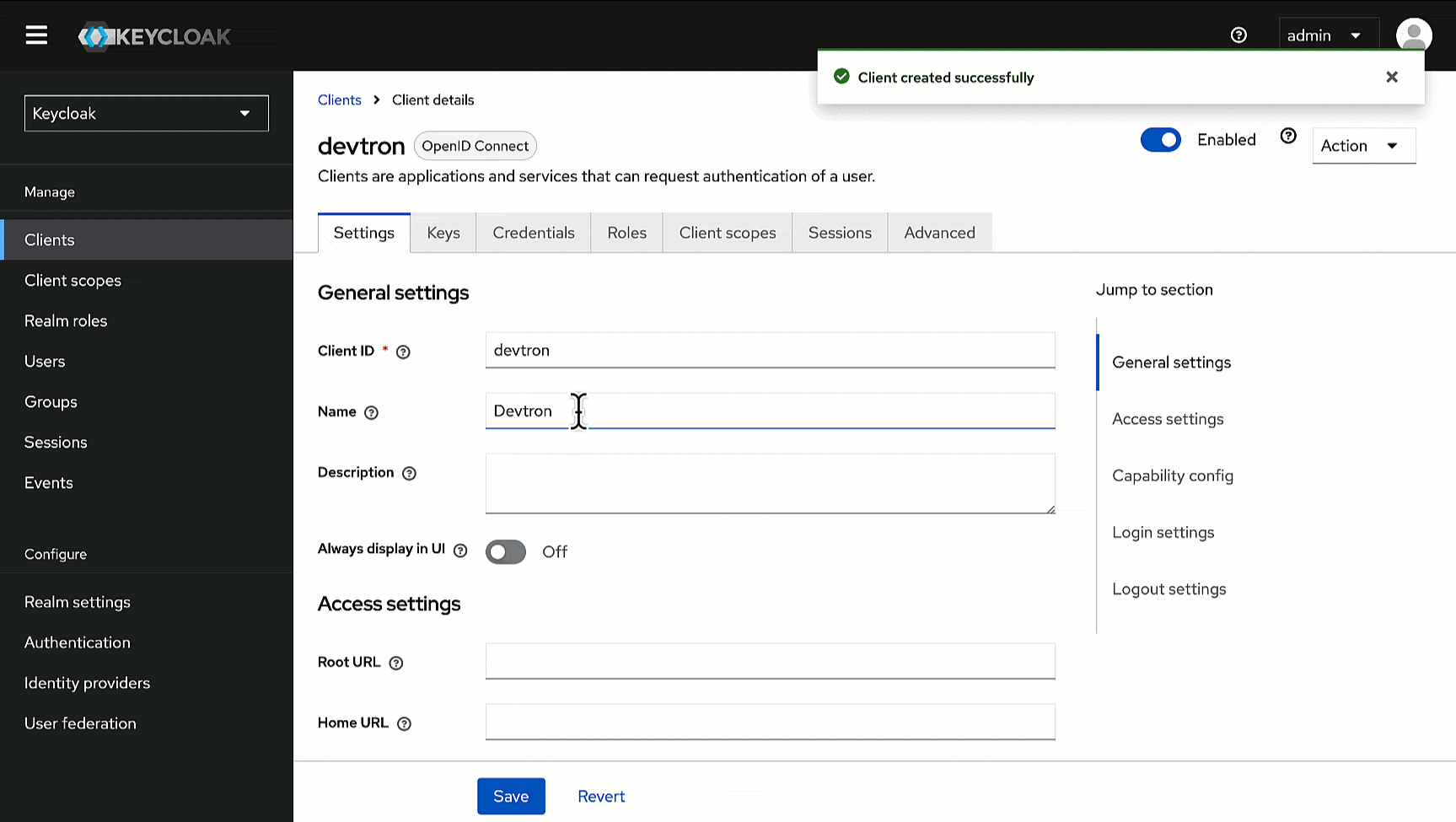
-
5. Click **Save**.
@@ -49,8 +67,8 @@ Here, we will obtain the secret we need while configuring SSO in Devtron.
1. Go to the **Credentials** tab of the client you created.
- 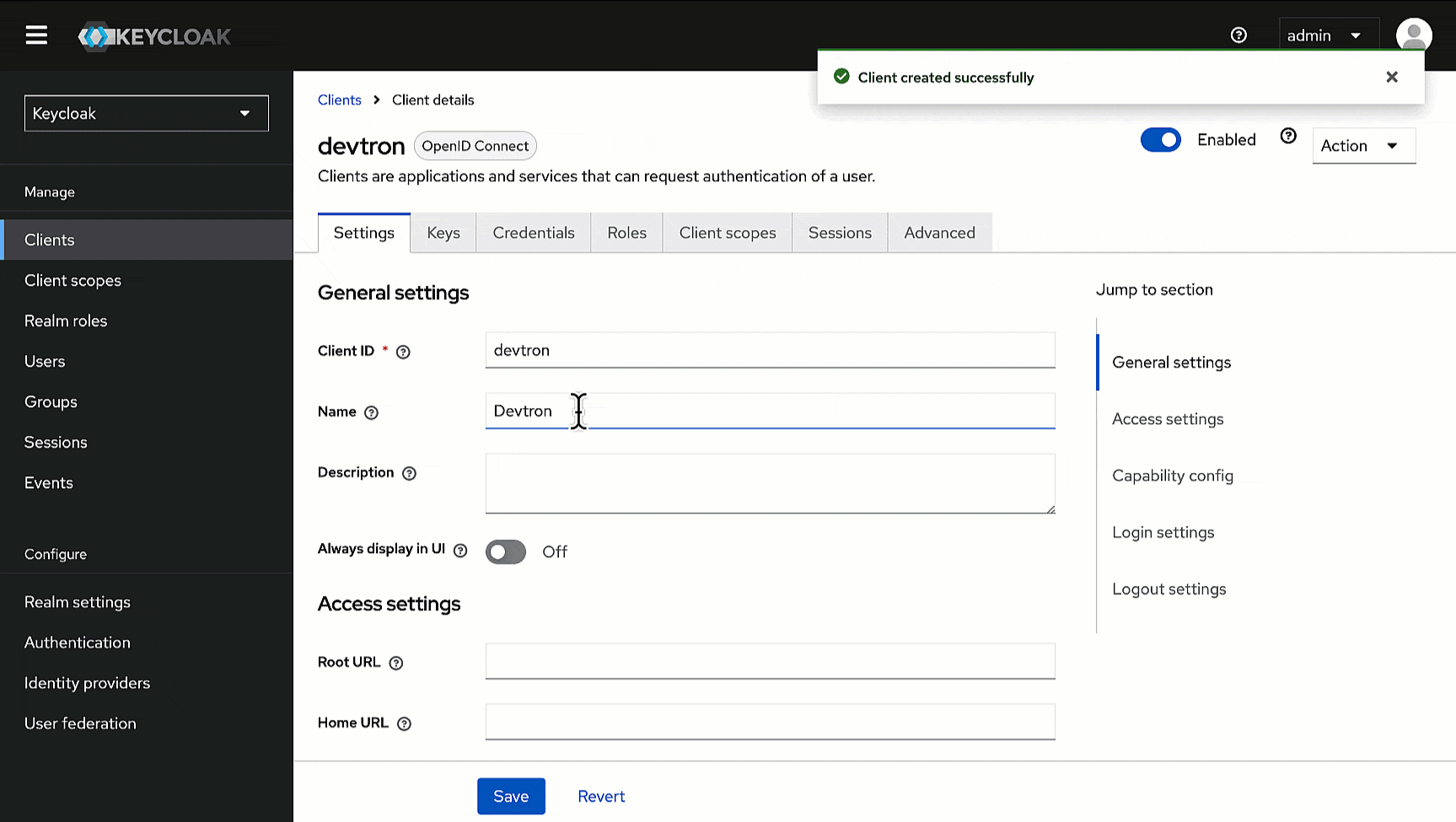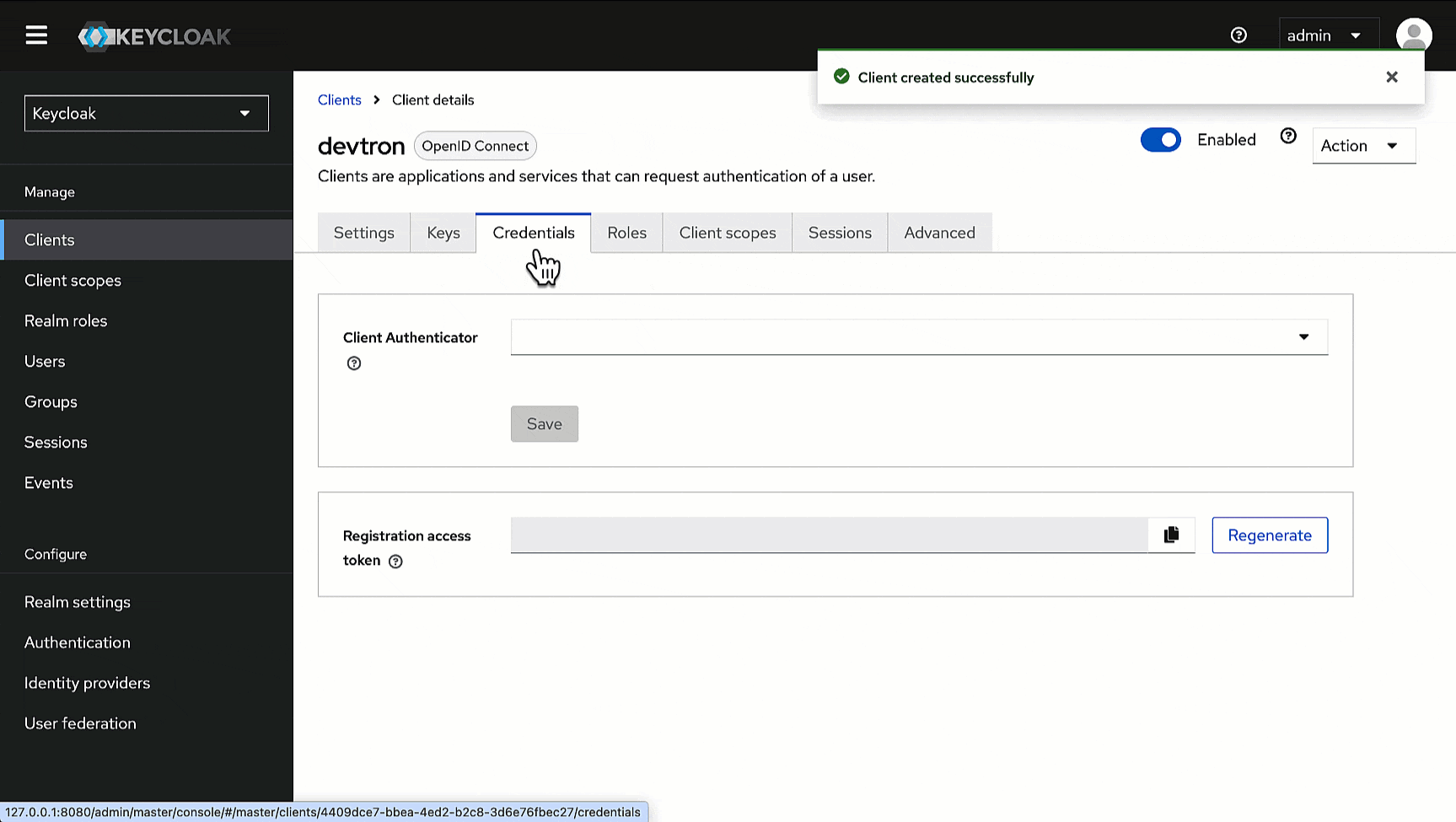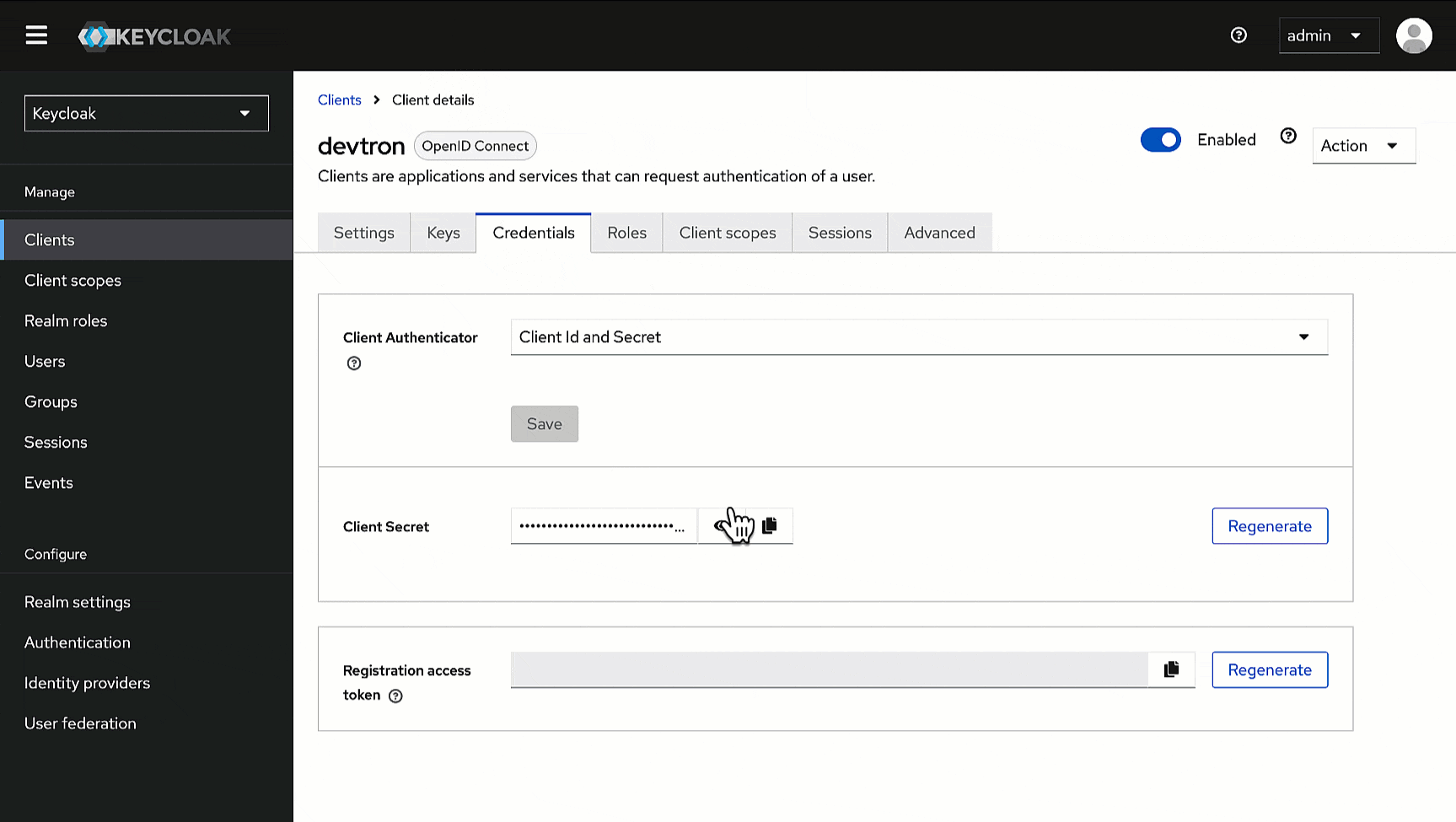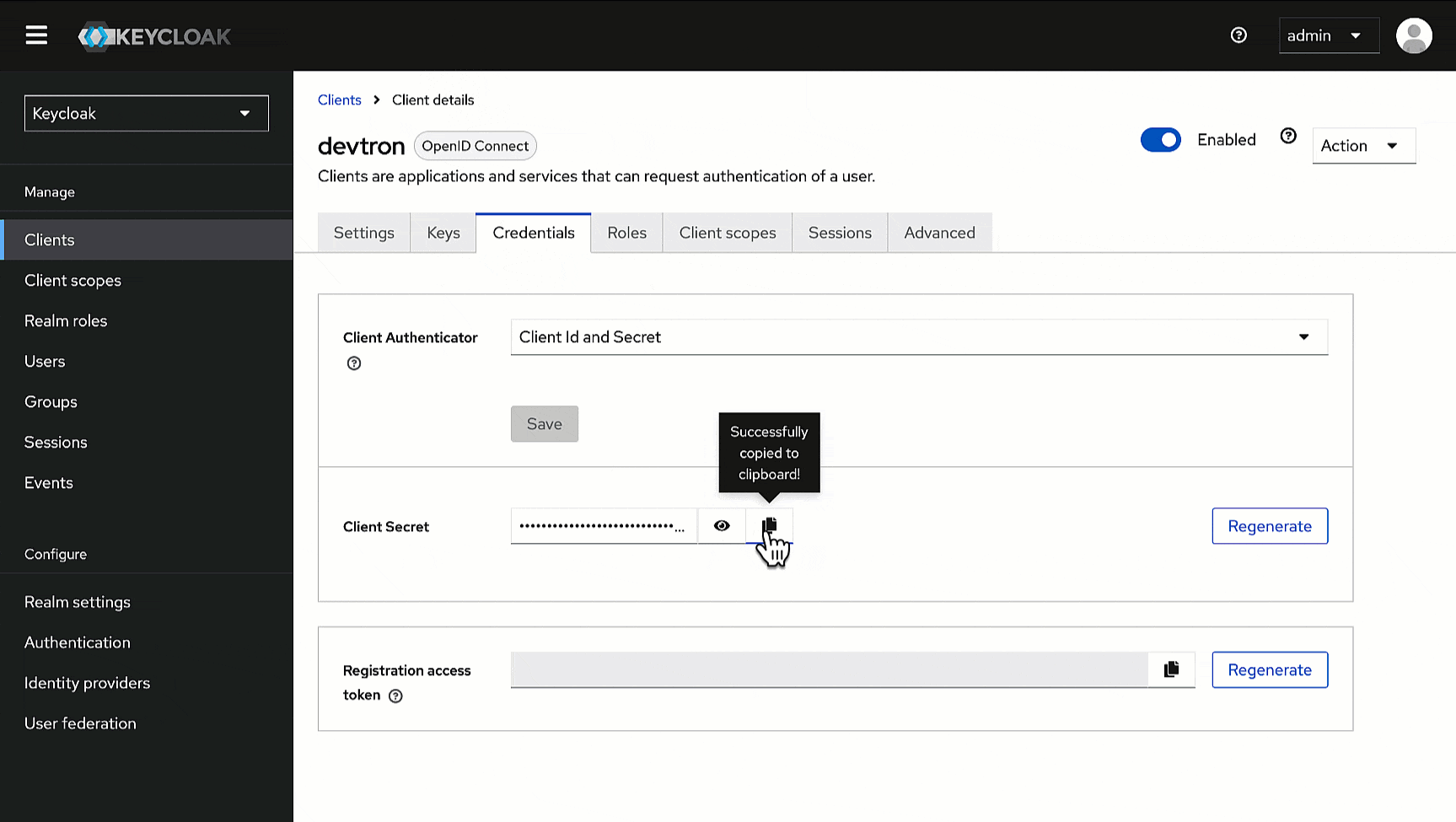
-
2. Use the copy button next to the **Client Secret** field and paste it somewhere for future reference.
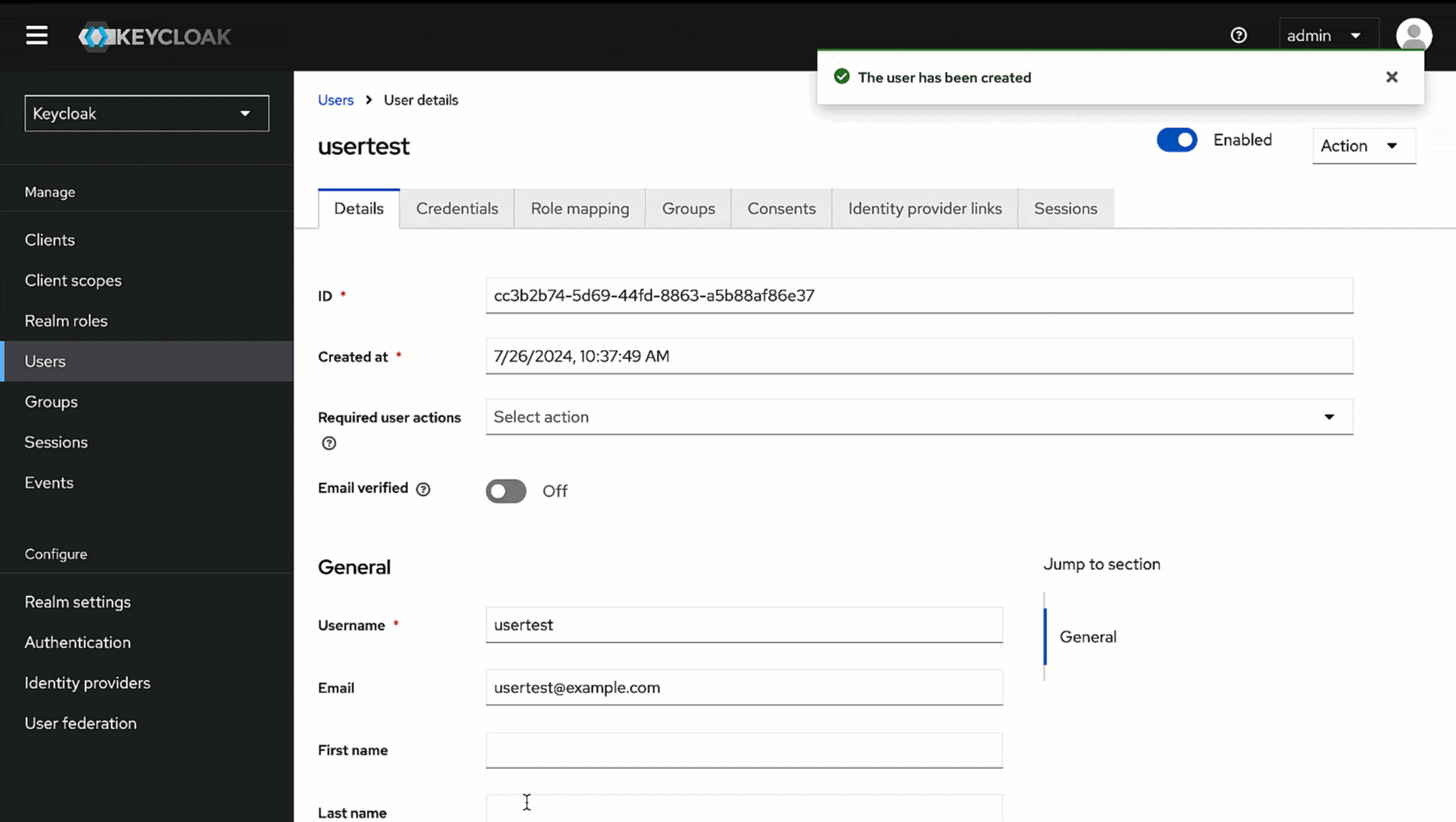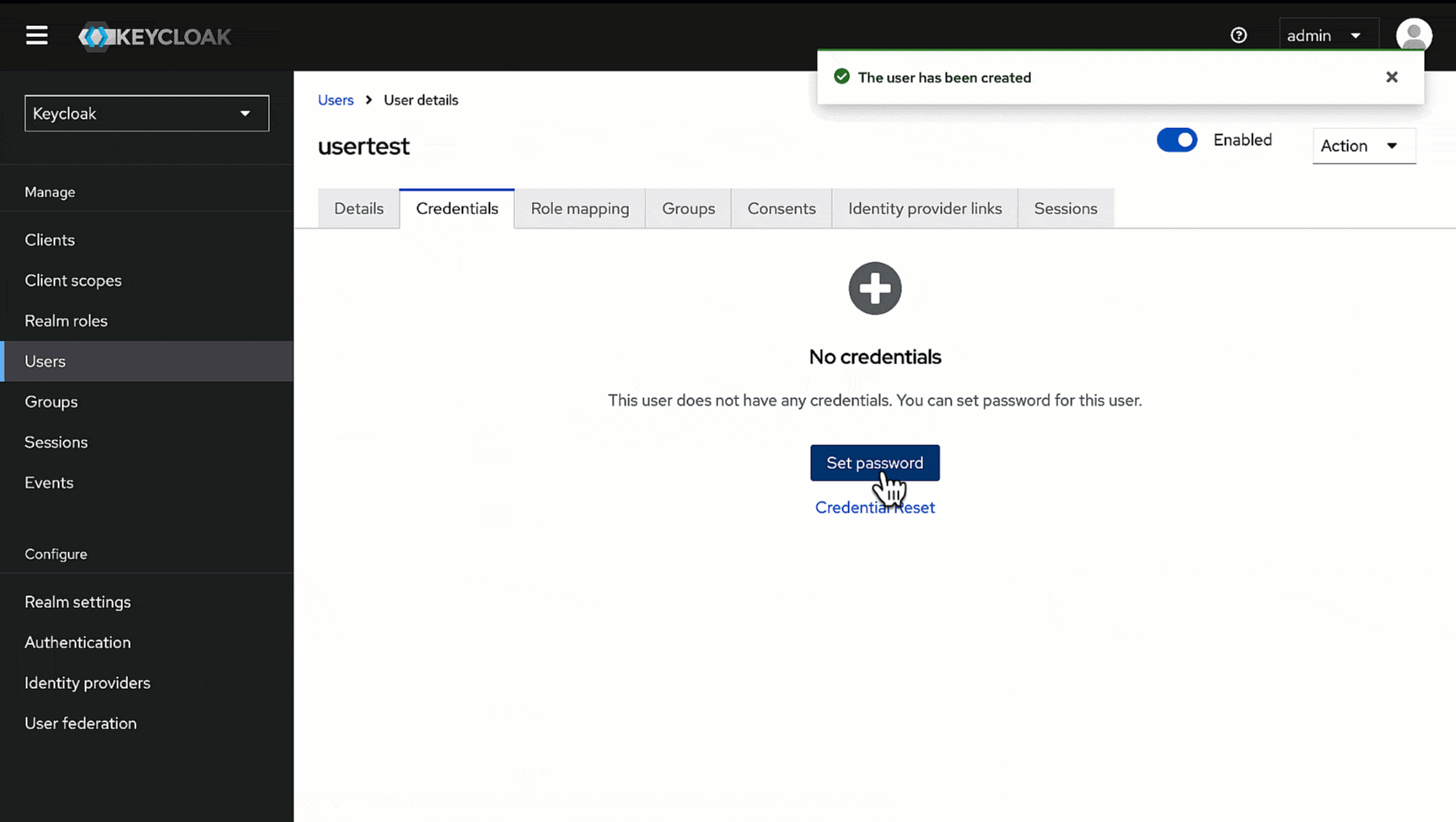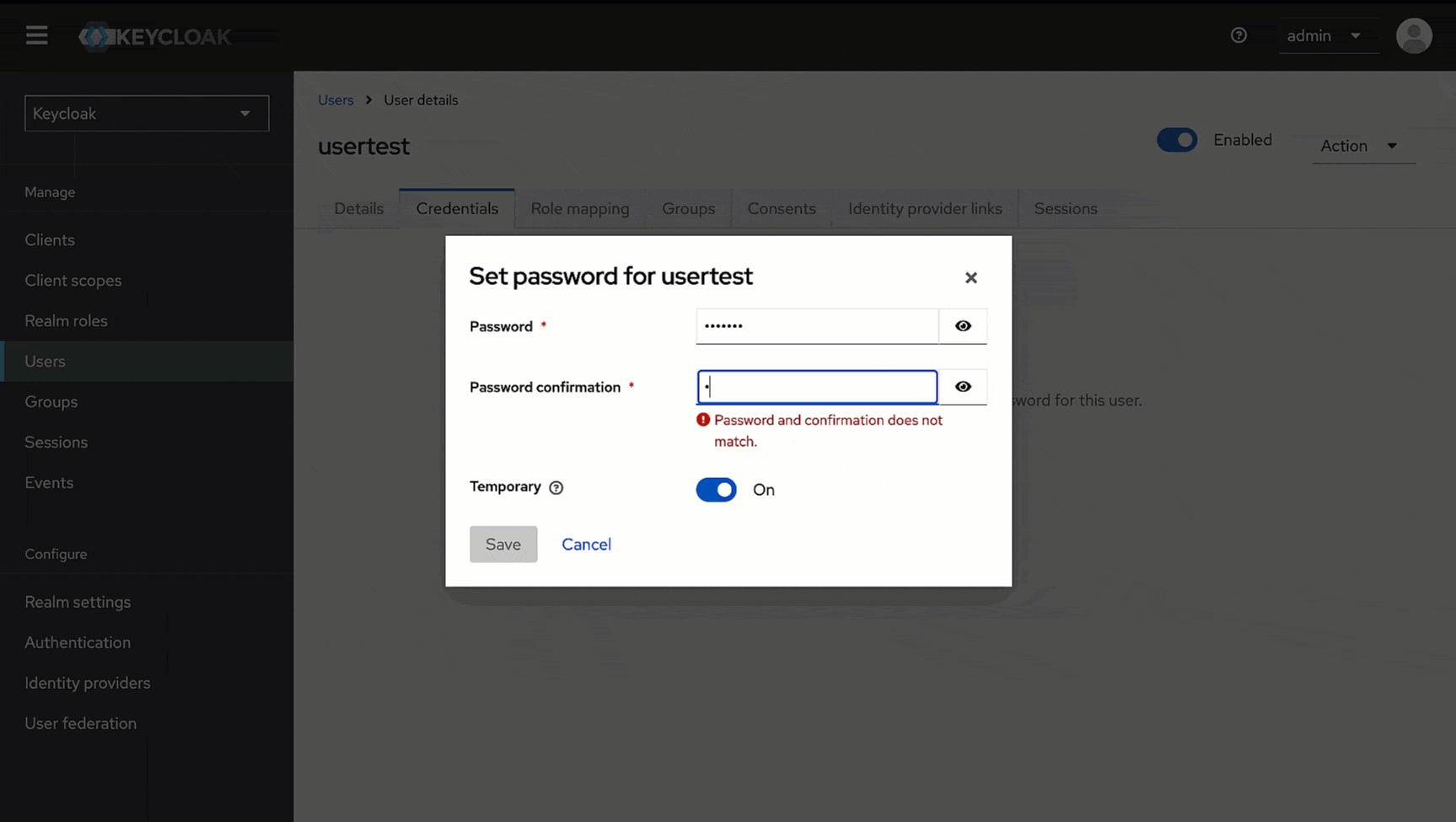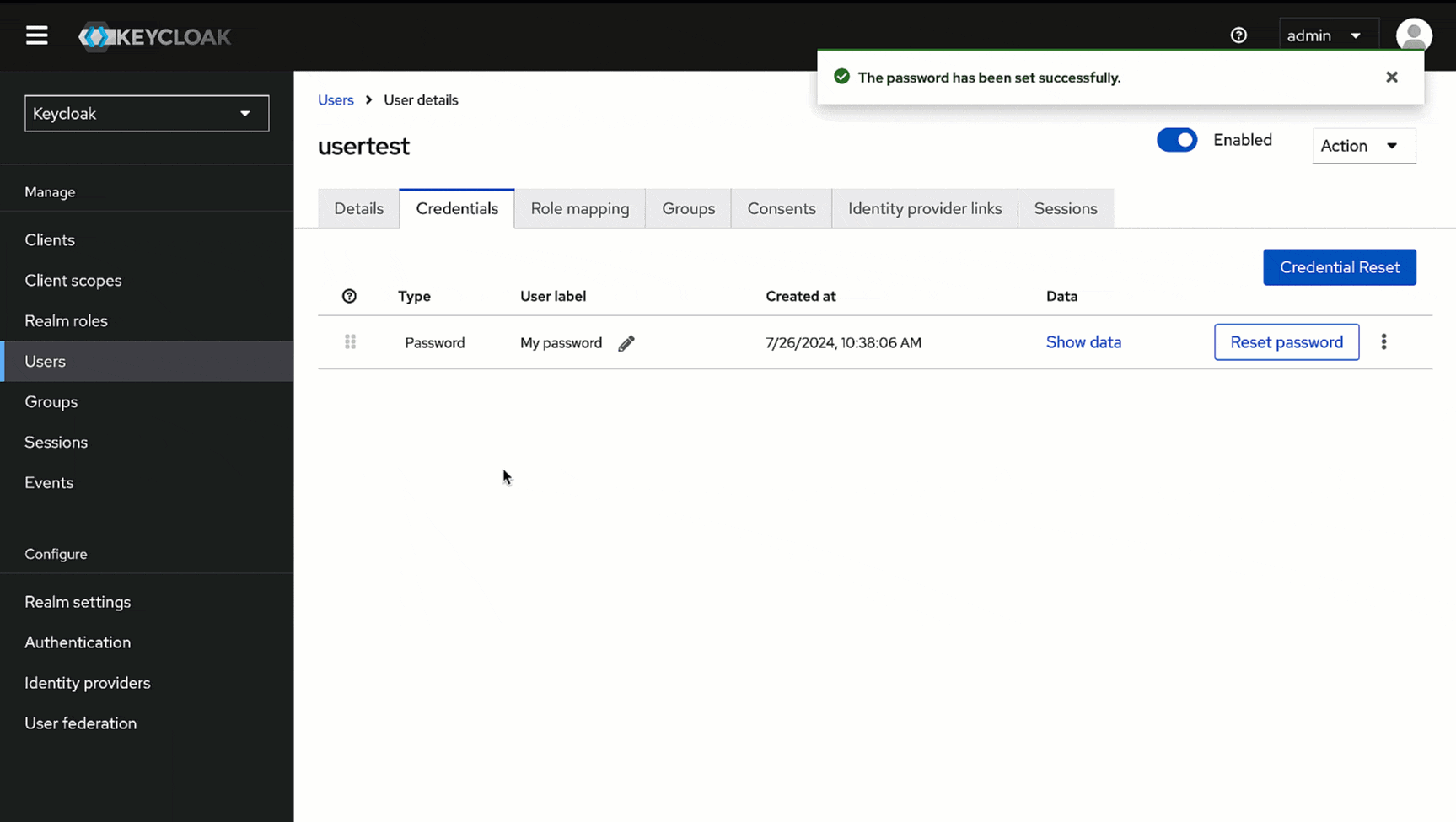
@@ -62,15 +80,15 @@ Here, we will create a user that can log in to Devtron via SSO. We will assign a
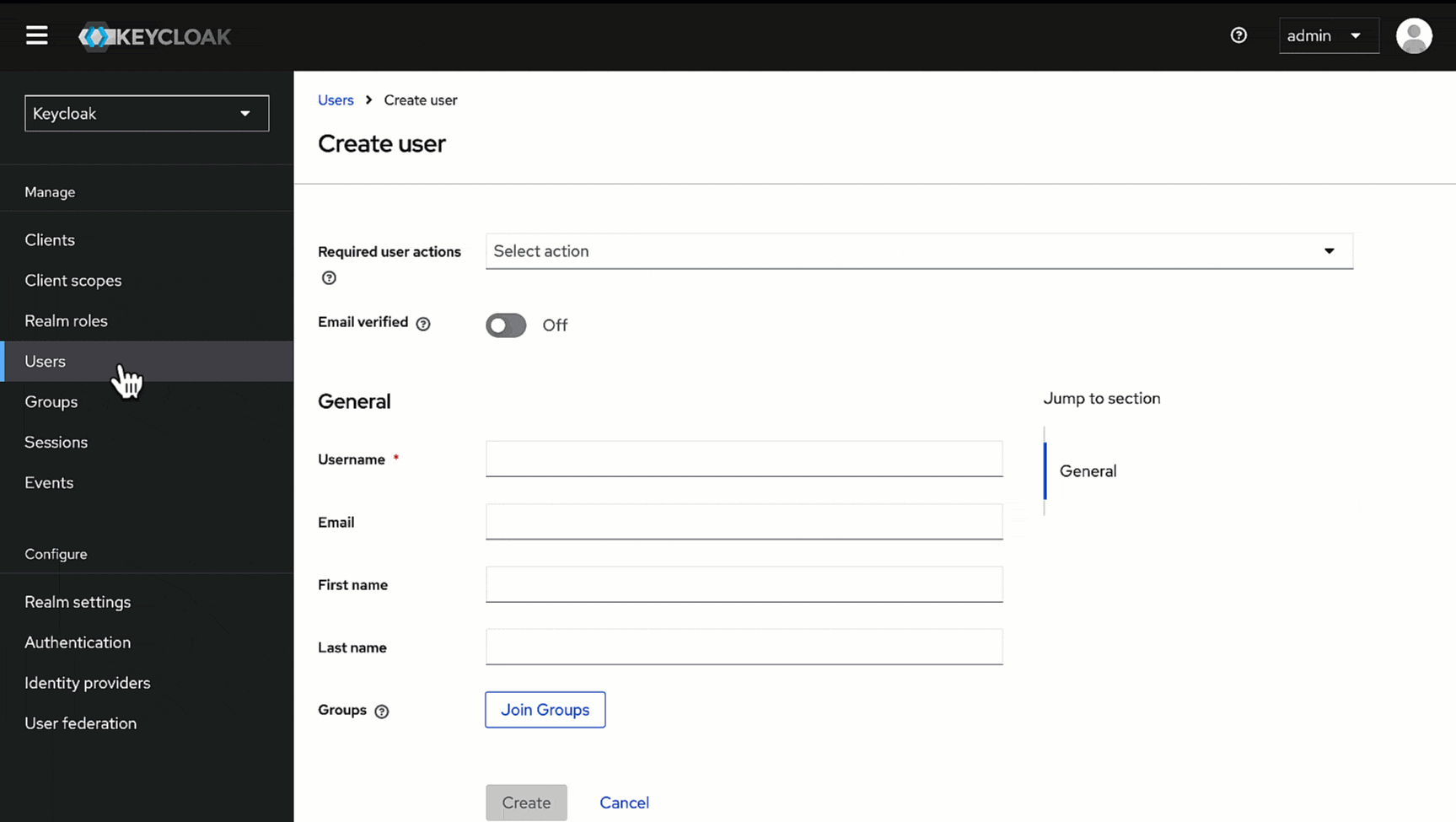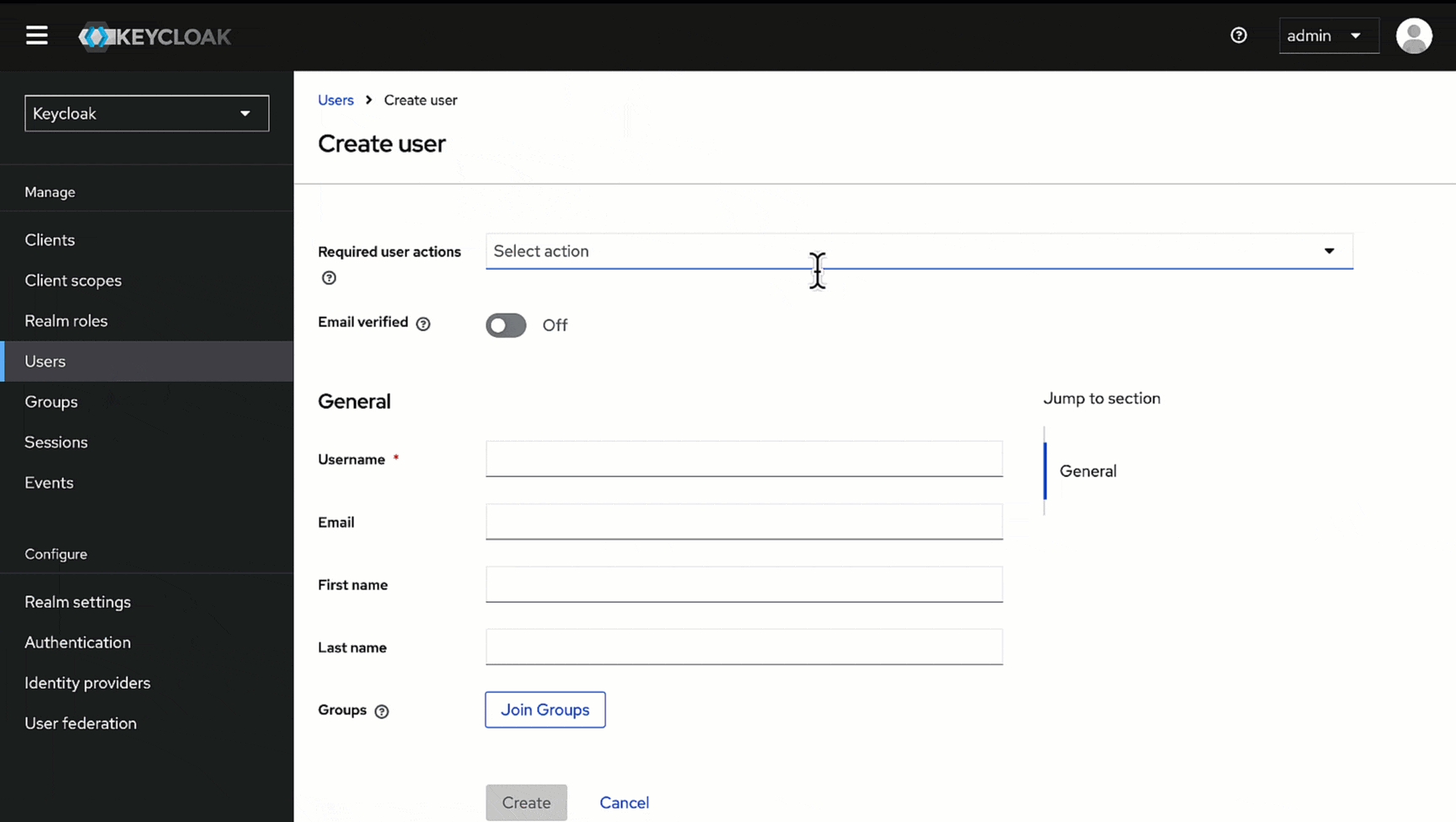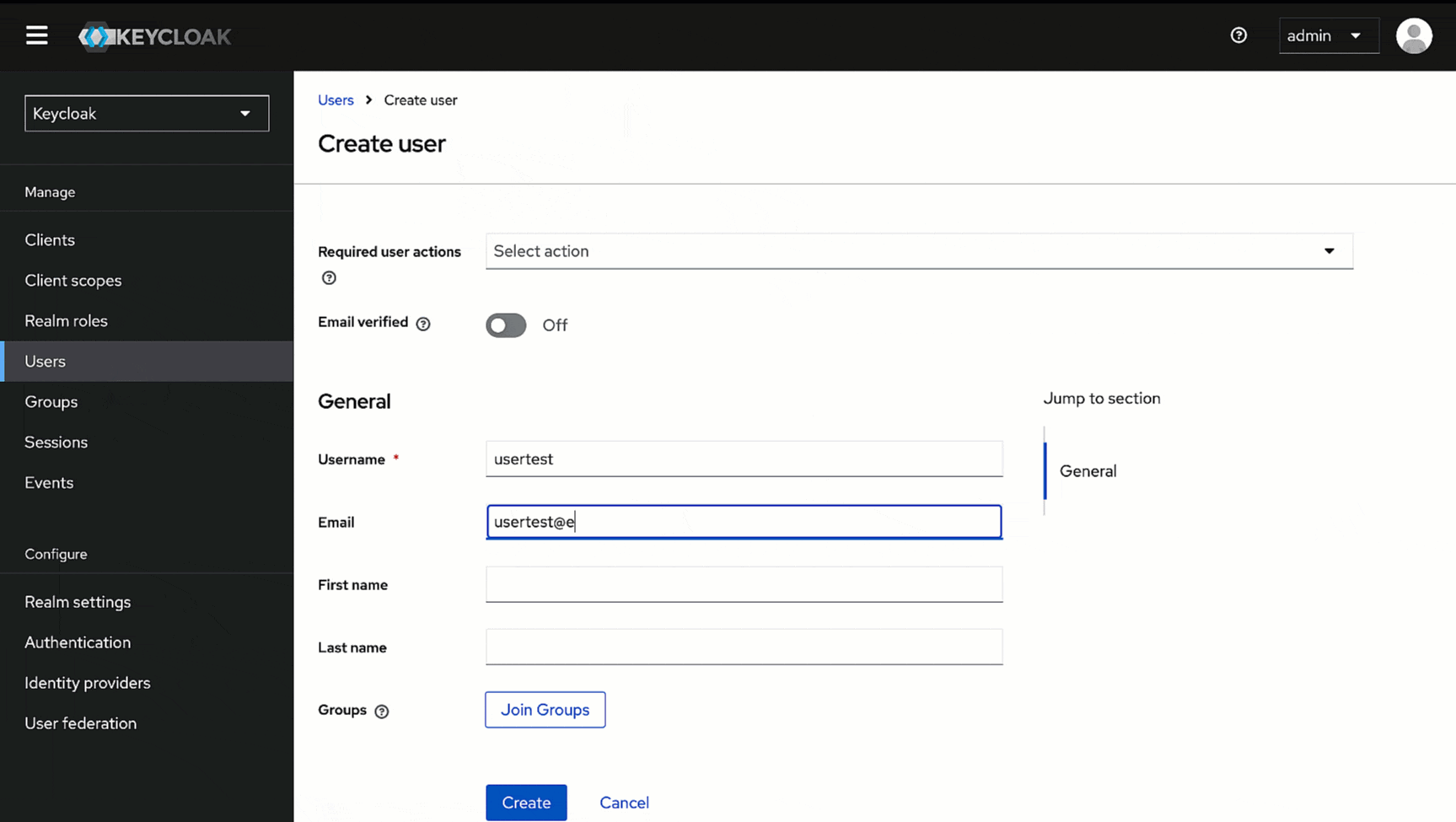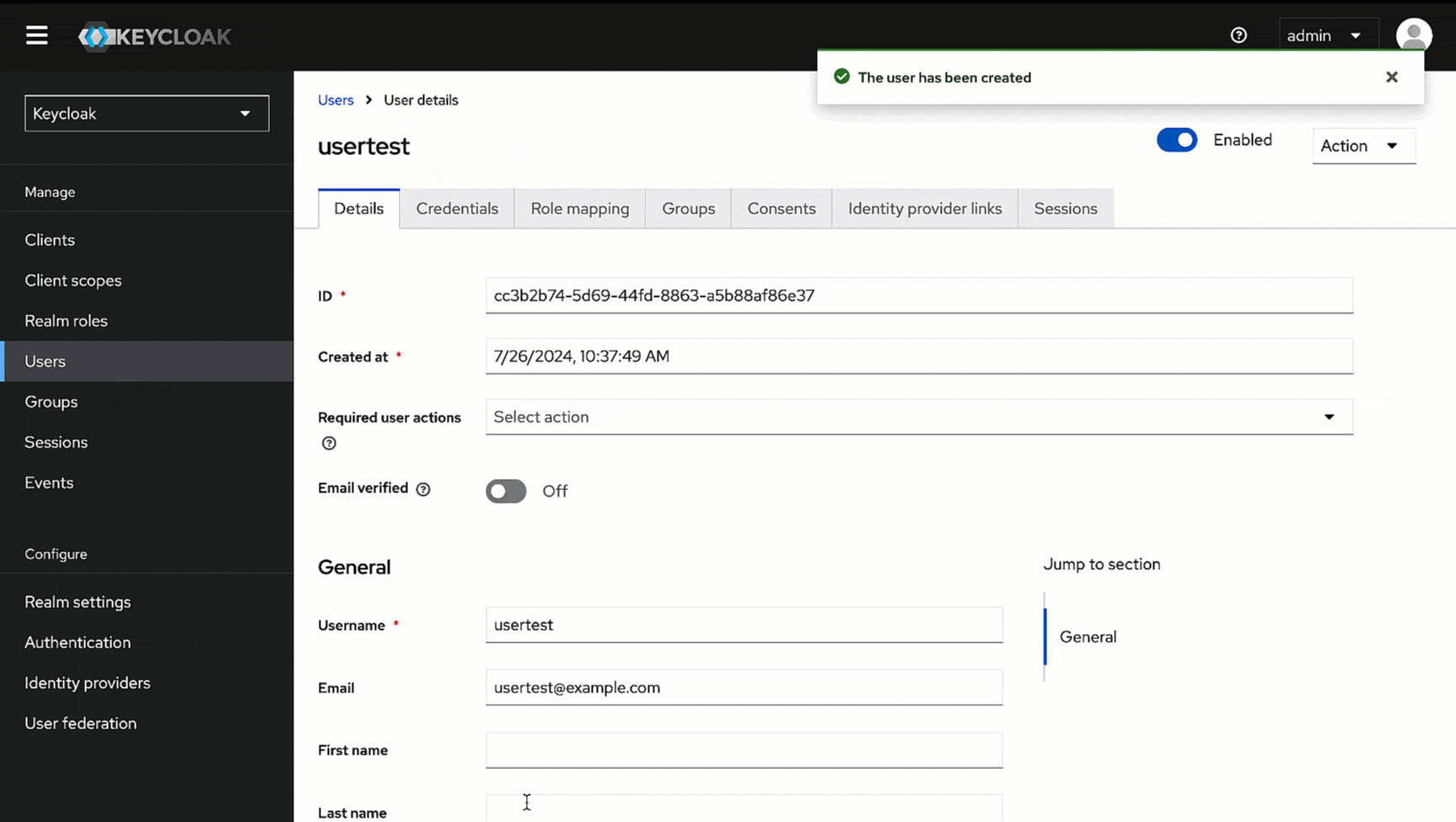
2. Give a username (e.g., *usertest*) in the **Username** field and enter the user's email address (e.g., *usertest@example.com*) in the **Email** field.
- 
-
3. Click **Create**. Your user creation will be successful.
4. Go to the **Credentials** tab of the user you created.
- 
-
5. Click **Set password**.
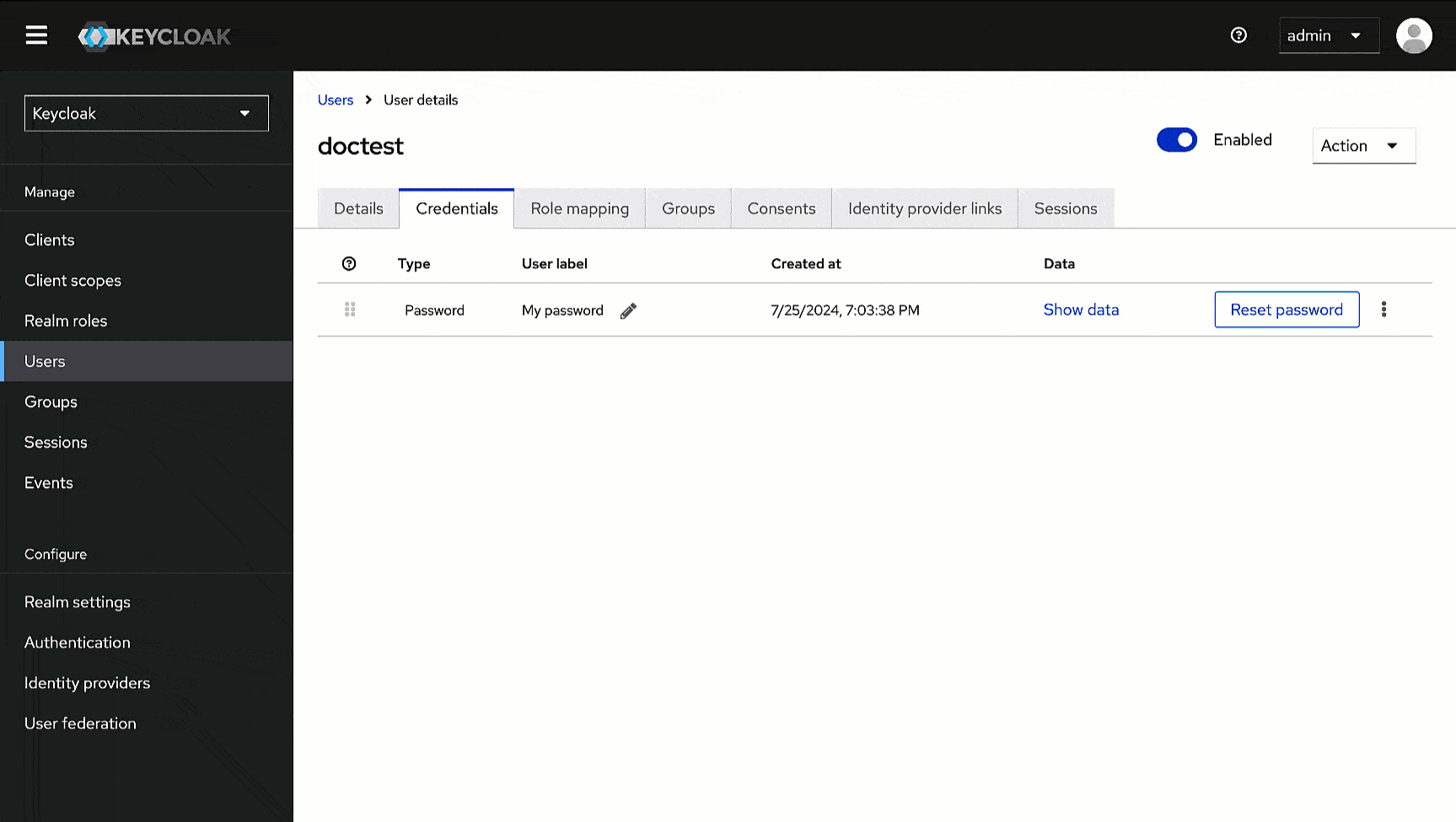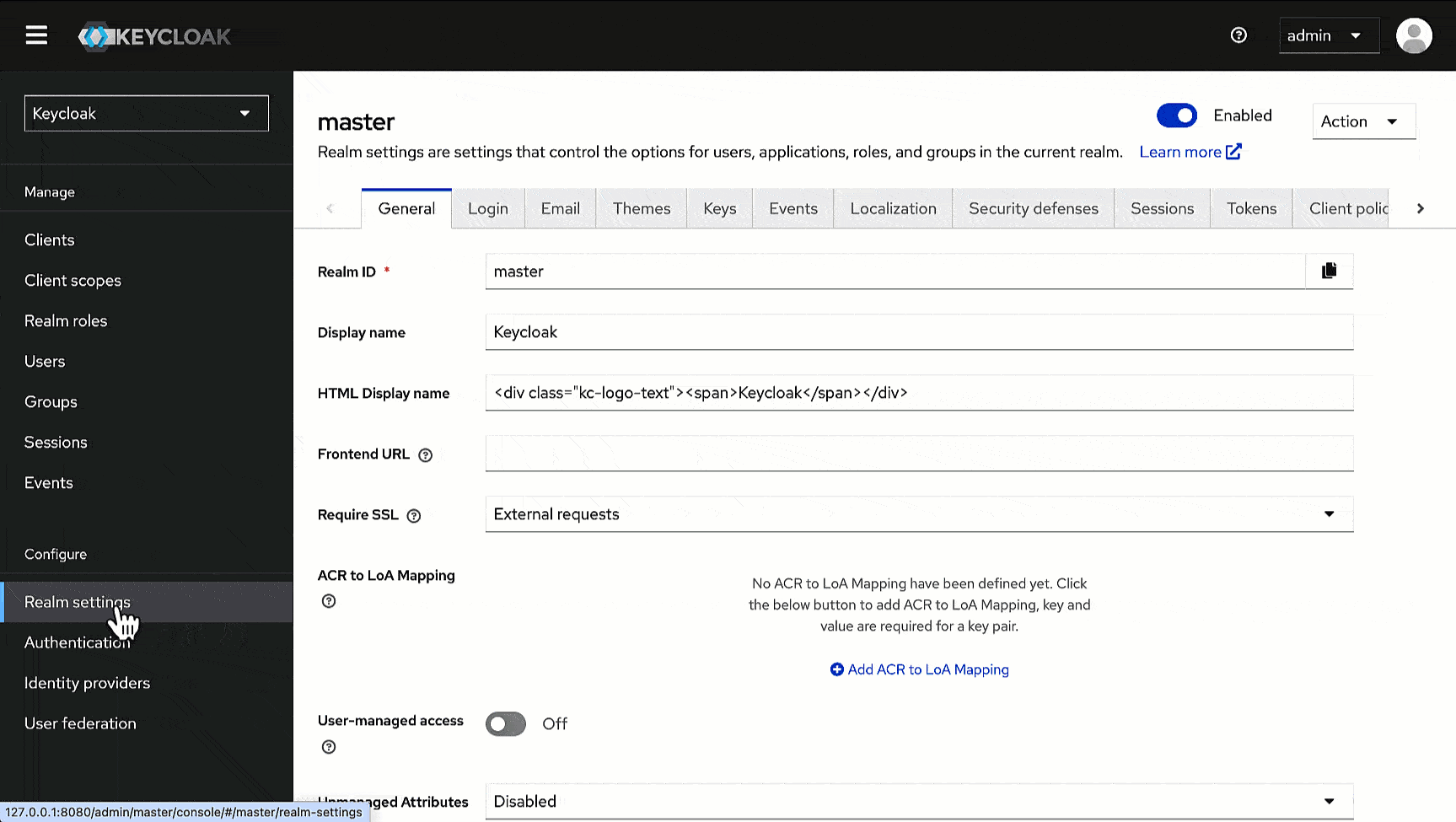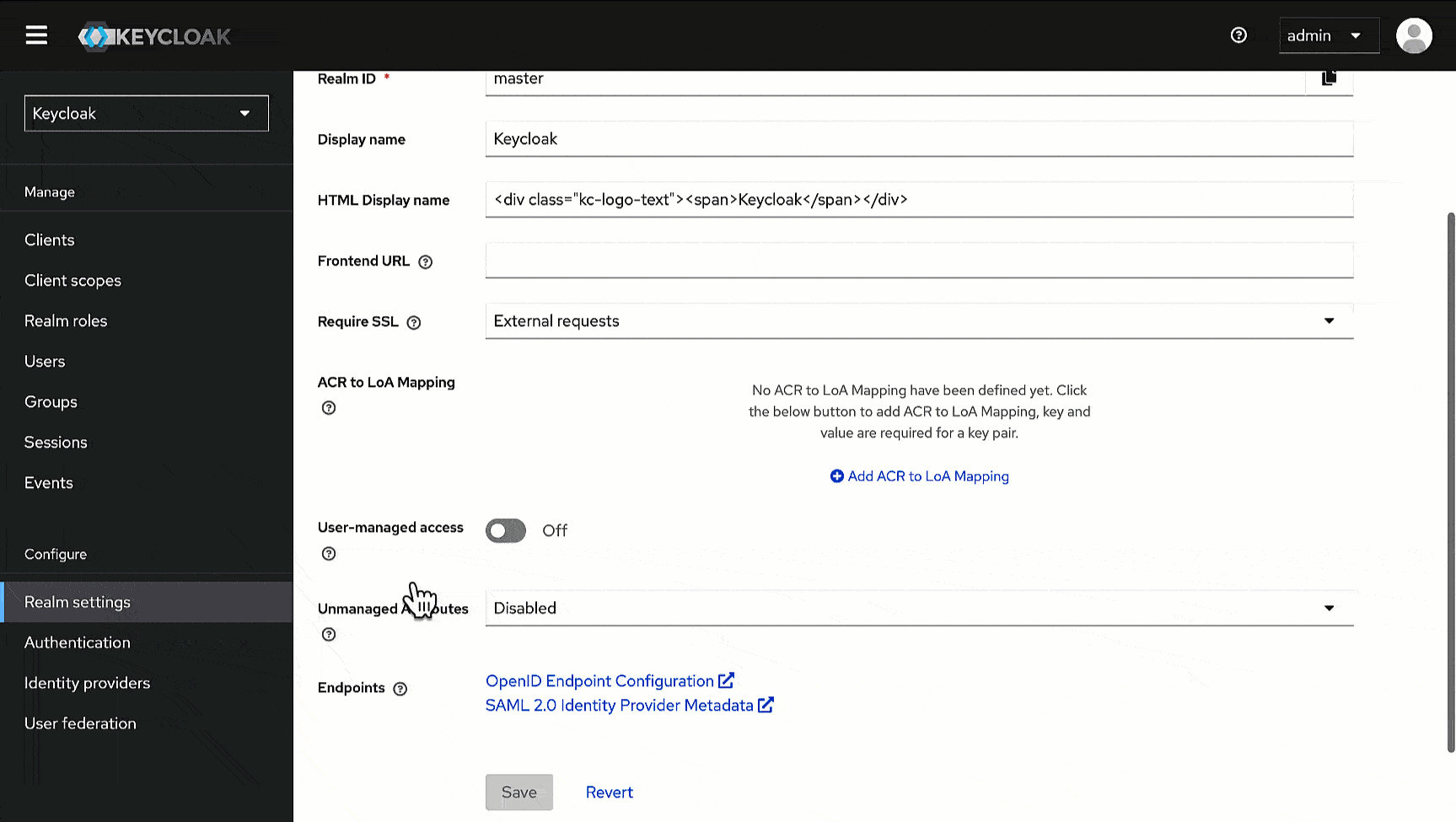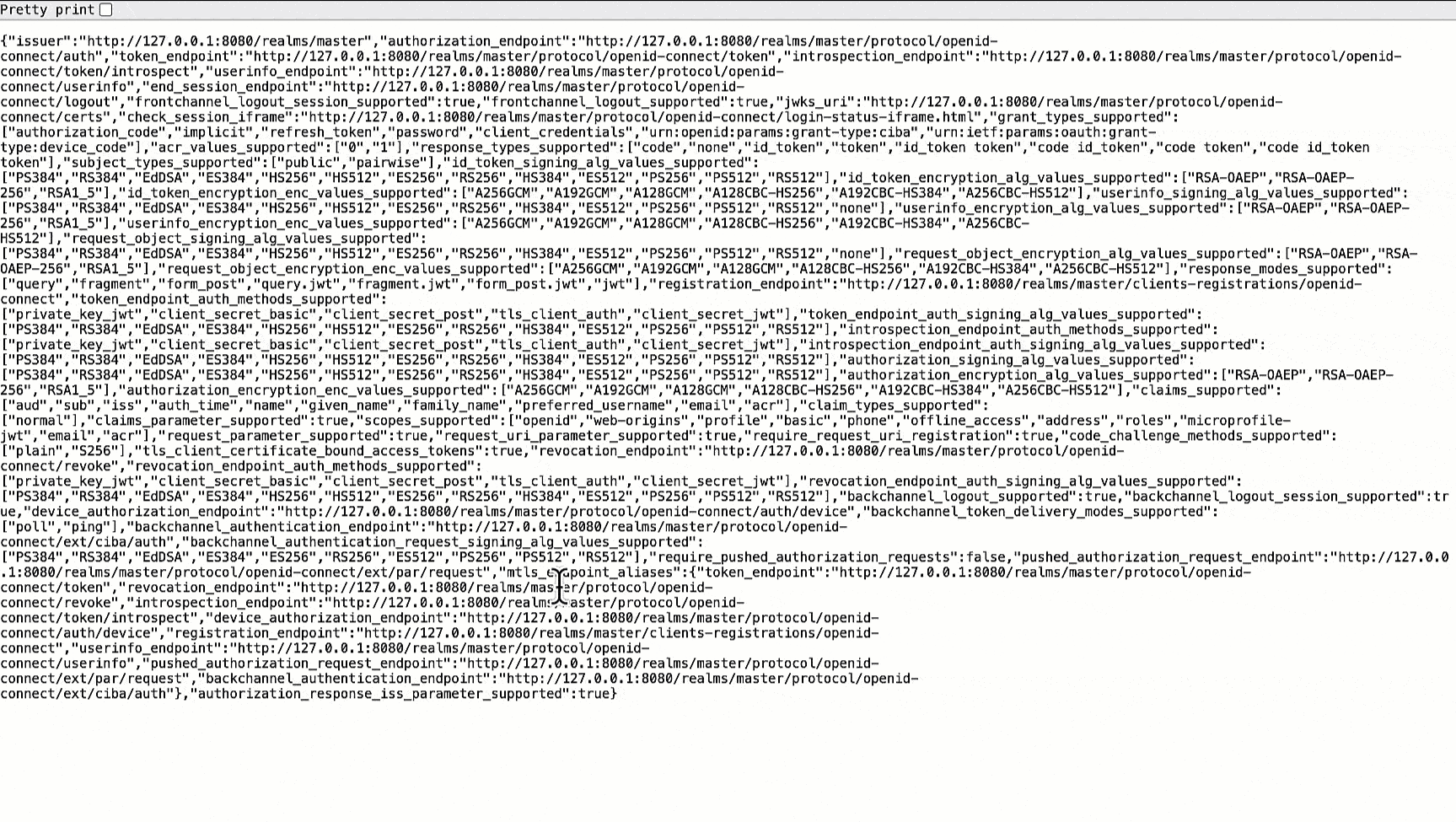
@@ -86,13 +104,13 @@ Here, we will obtain the Issuer URL we need while configuring SSO in Devtron.
2. In the **General** tab, scroll down to the **Endpoints** field, and click the **OpenID Endpoint Configuration** link.
- 
-
3. This will open a new page, copy the value of the key named `issuer`, and paste it somewhere for future reference.
- 
-
---
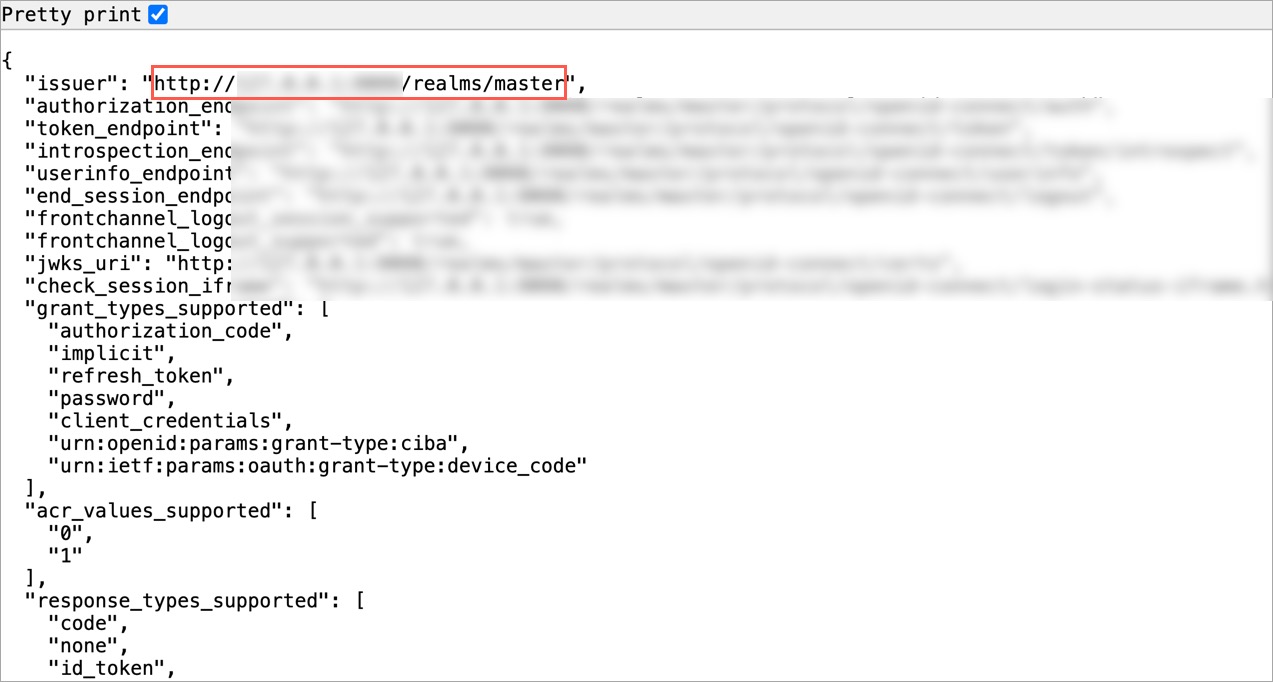
@@ -108,24 +126,16 @@ Here, we will set up an OIDC SSO and enter the values we obtained in the [previo
1. Go to **Global Configurations** → **SSO Login Services** → **OIDC**.
- 
-
Figure 10: Choosing OIDC SSO
-
-2. Below the URL field, take the help of the **Click to use** option to populate the exact URL if the displayed one is incorrect.
-
- 
-
Figure 11: Populating Correct Orchestrator URL
-
-3. In the **Configuration** editor, do the following:
+2. In the **Configuration** editor, do the following:
* In the `issuer` field, paste the URL you got while [retrieving issuer URL](#retrieving-issuer-url).
* In the `clientID` field, paste the ID you entered while [creating the client](#creating-a-client).
* In the `clientSecret` field, paste the secret you got under [client credentials tab](#getting-client-secret).
* In the `redirectURI` field, make sure to enter the same redirect URI you gave in step 4 of [client creation](#creating-a-client).
- 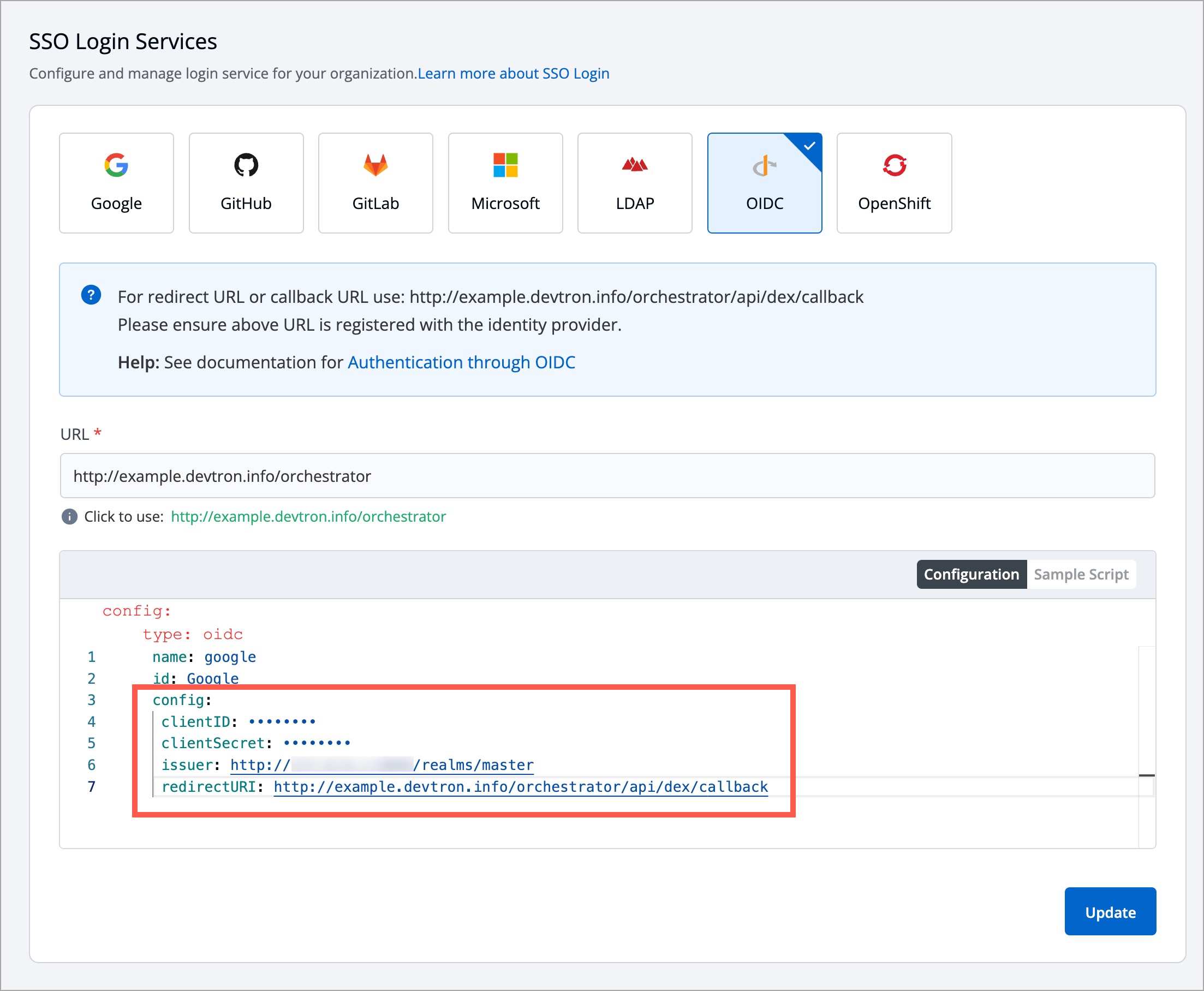
+ 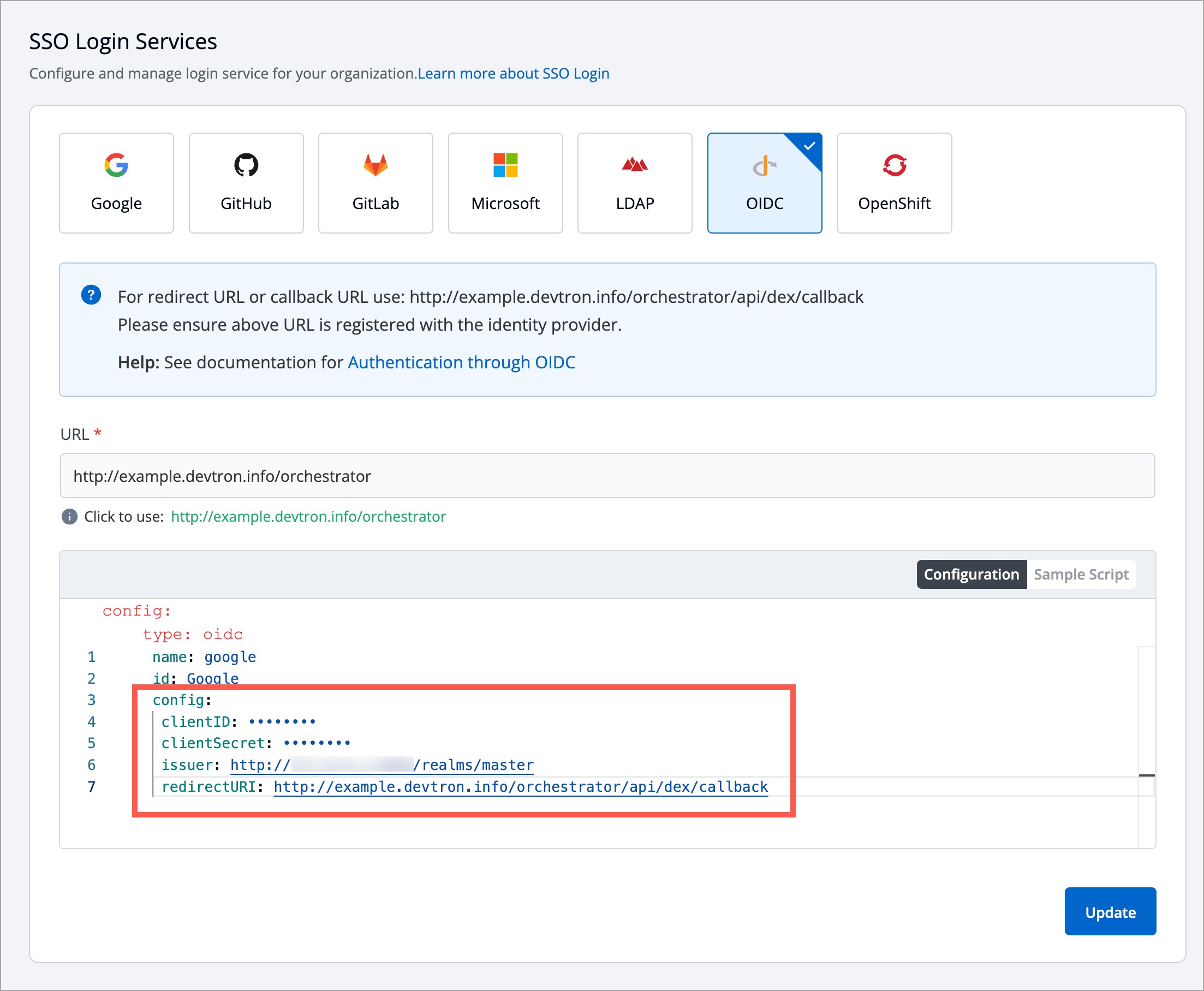
Figure 12: Sample Keycloak SSO Config
-4. Click **Save** or **Update** to activate Keycloak SSO login.
+3. Click **Save** or **Update** to activate Keycloak SSO login.
### Adding Users
@@ -139,12 +149,12 @@ Here, we will add the user we created in the Keycloak Admin Console. If this ste
2. Click **+ Add Users**.
- 
+ 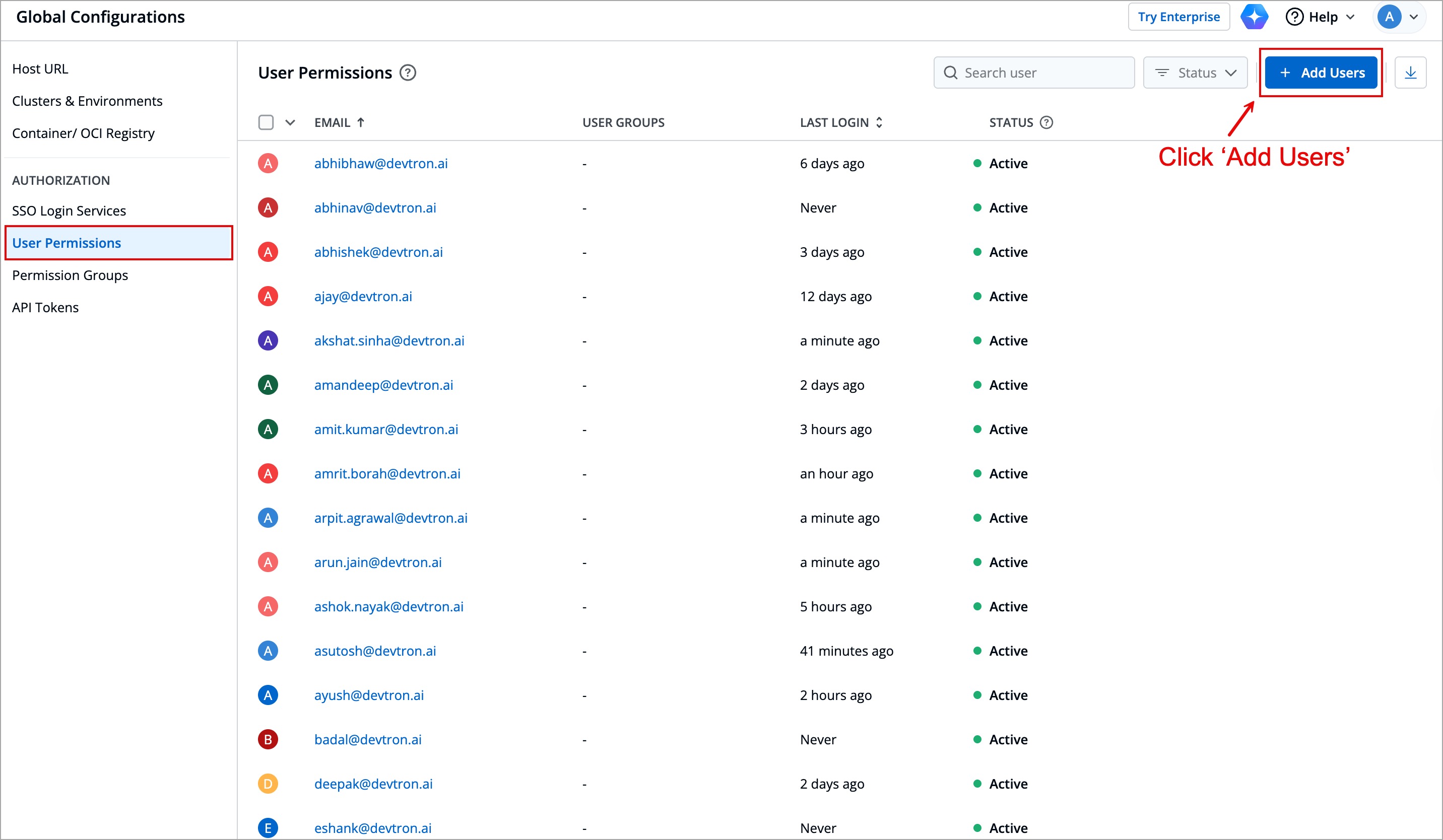
Figure 13: Adding Users to Devtron
3. In the **Email addresses** field, enter the email address of the user you created in Keycloak.
- 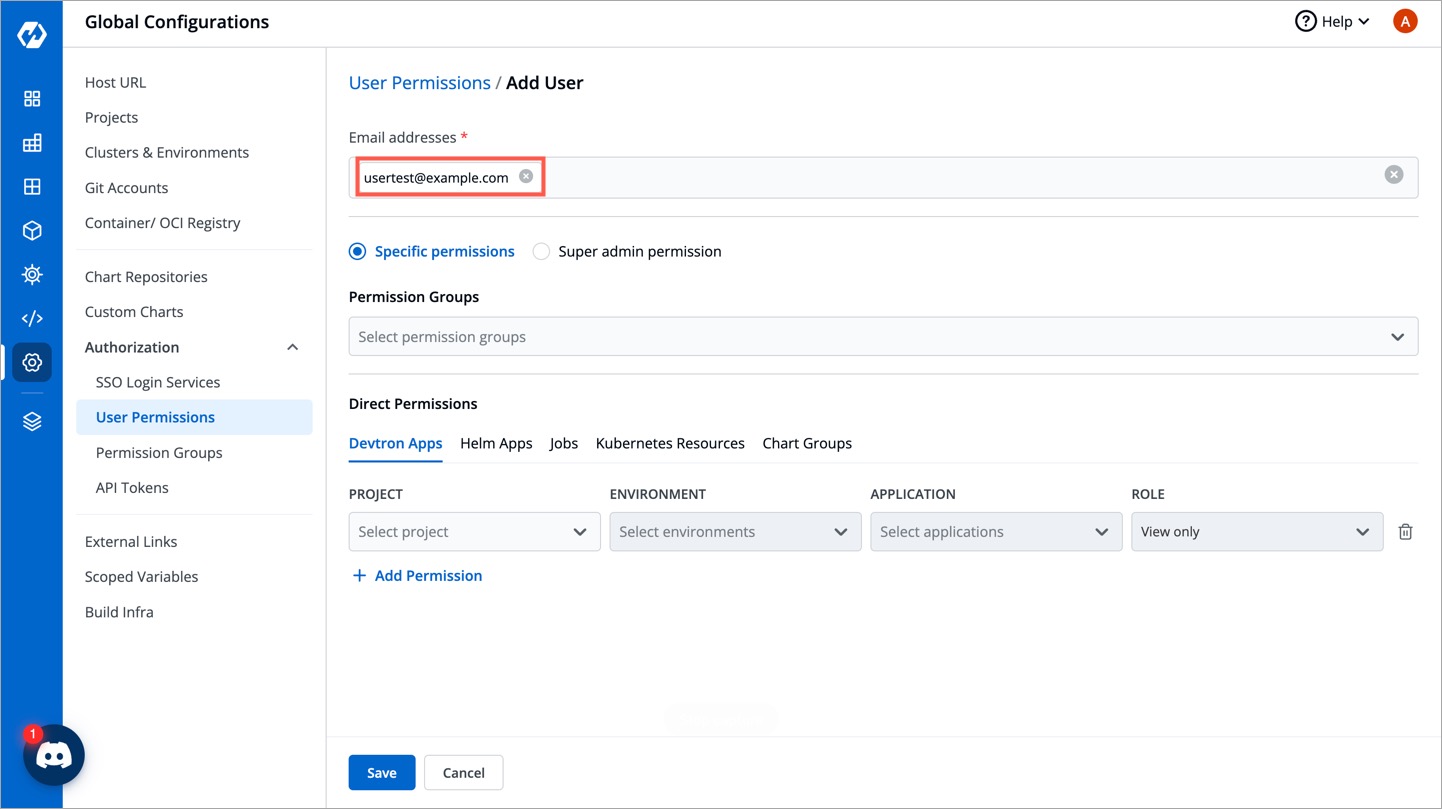
+ 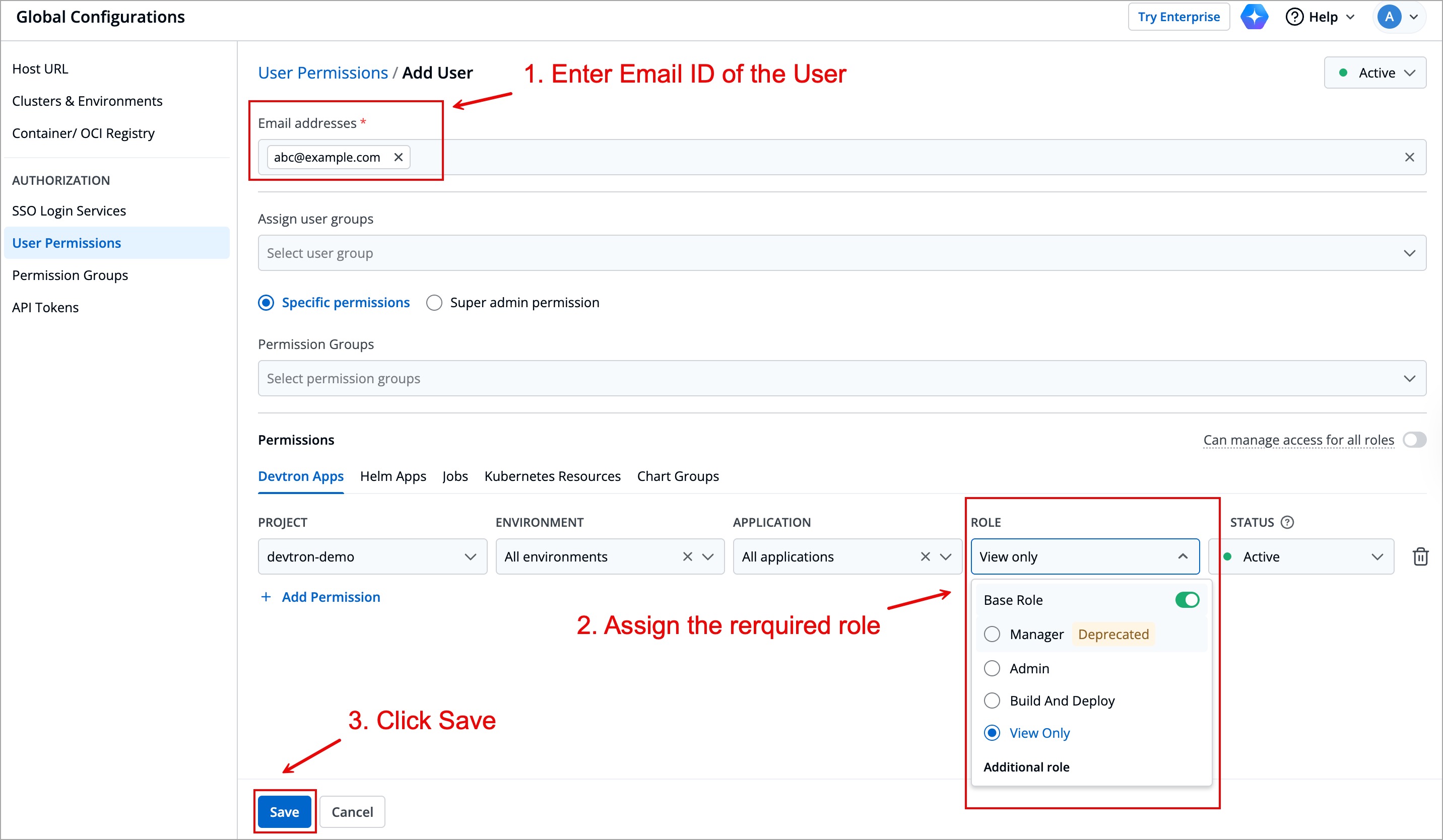
Figure 14: Entering User Data and Permissions
4. Assign necessary permissions to this new user. Refer [user permissions](../user-access.md) to know more.
@@ -153,11 +163,11 @@ Here, we will add the user we created in the Keycloak Admin Console. If this ste
Now, you may log out and test the Keycloak OIDC login method using the [user credentials](#creating-users). Clicking the **Login with Oidc** button will land you on Keycloak's login page.
-
+
:::caution Note
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/okta.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/okta.md
index 54897c961..340a2e41e 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/okta.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/sso/okta.md
@@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ Once your Okta org is set up, create an app integration on Okta to get a Client
### Sample Configuration
-
+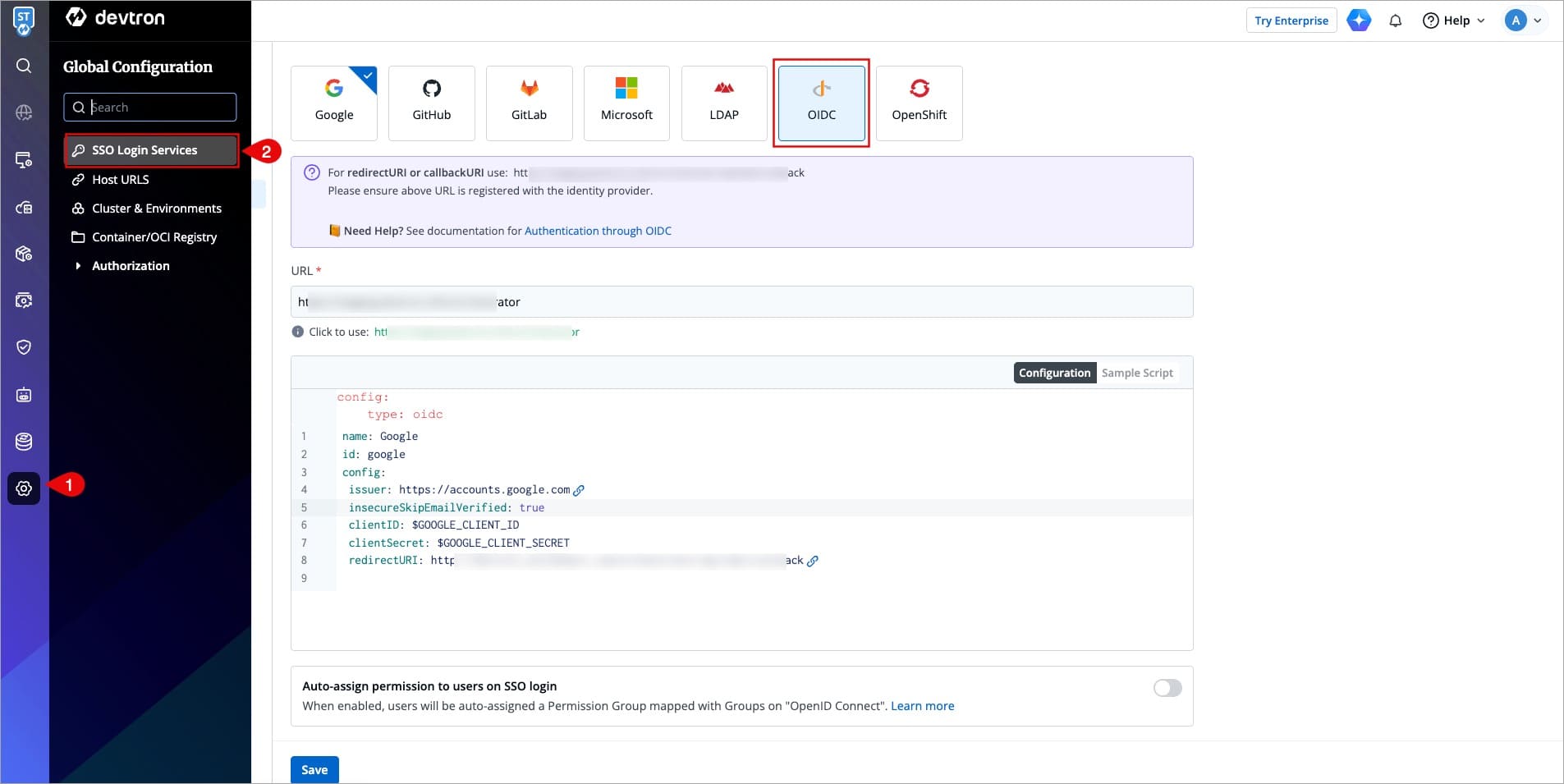
Figure 1: Sample Configuration
Now your users will be able to log in to Devtron using the Okta authentication method. Note that existing signed-in users will be logged out, and they have to log in again using their OIDC account.
@@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ If you’ve defined groups in your Okta Universal Directory, you can create corr
4. Click **Update**.
-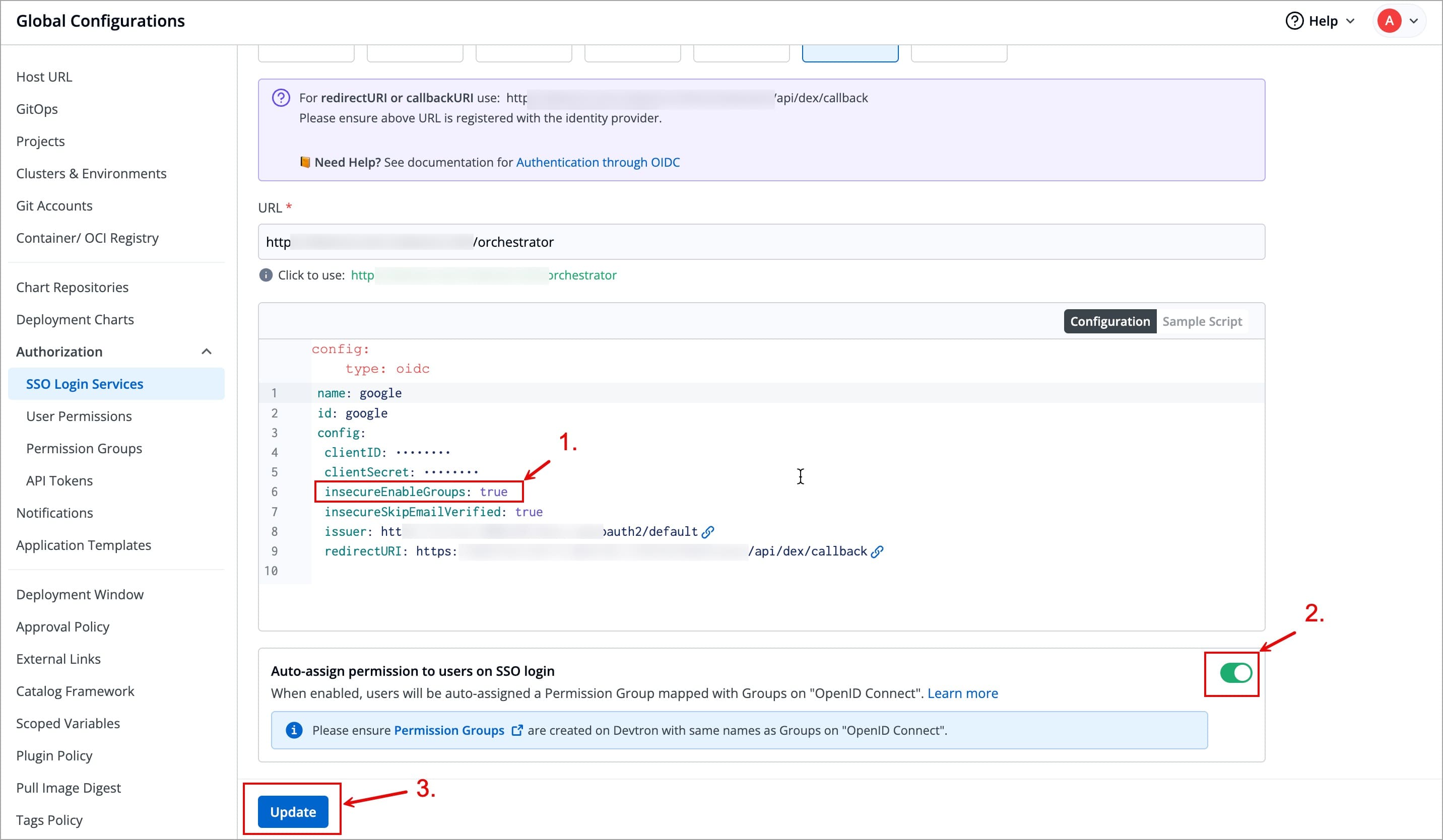
+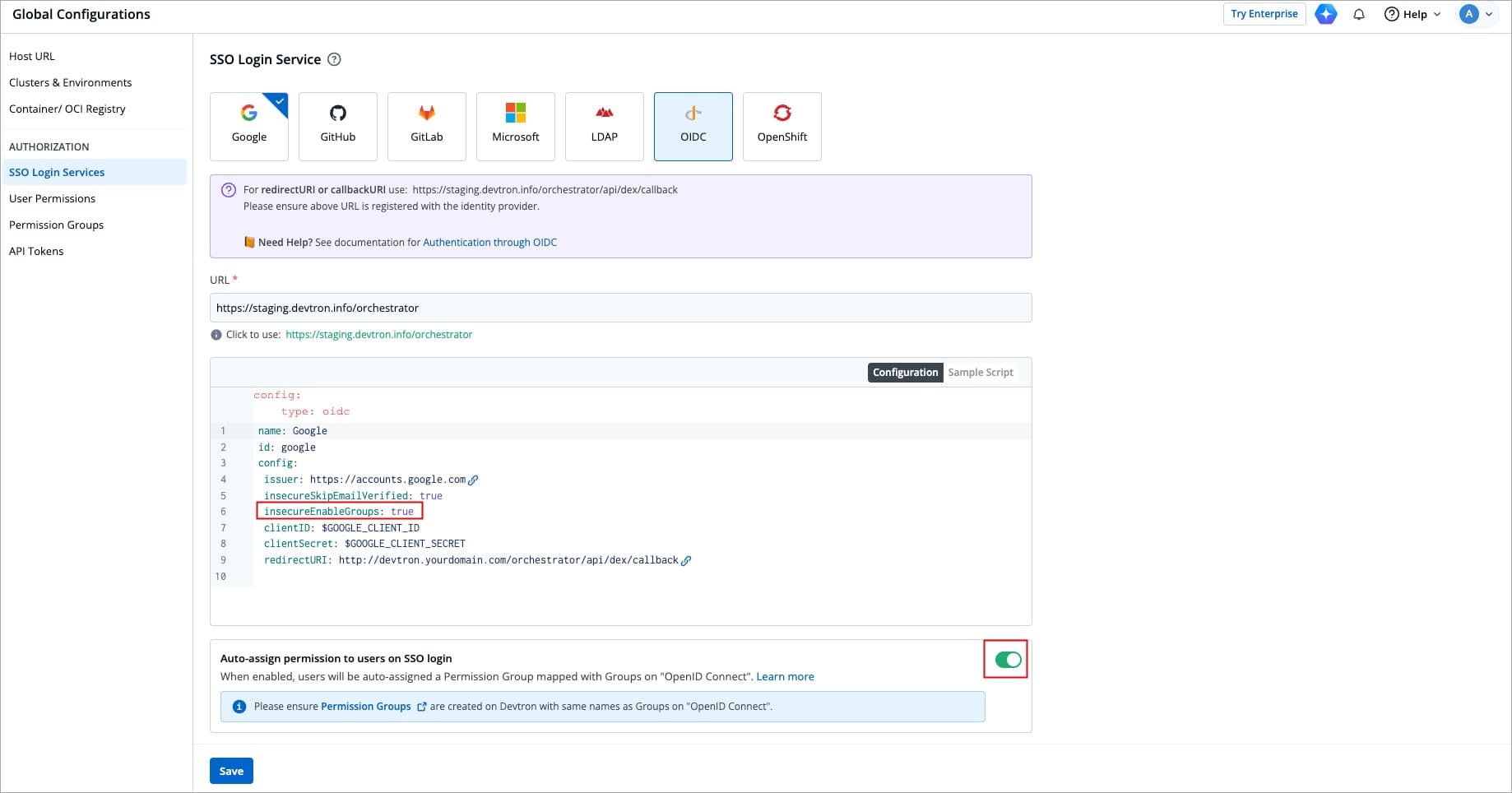
Figure 2: Sample Configuration for Auto -assign Permission
:::caution Note
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md
index d28d87711..31a2cae66 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/authorization/user-access.md
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@
Here you can manage who can access your Devtron instance and what actions they can perform. Use this section to add team members, assign them roles, and control their access by granting fine-grained permissions. Moreover, you can also download all user data in a CSV format.
-
+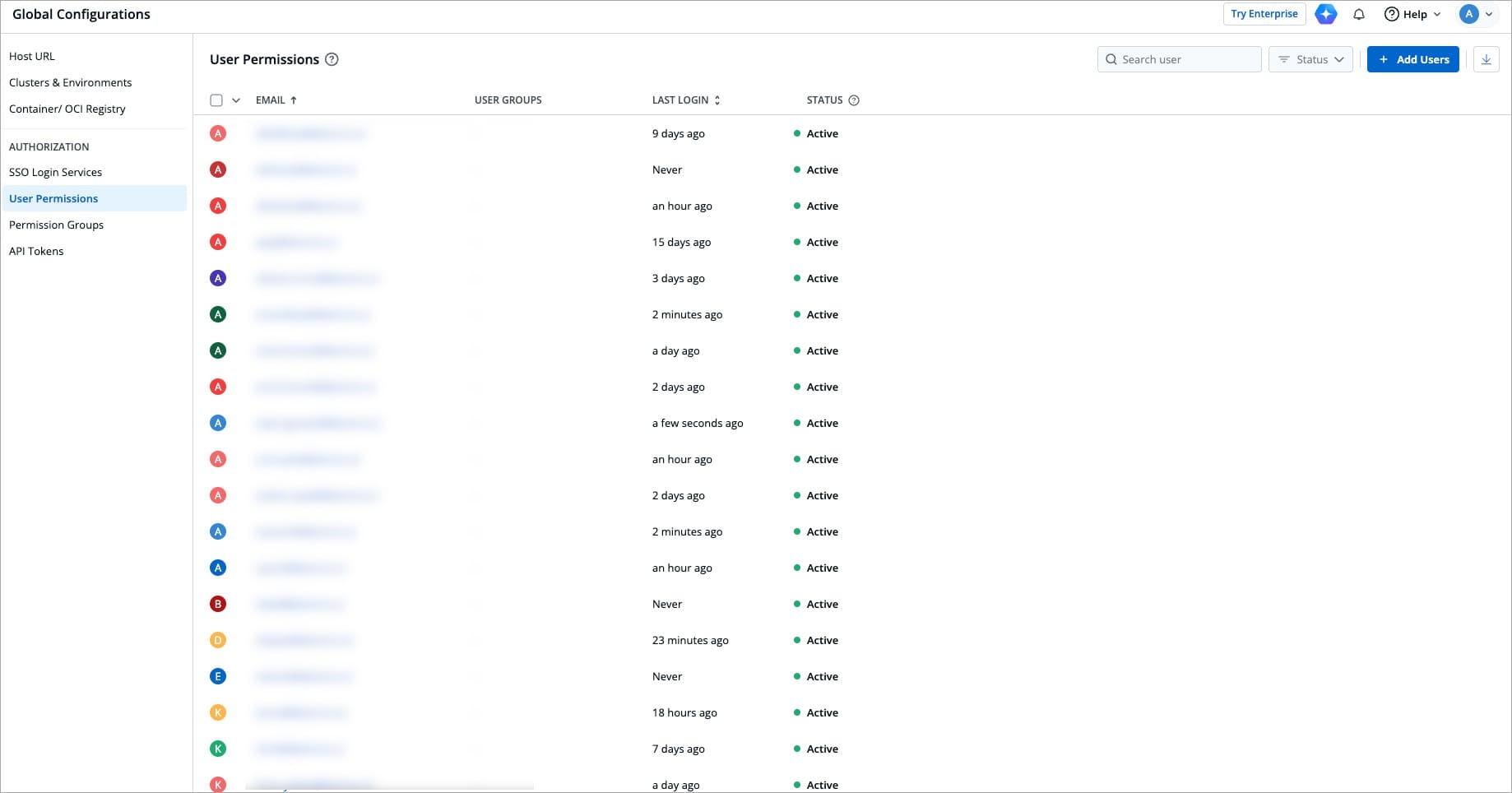
Figure 1: User Permissions - Example
---
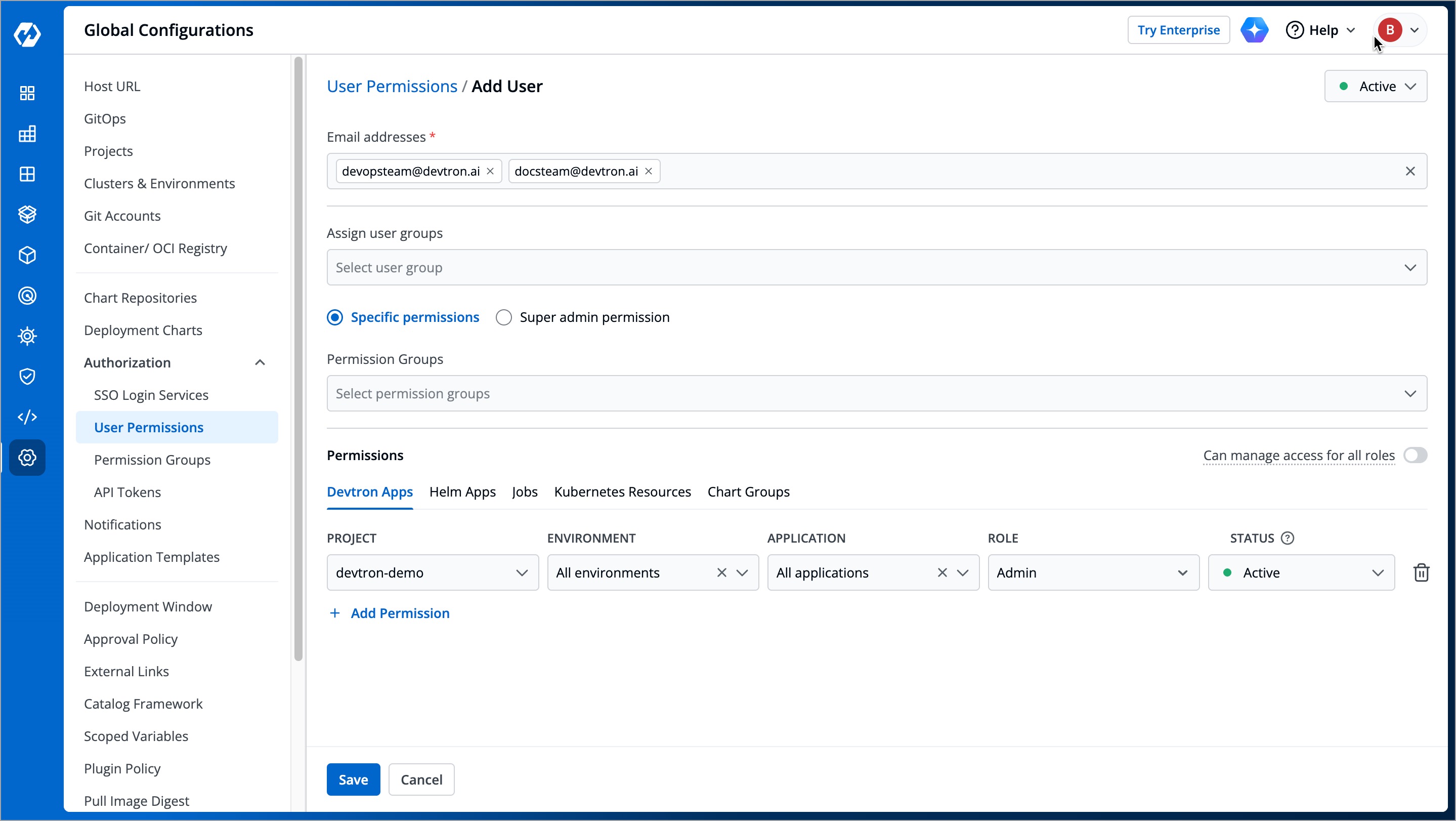
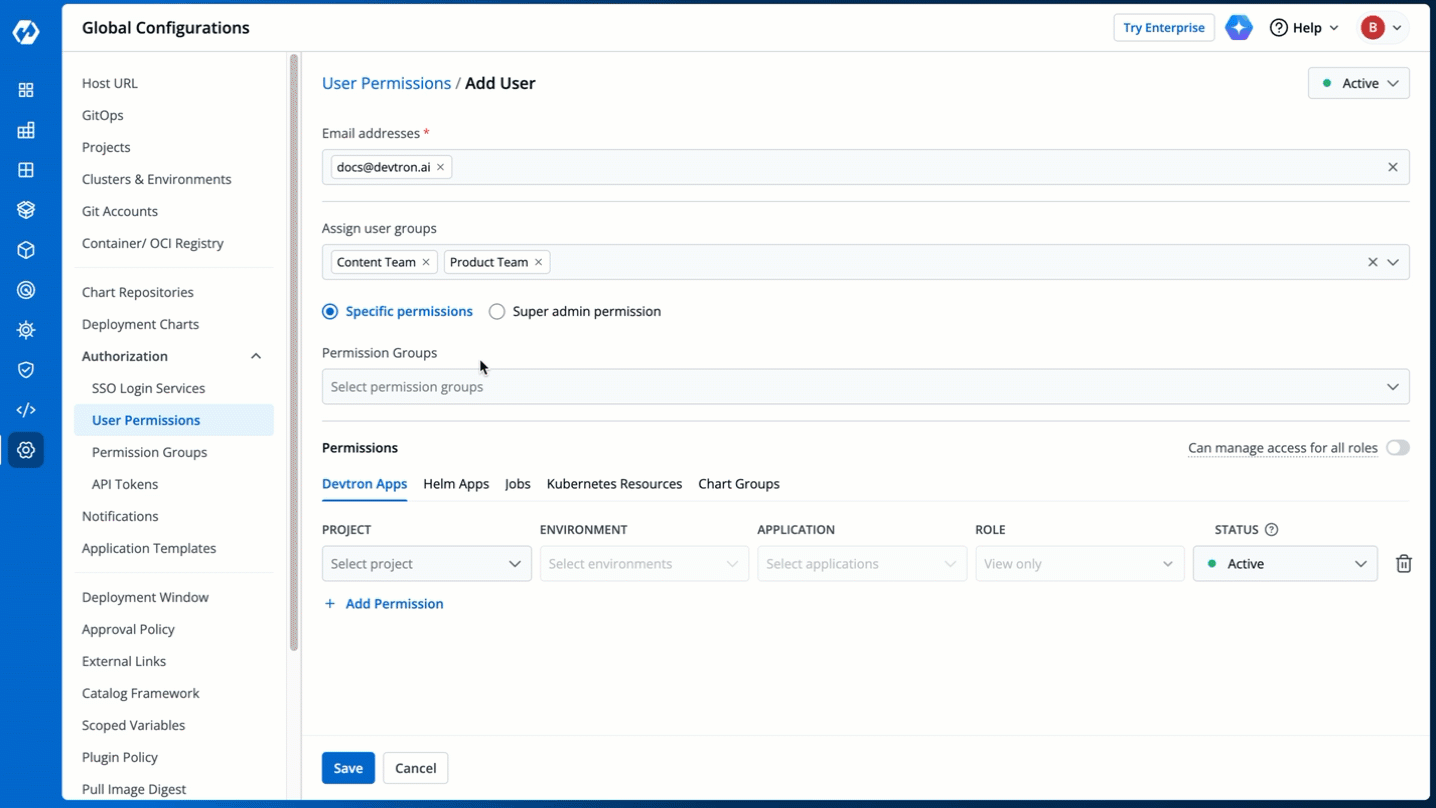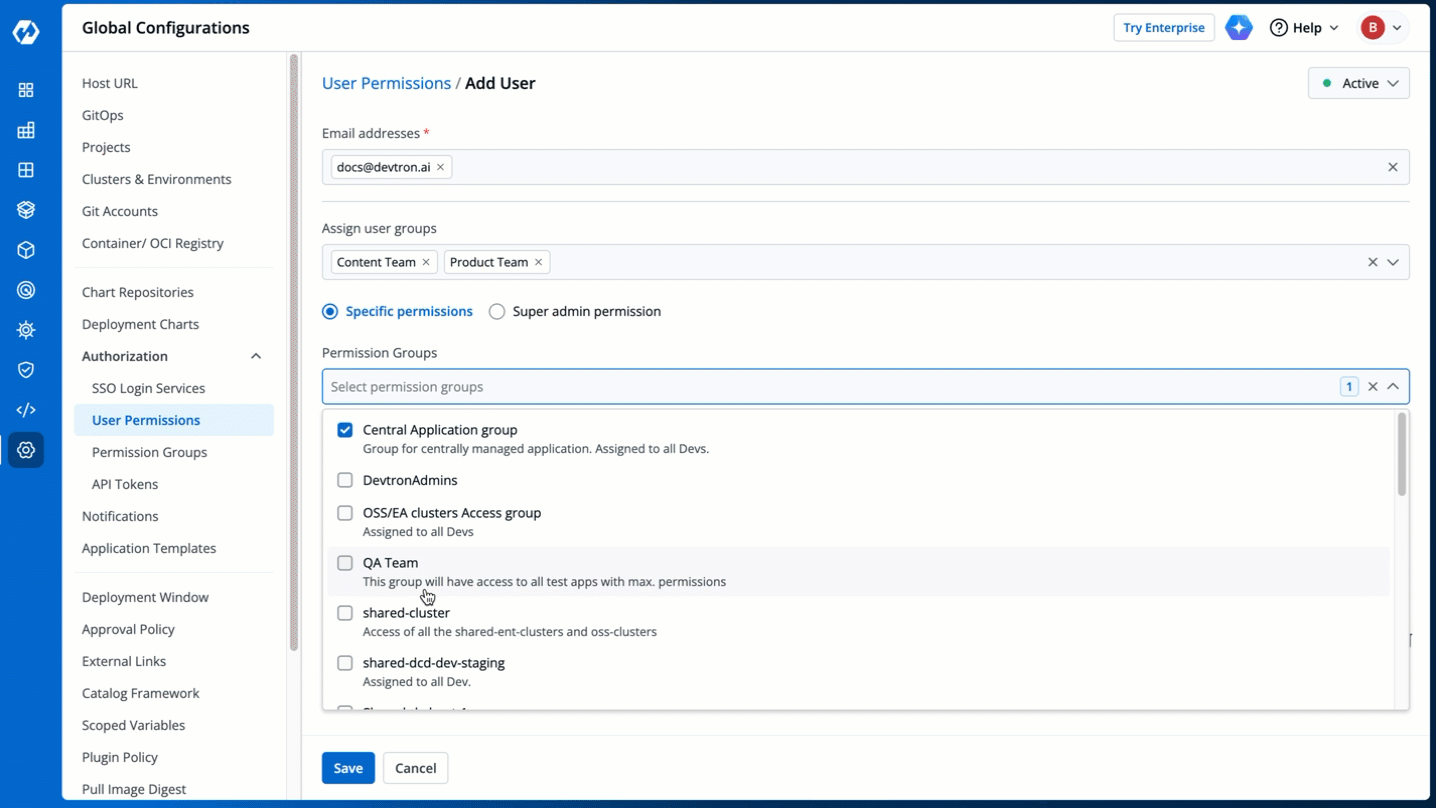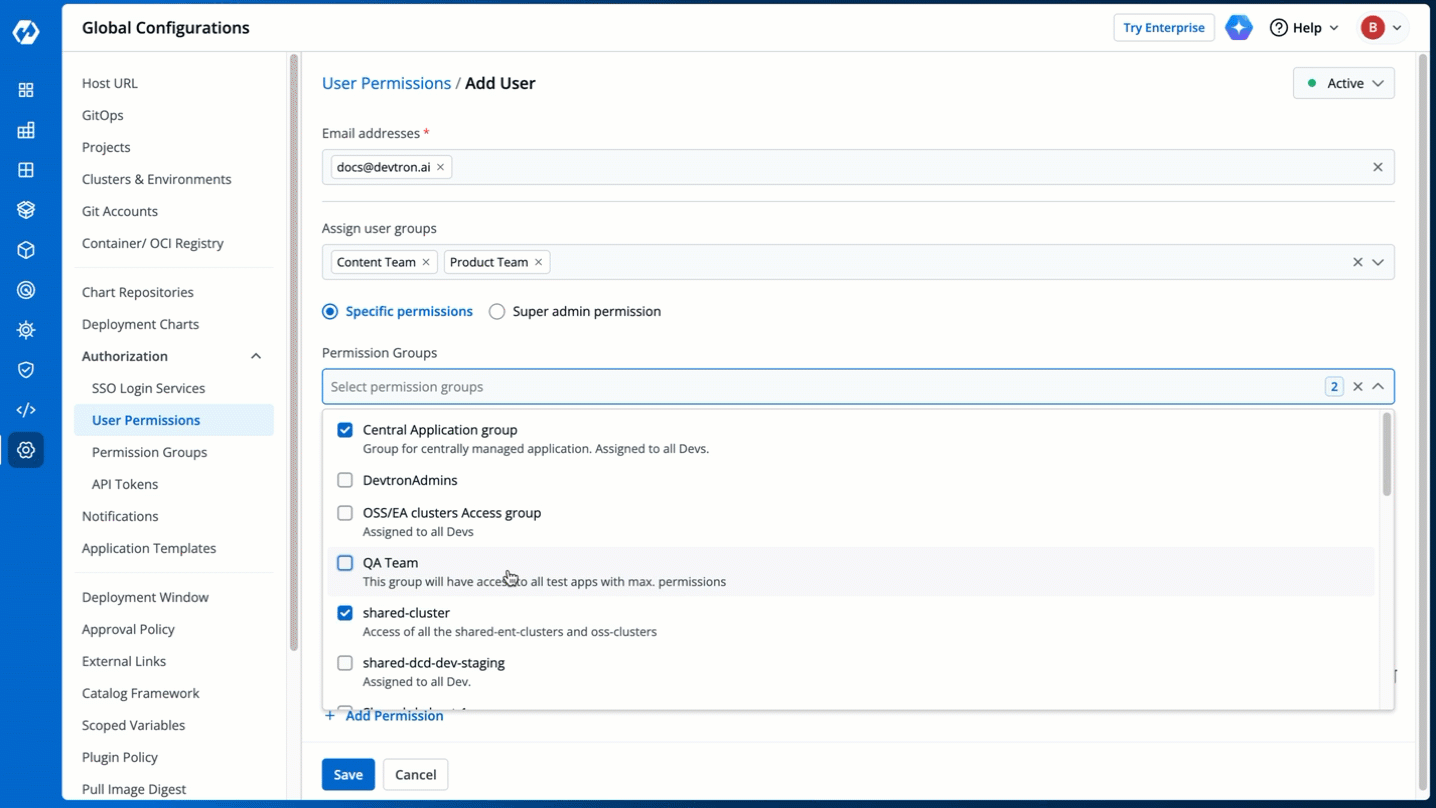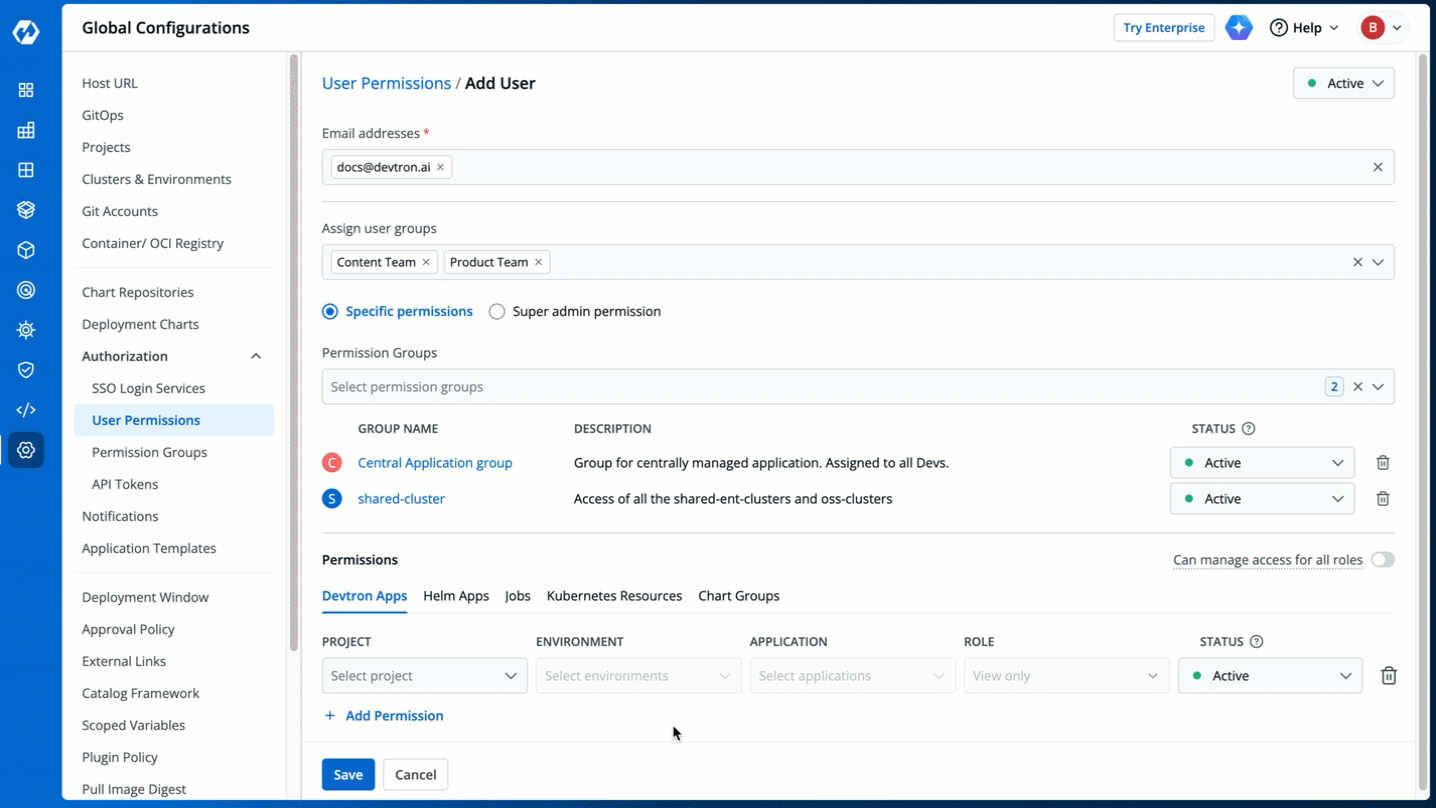
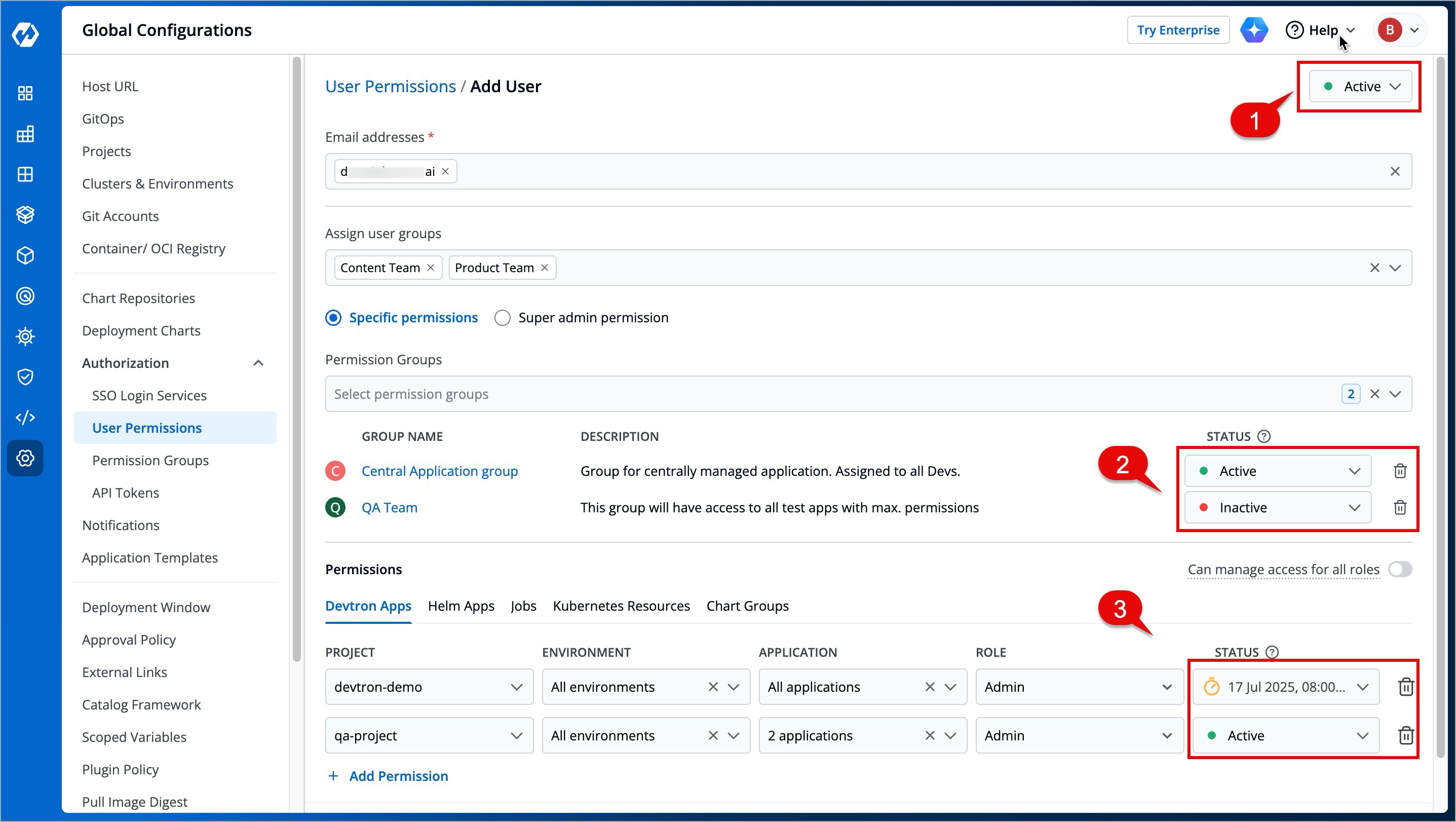
@@ -21,29 +21,29 @@ Only managers and super-admins can add users.
1. Go to **Global Configurations** → **Authorization** → **User Permissions**.
- 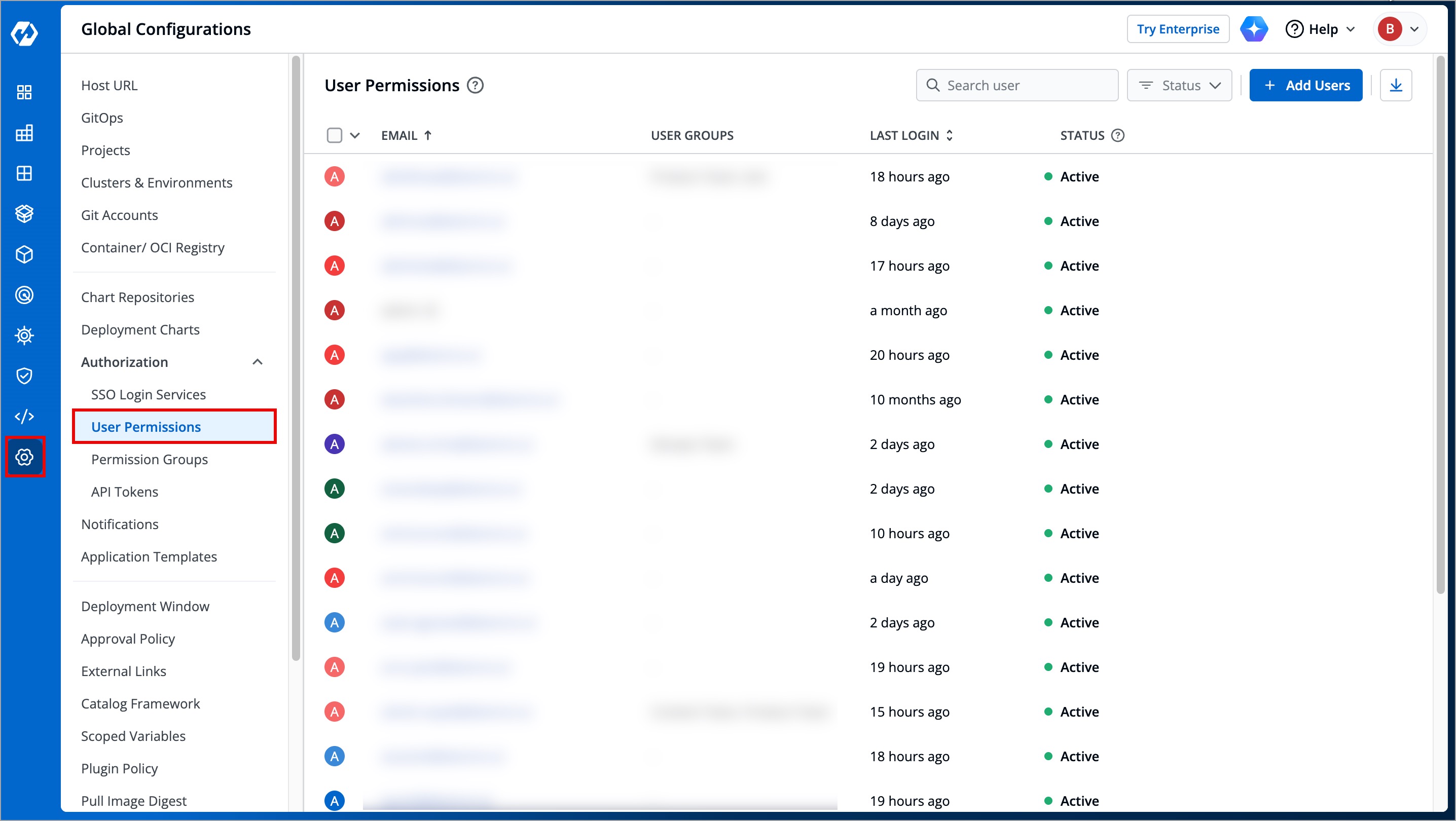
+ 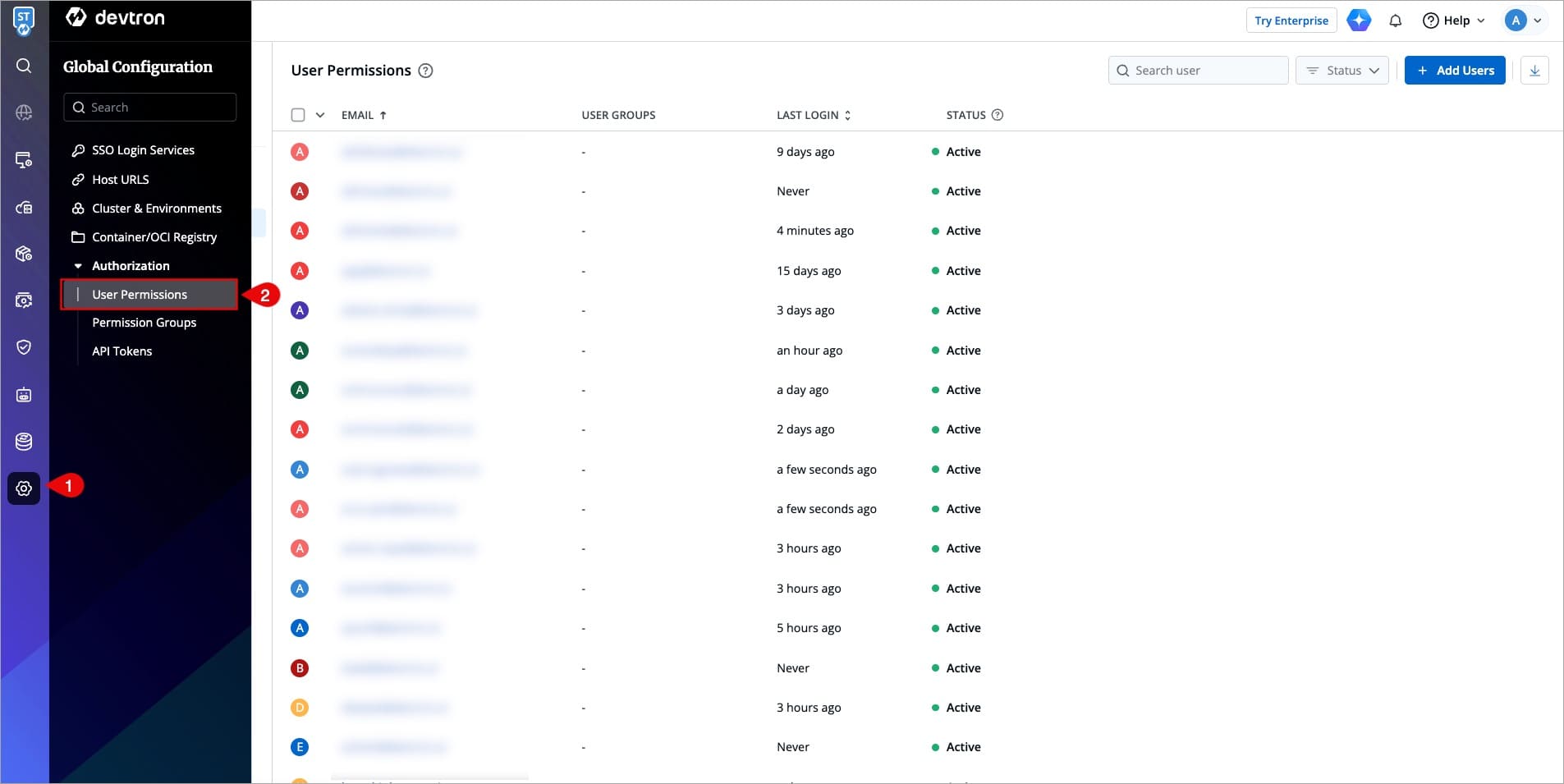
Figure 2: User Permissions in Global Configurations
3. In the **Email addresses** field, type the email address of the user you wish to add. You may add more than one email address.
- 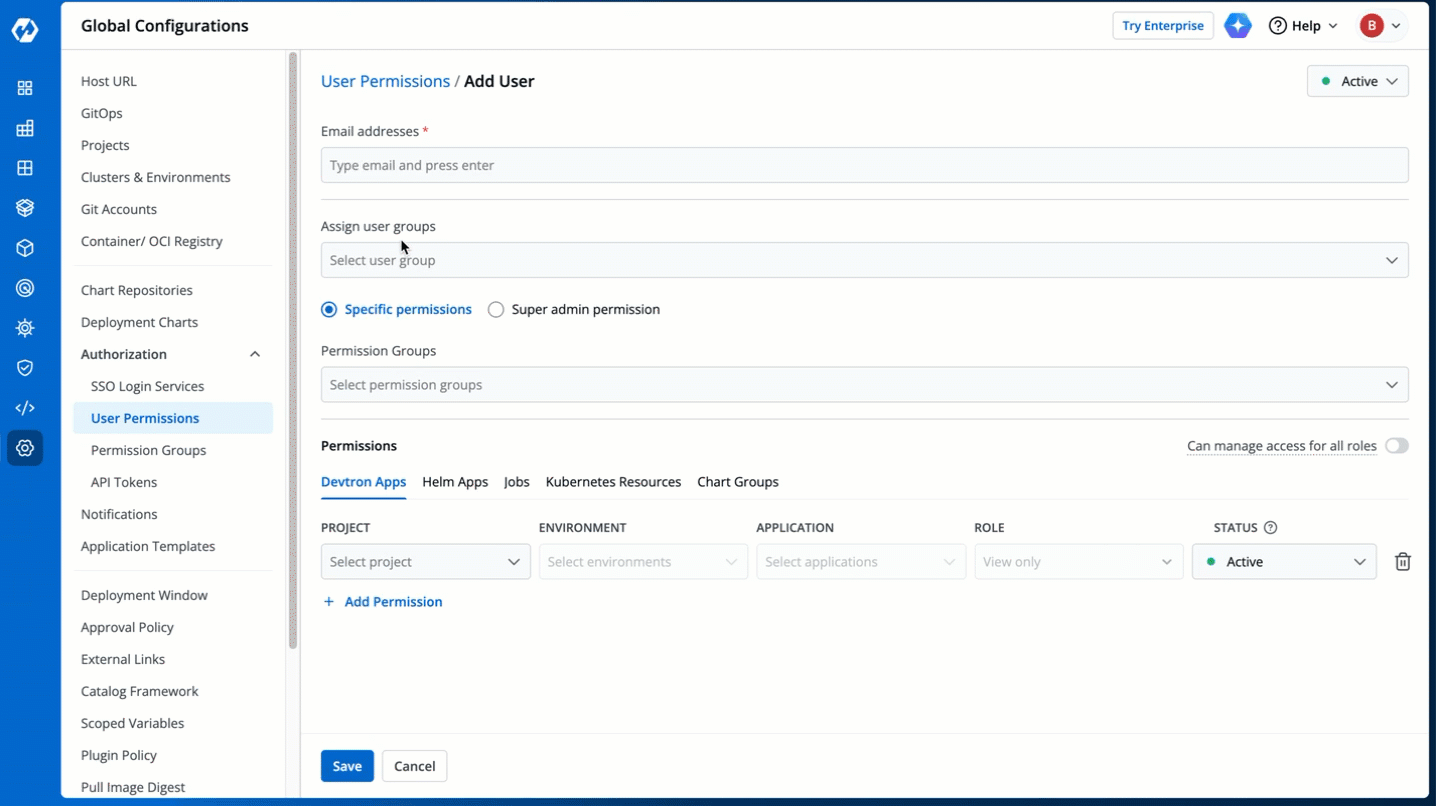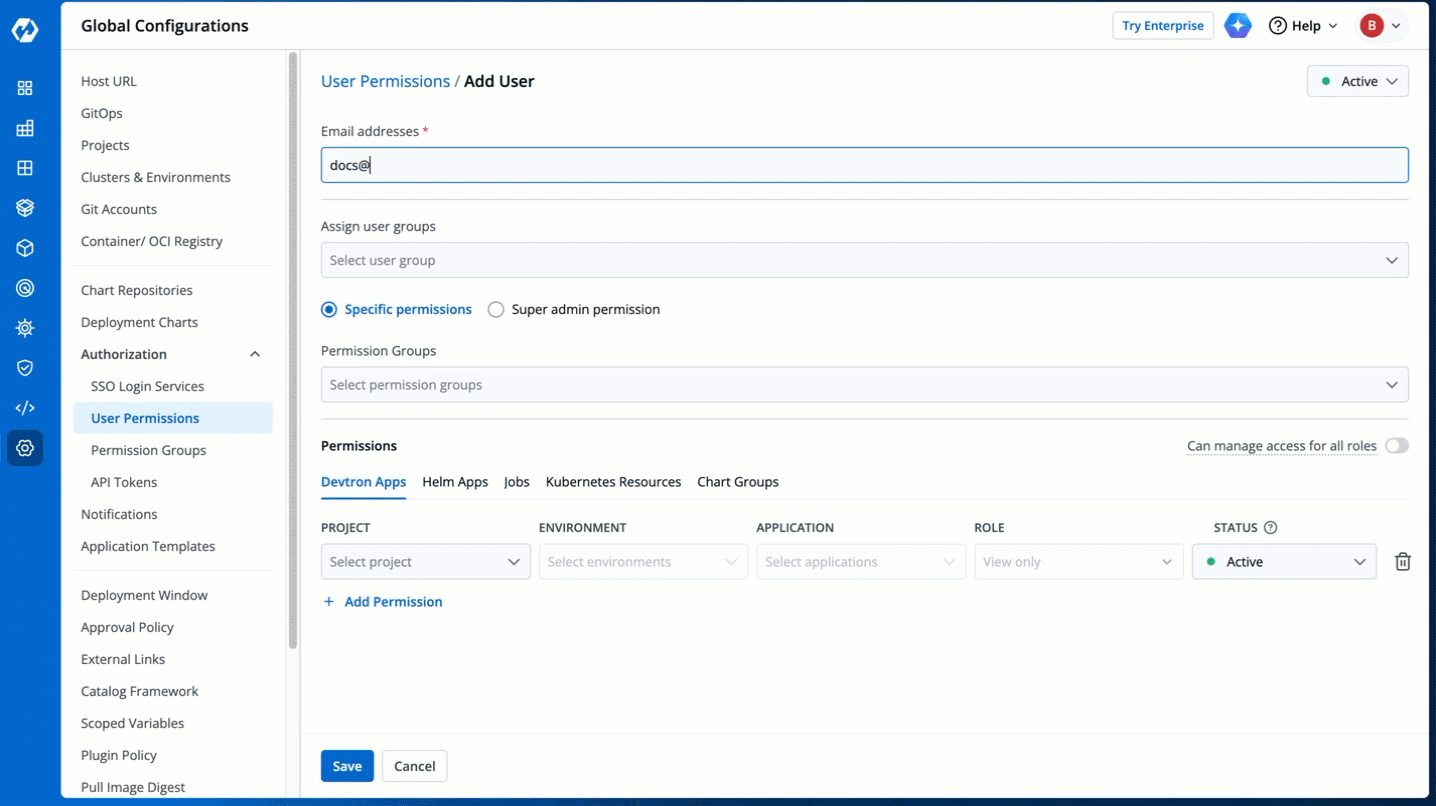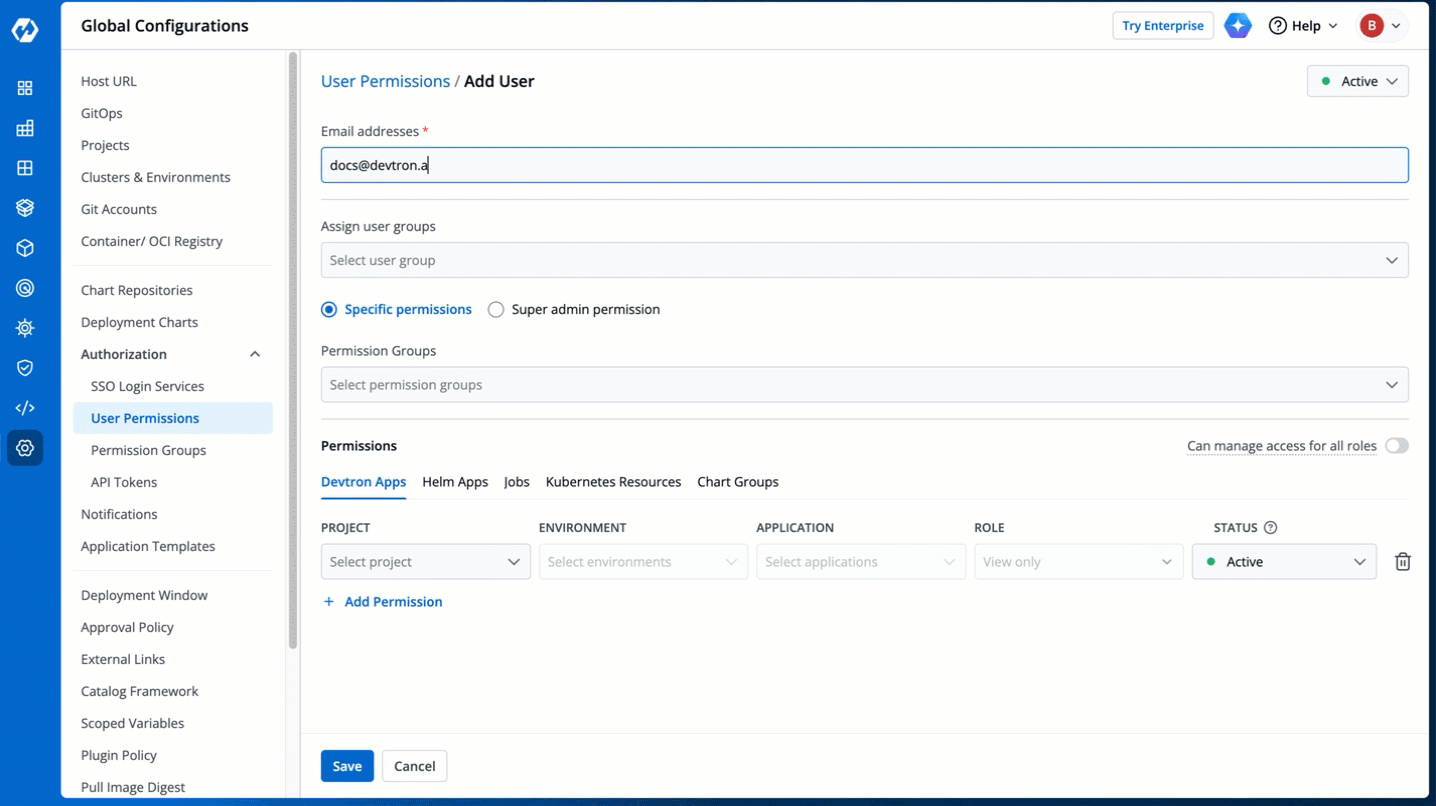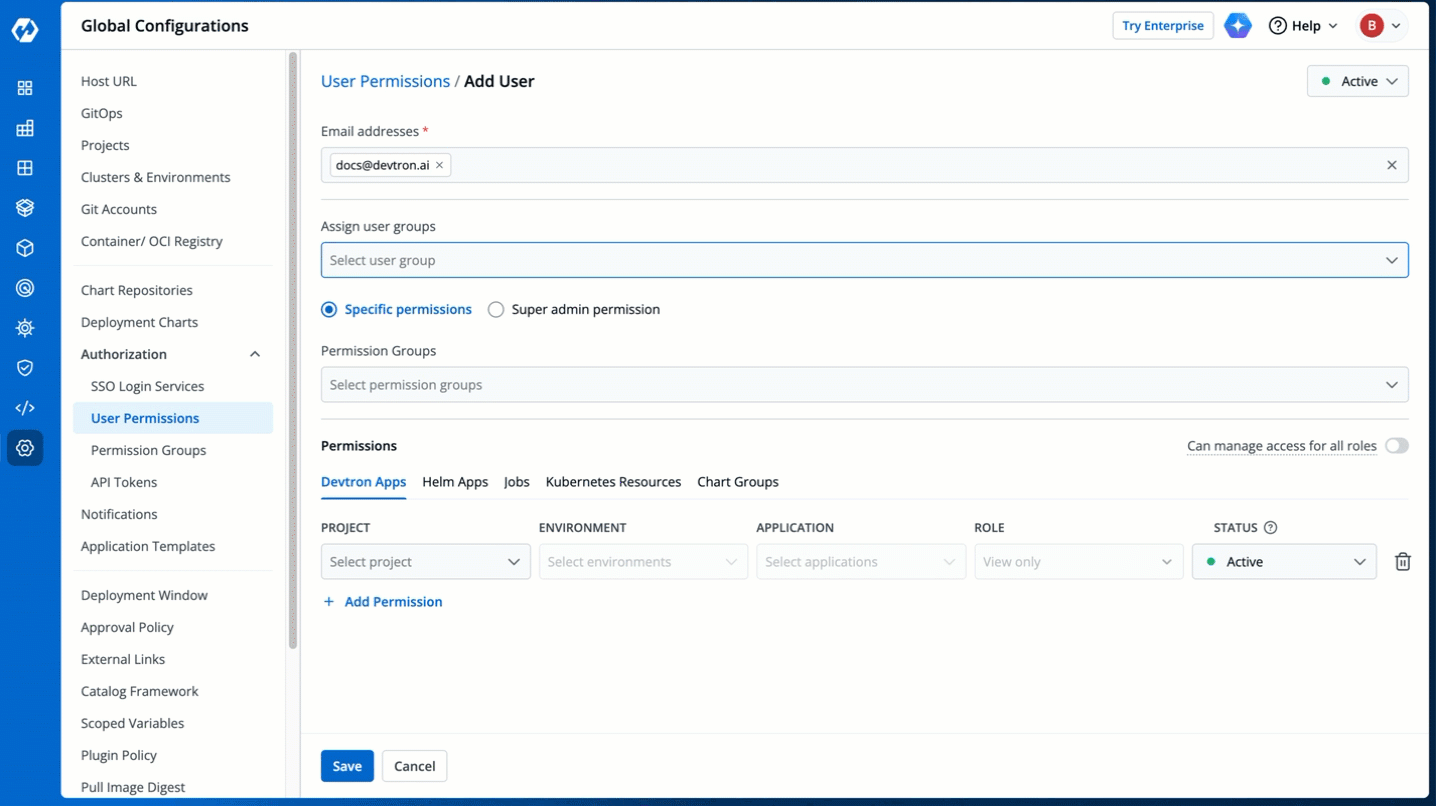
+ 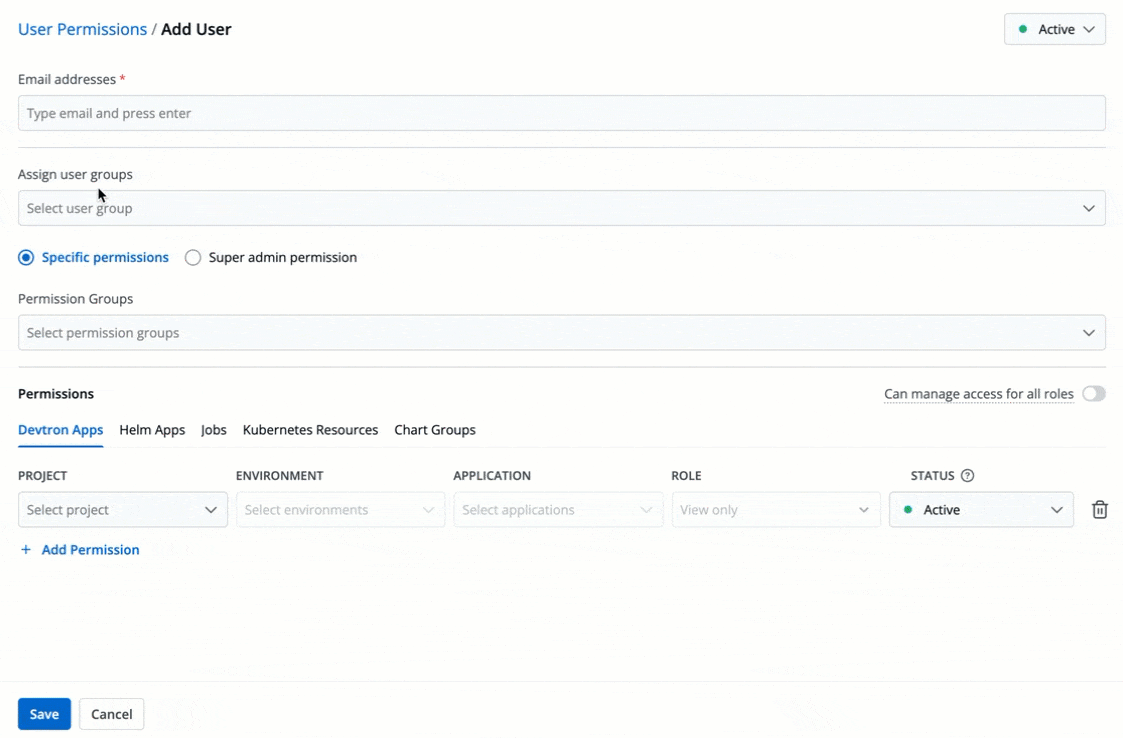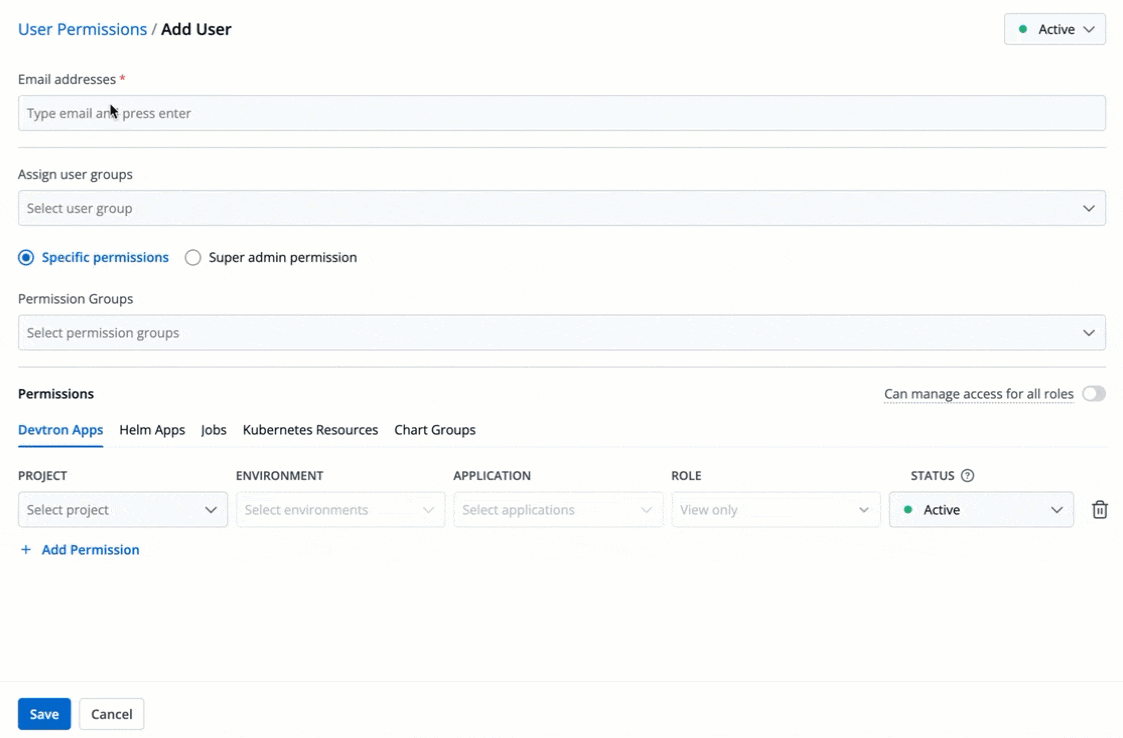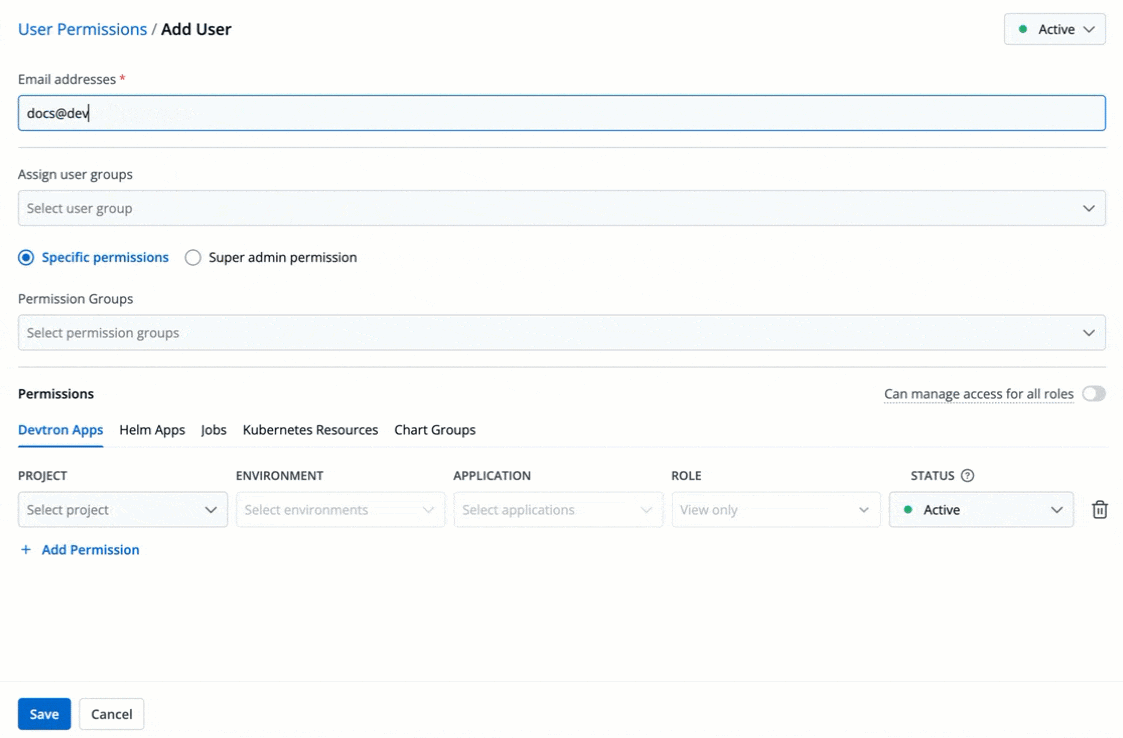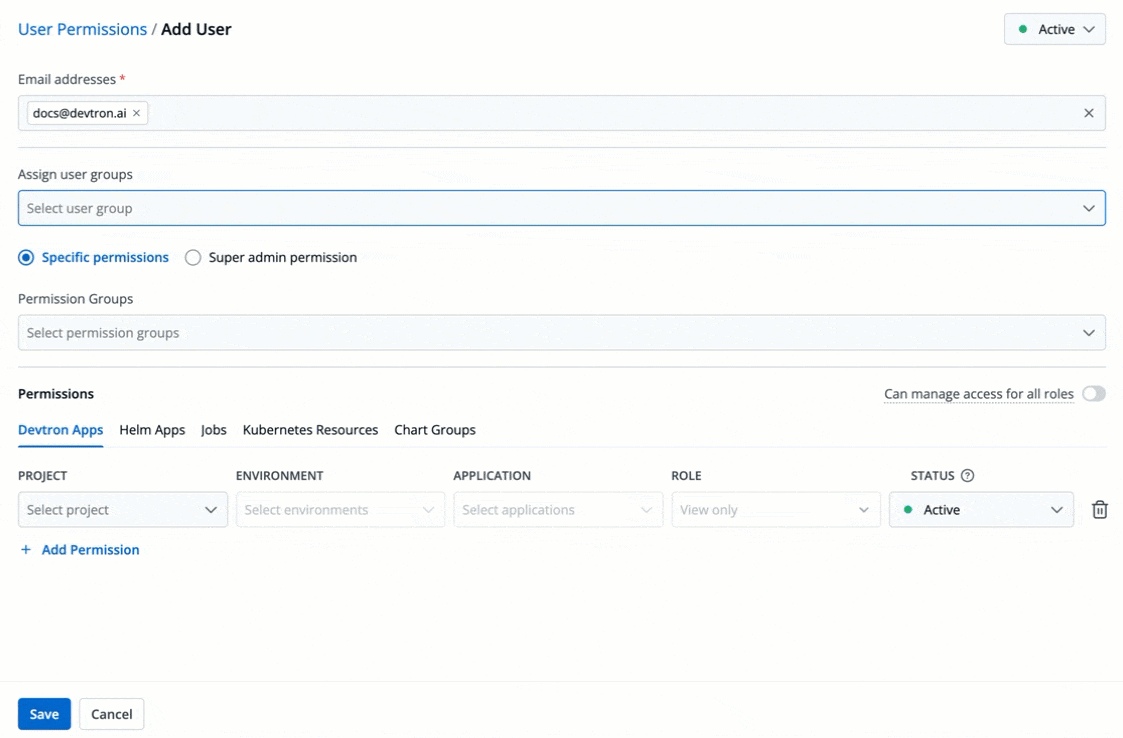
Figure 4: Adding Email Addresses of Users
4. (Optional) From the **Assign user groups** dropdown, you may assign one or more user groups to the user. This helps in identifying the group/team to which the user belongs (e.g., Security Team, Frontend Team, Department Leads) especially when adding larger teams.
- 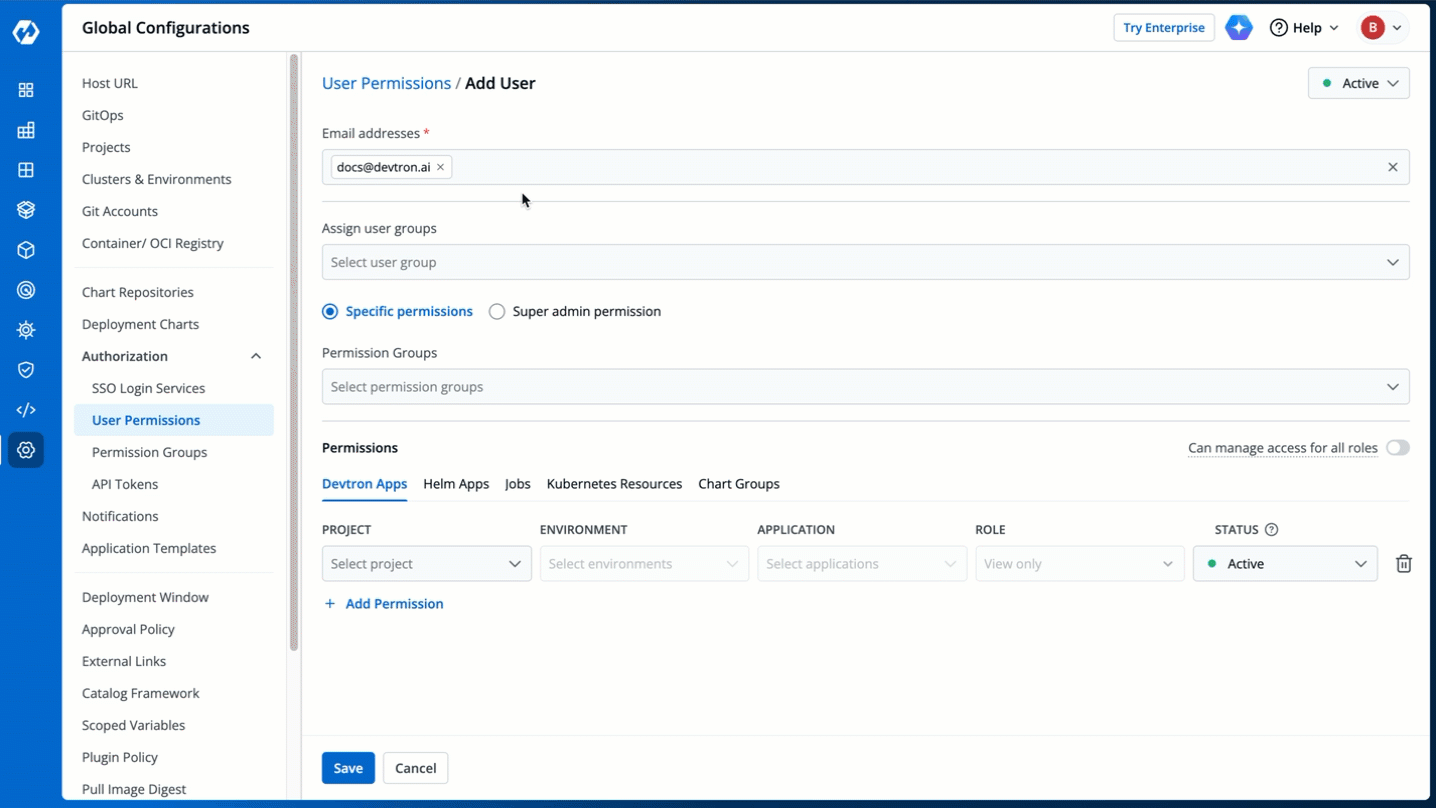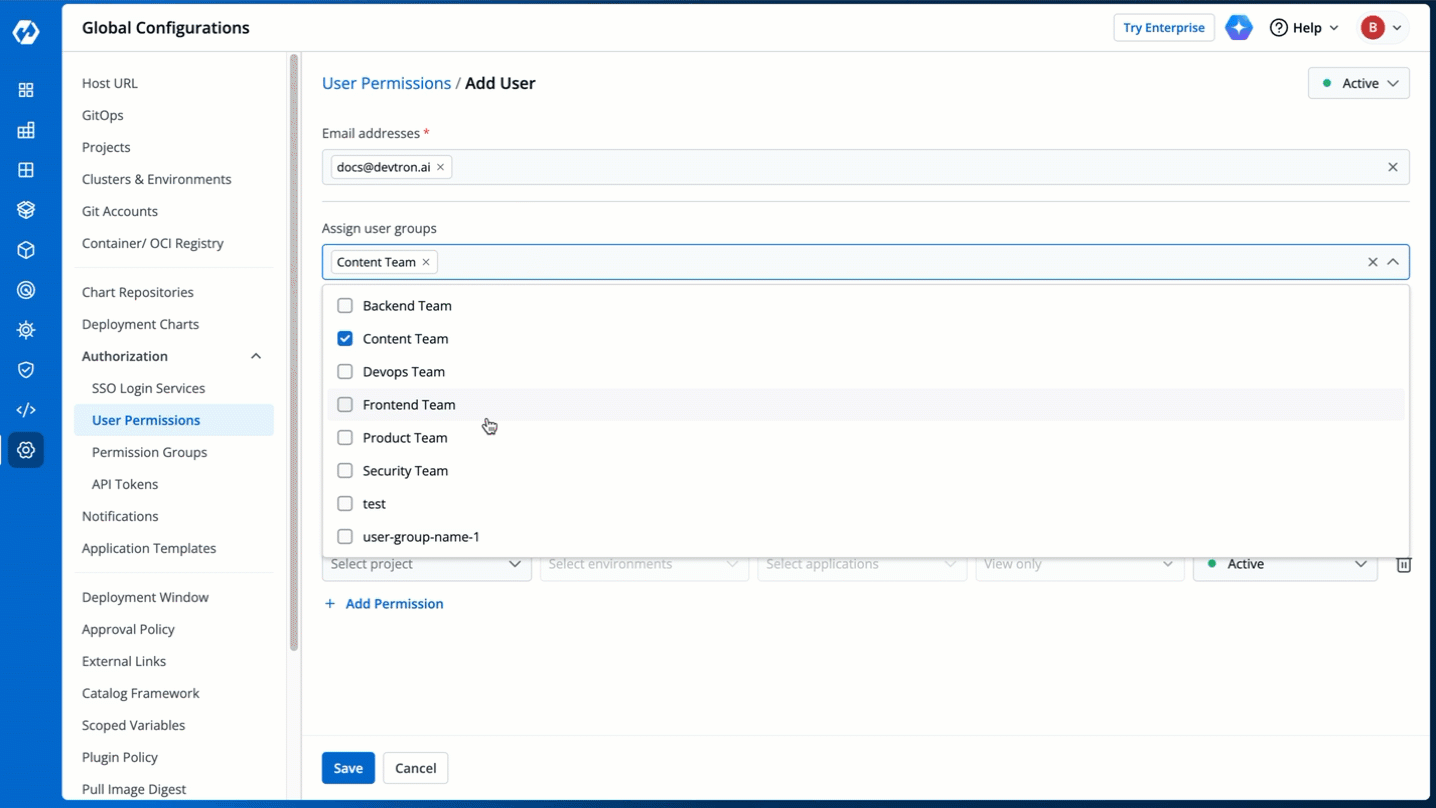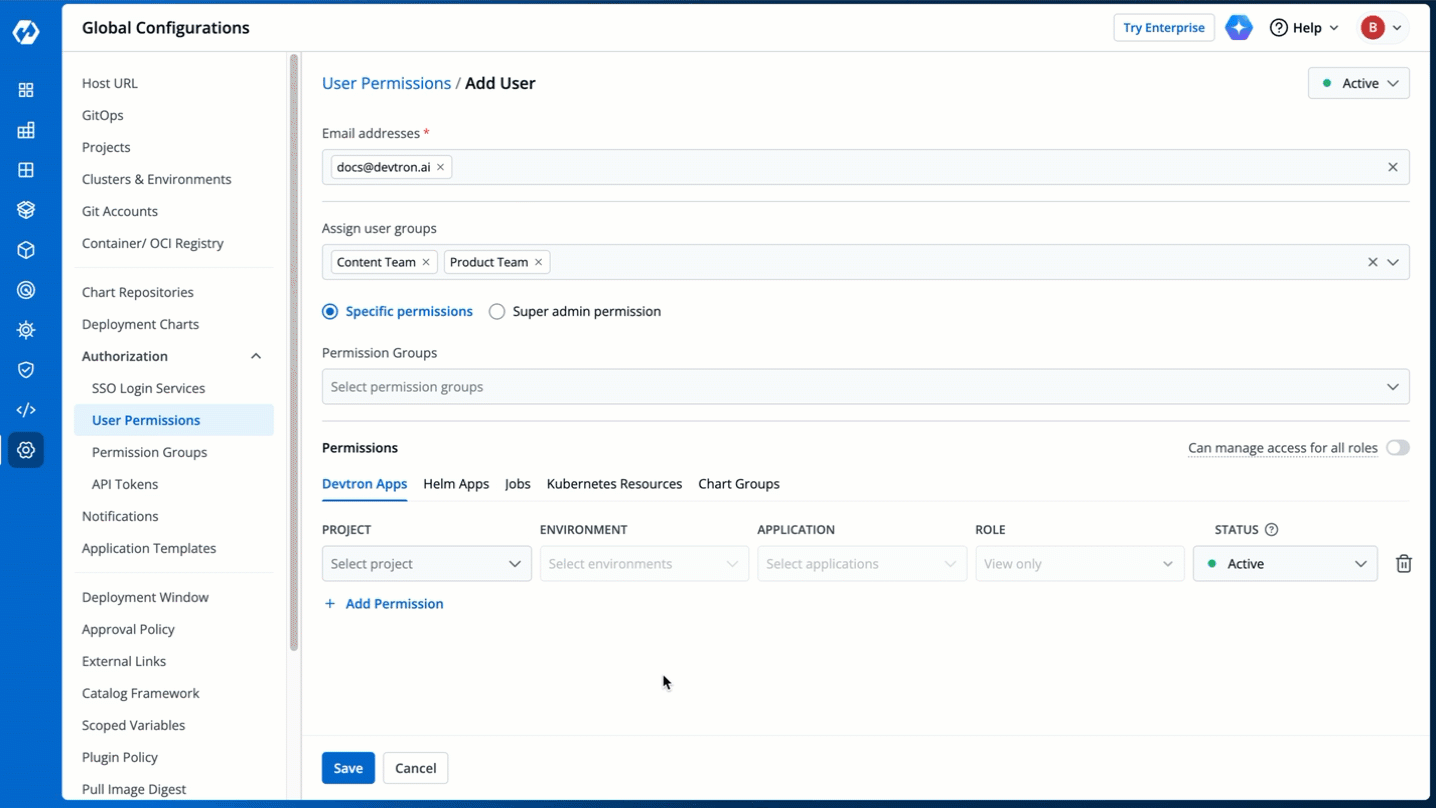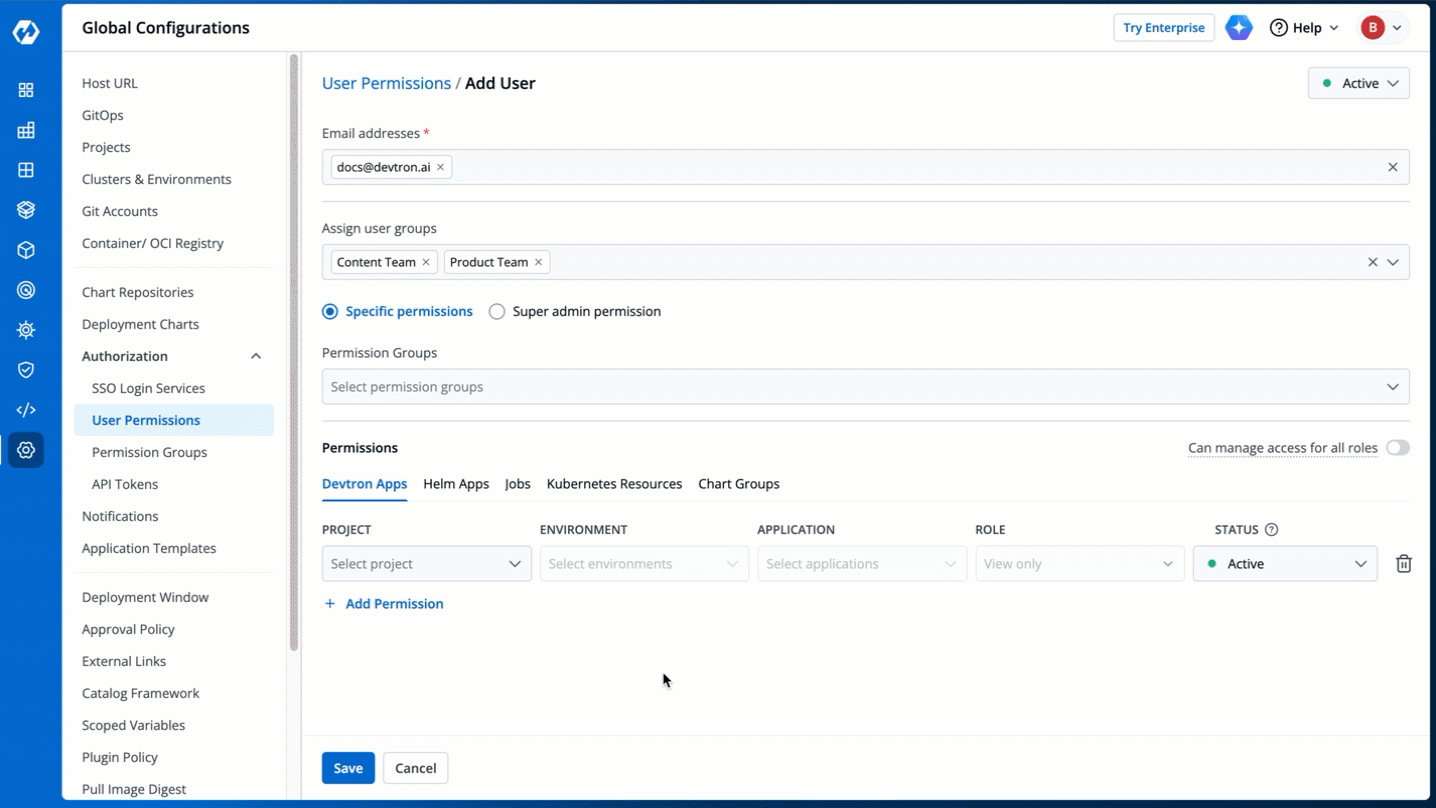
+ 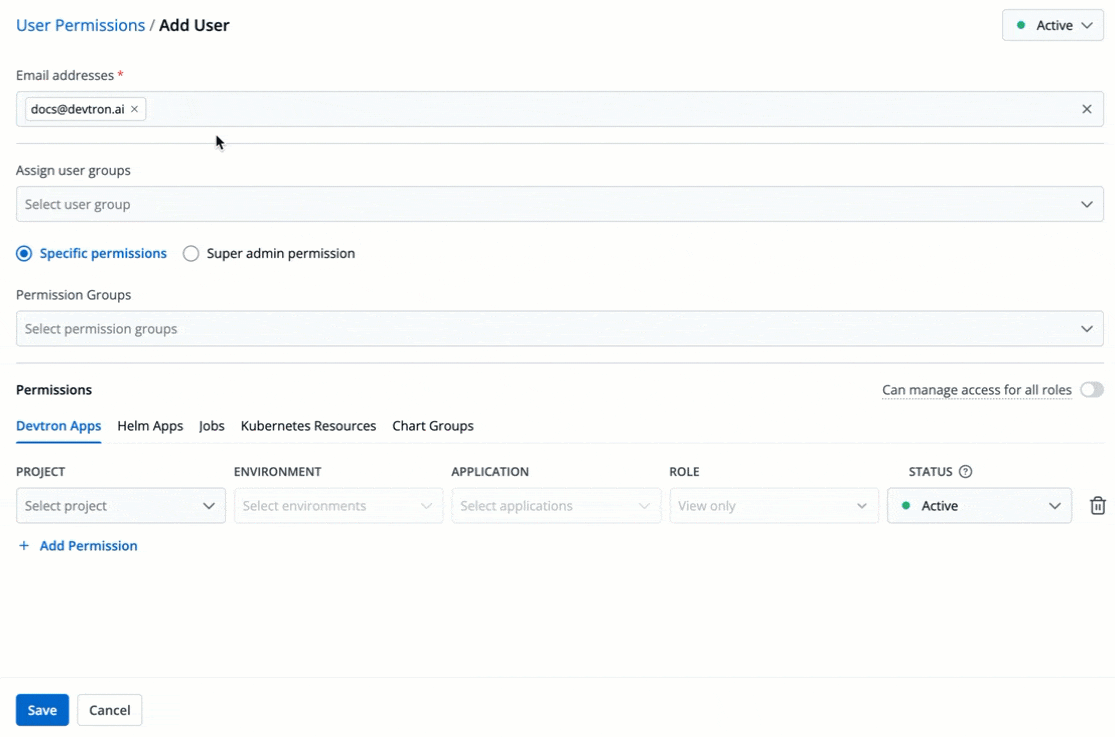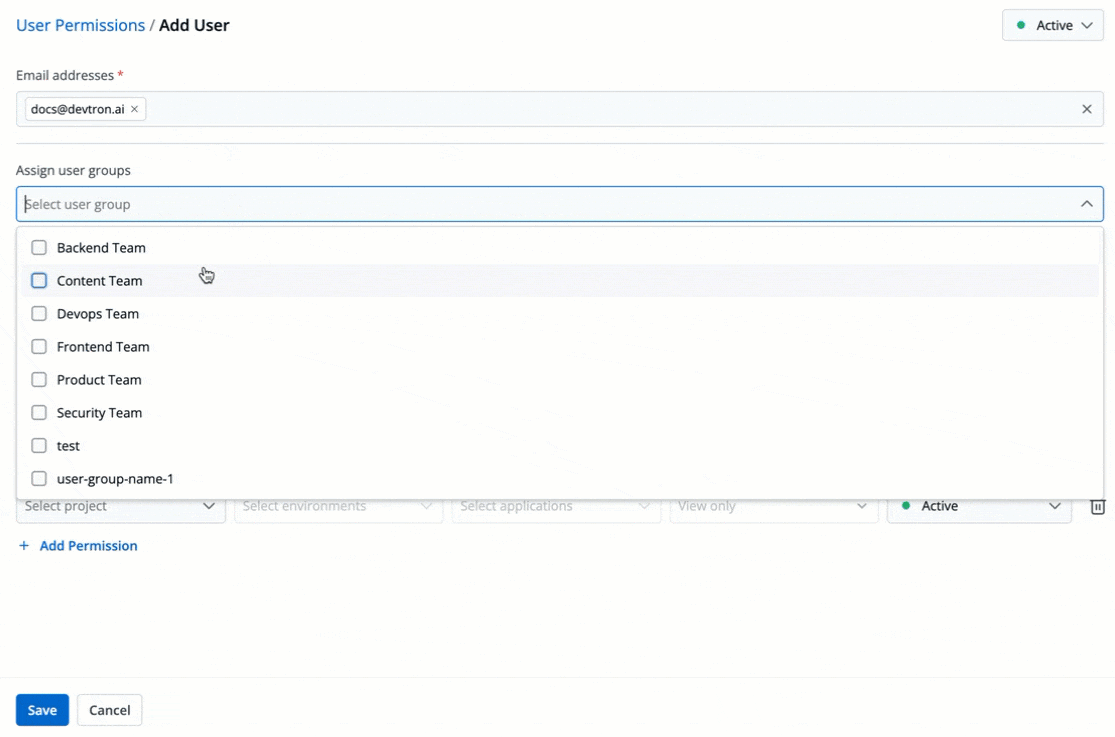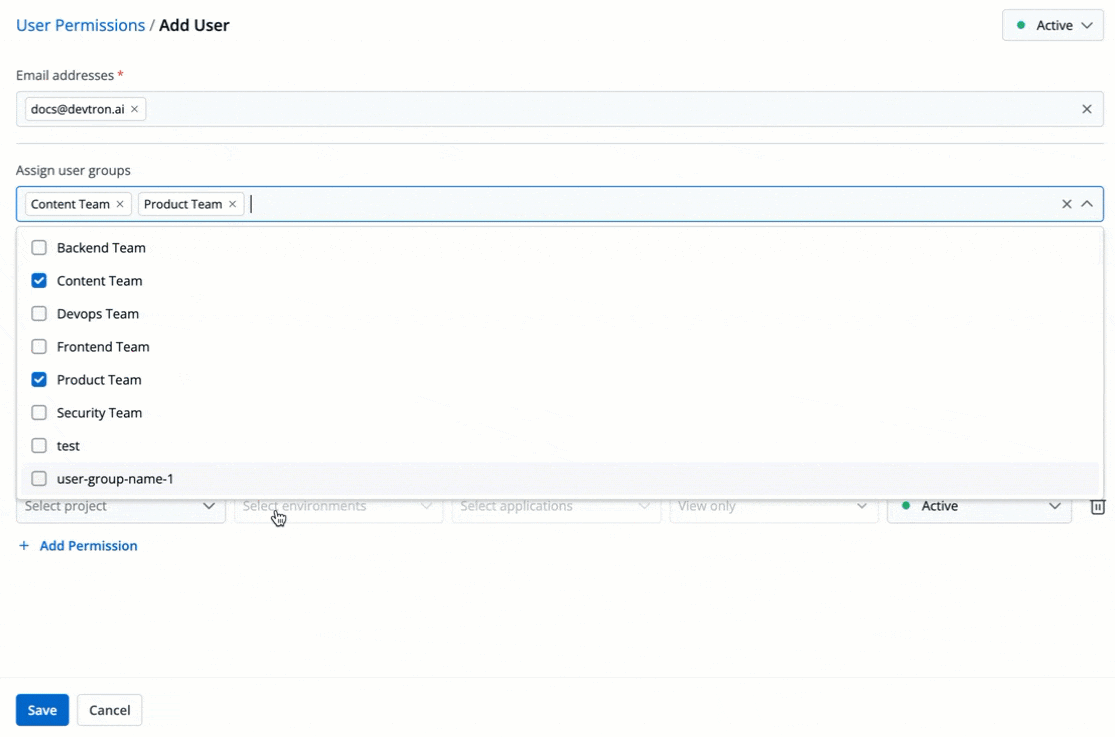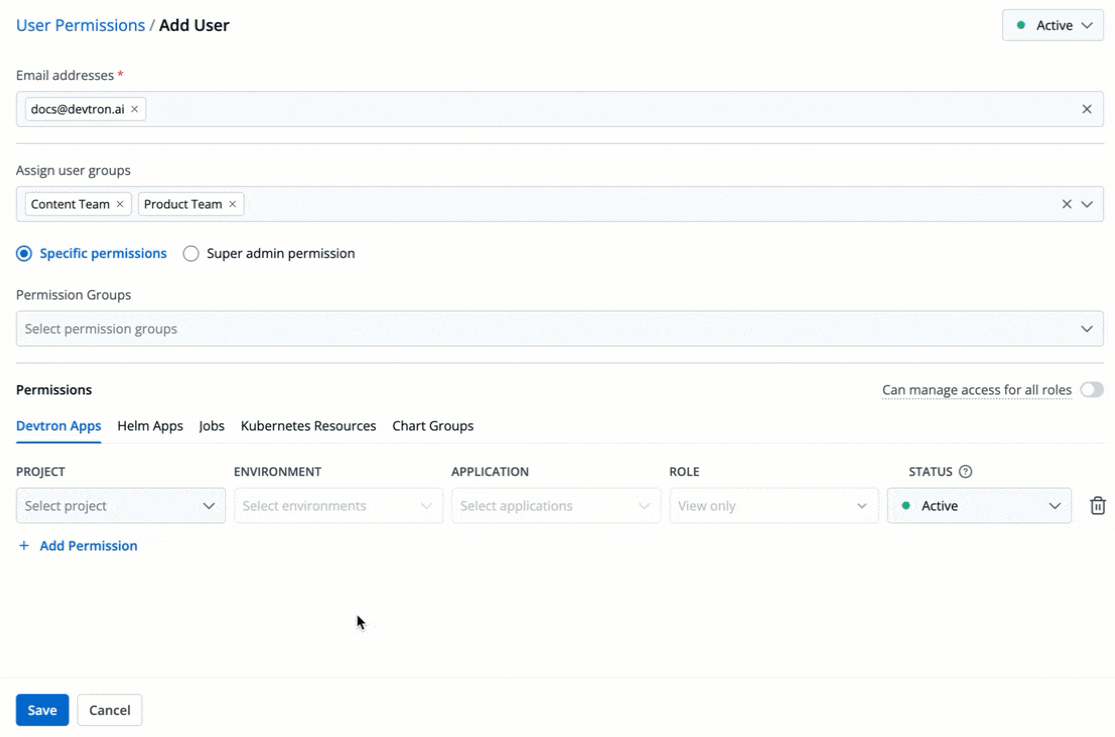
Figure 5: Assigning User Group(s)
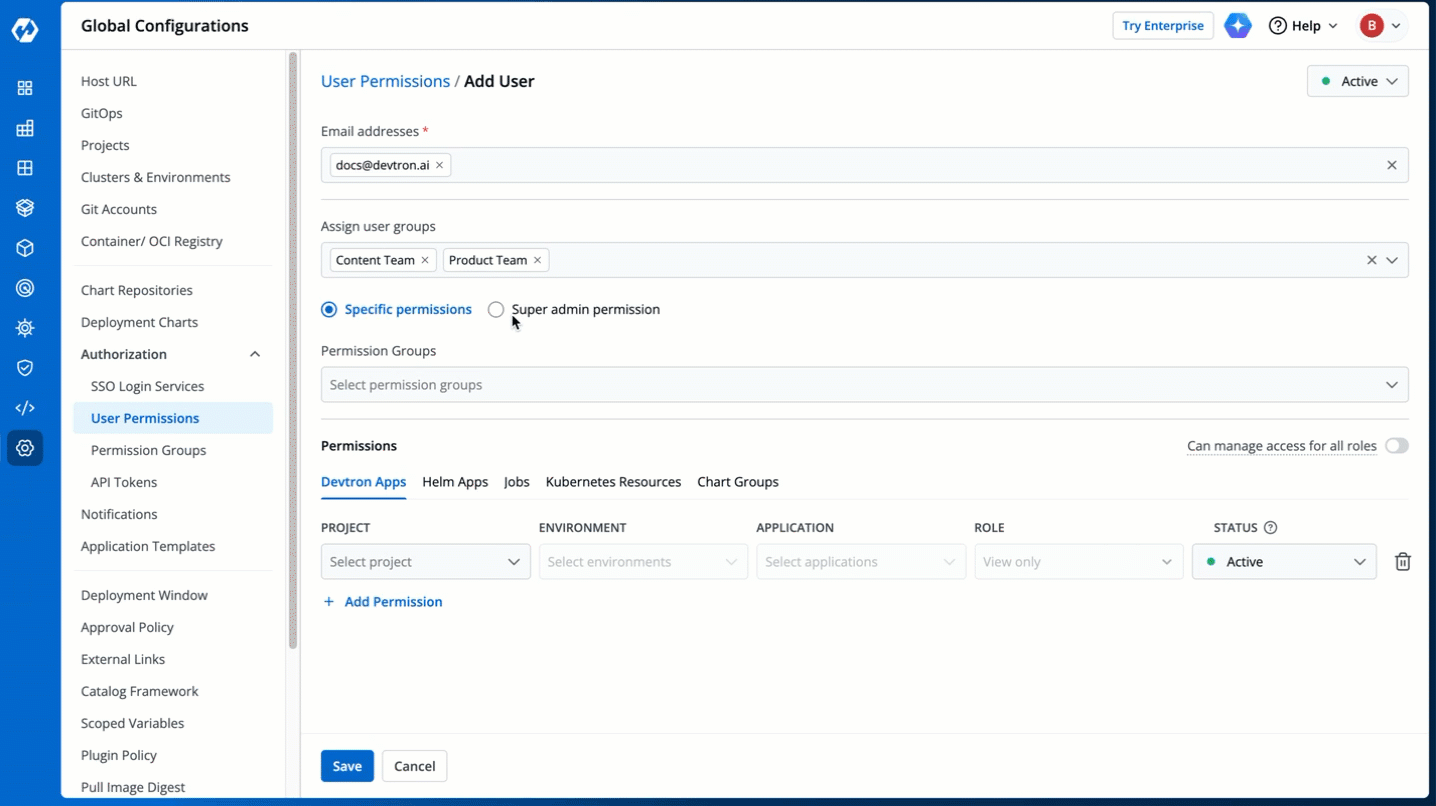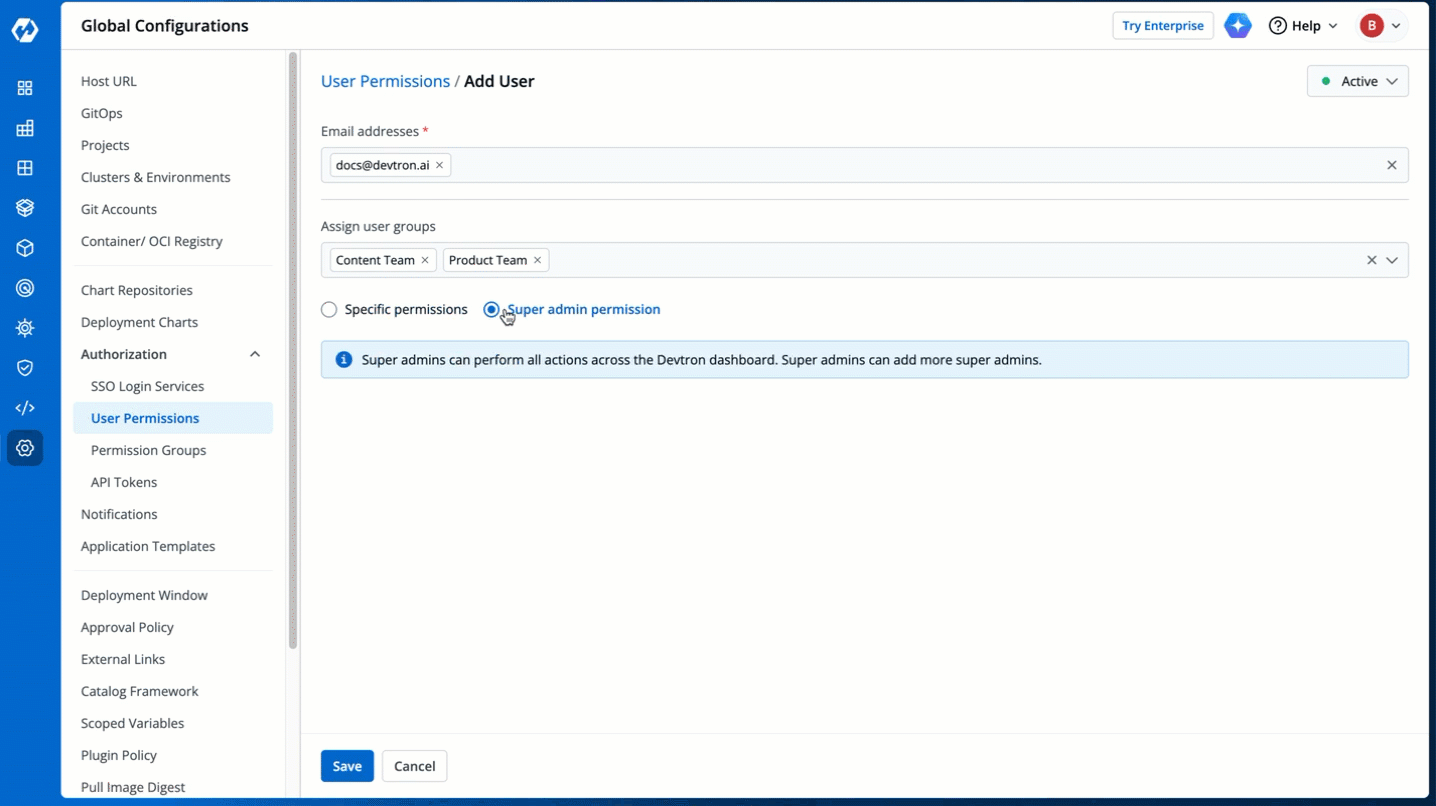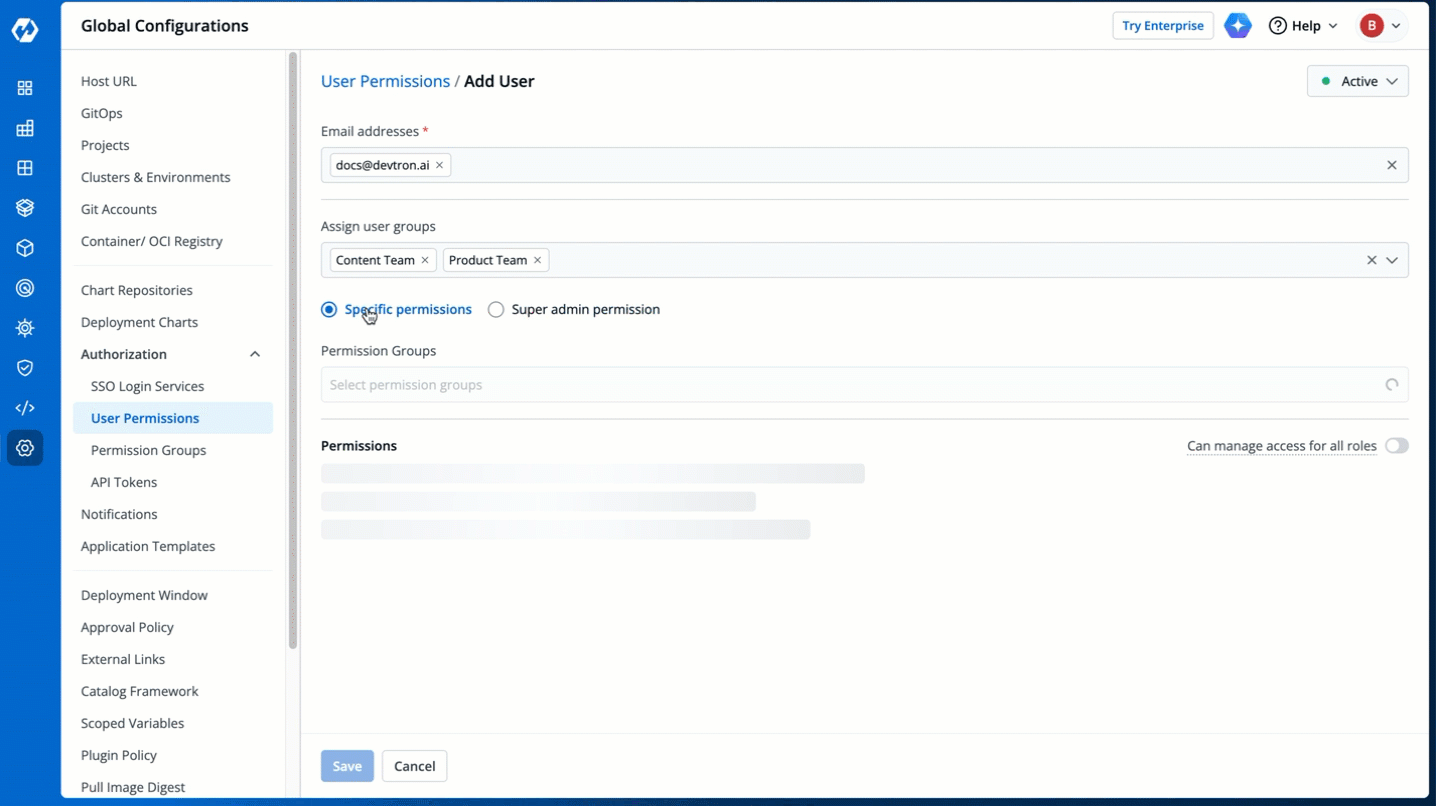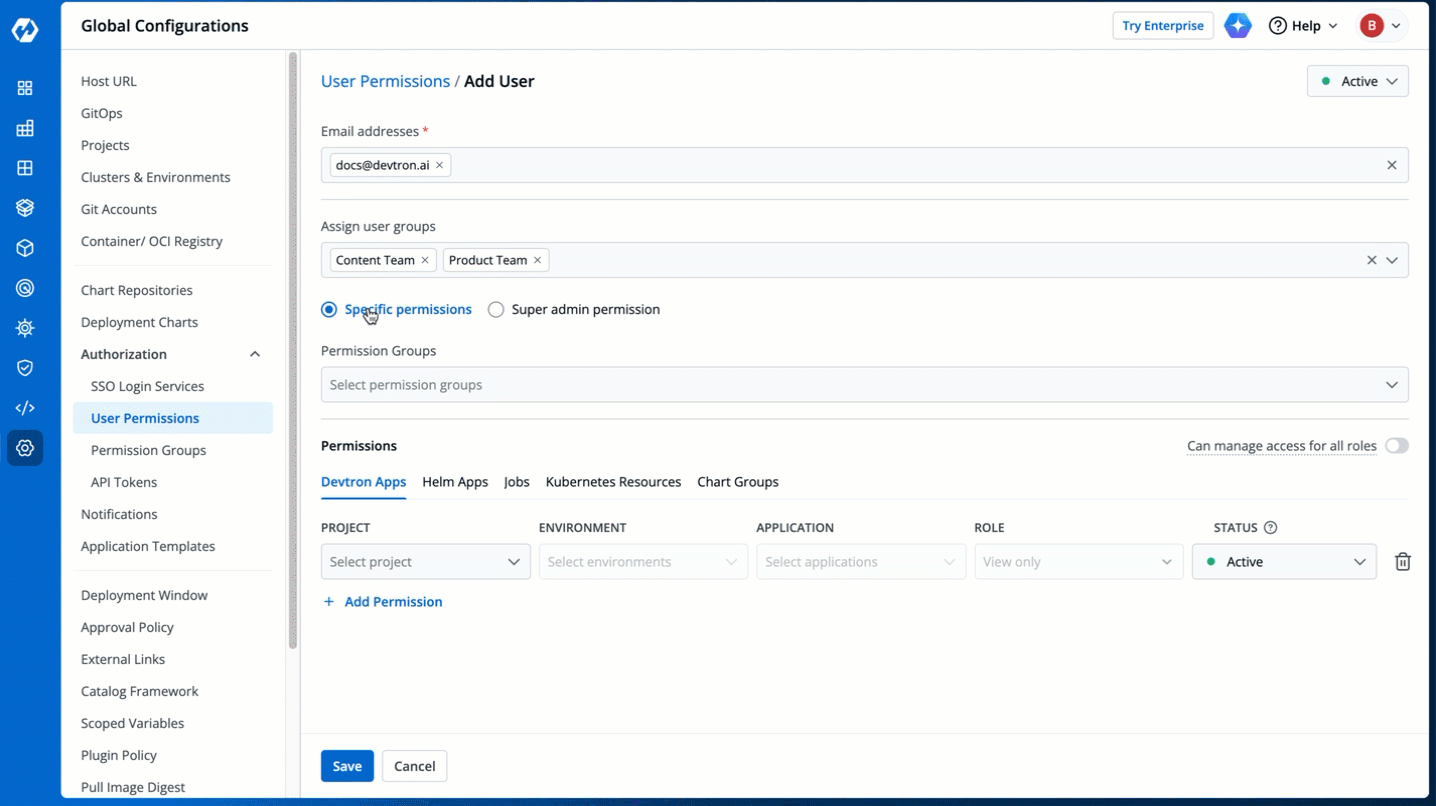
5. There are two types of permissions in Devtron (click the links below to learn more):
* [Super admin permission](#grant-super-admin-permission) for granting full access.
* [Specific permissions](#grant-specific-permissions) for granting cherry-picked access.
- 
+ 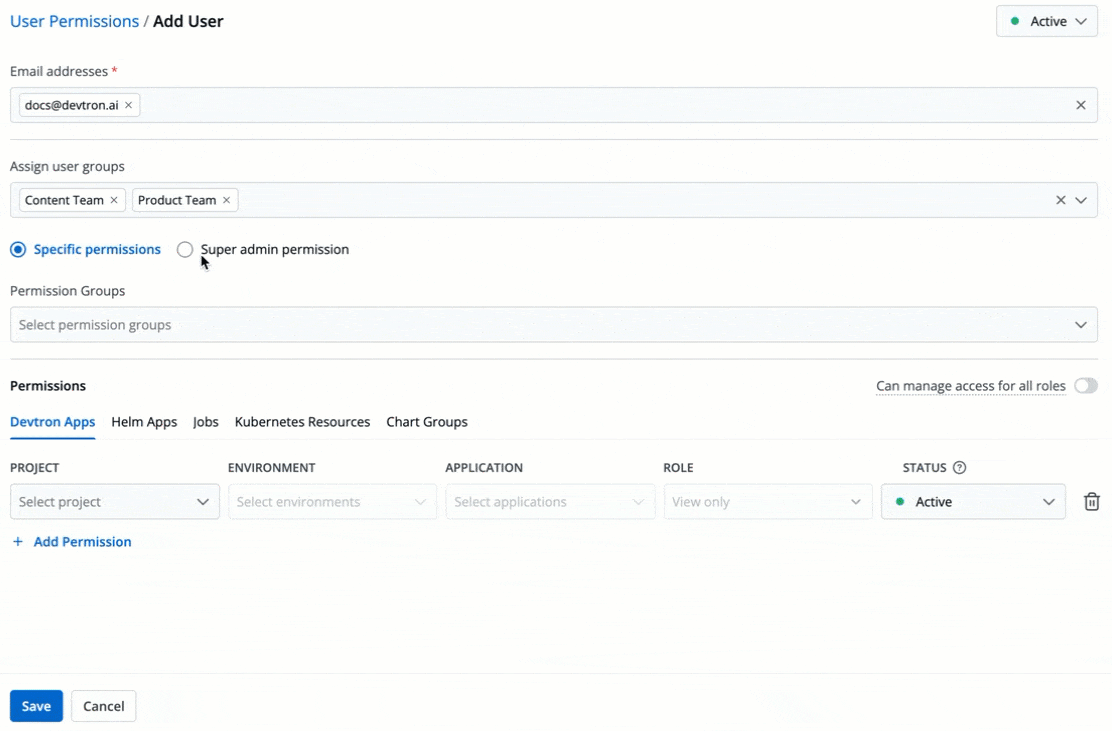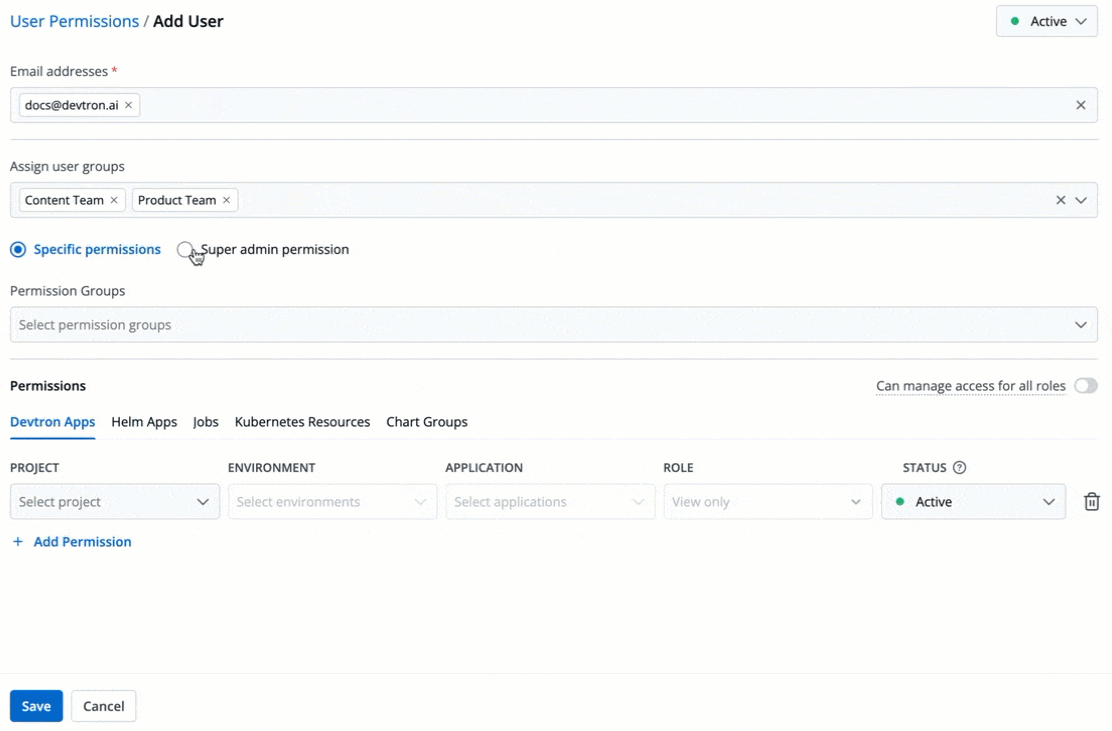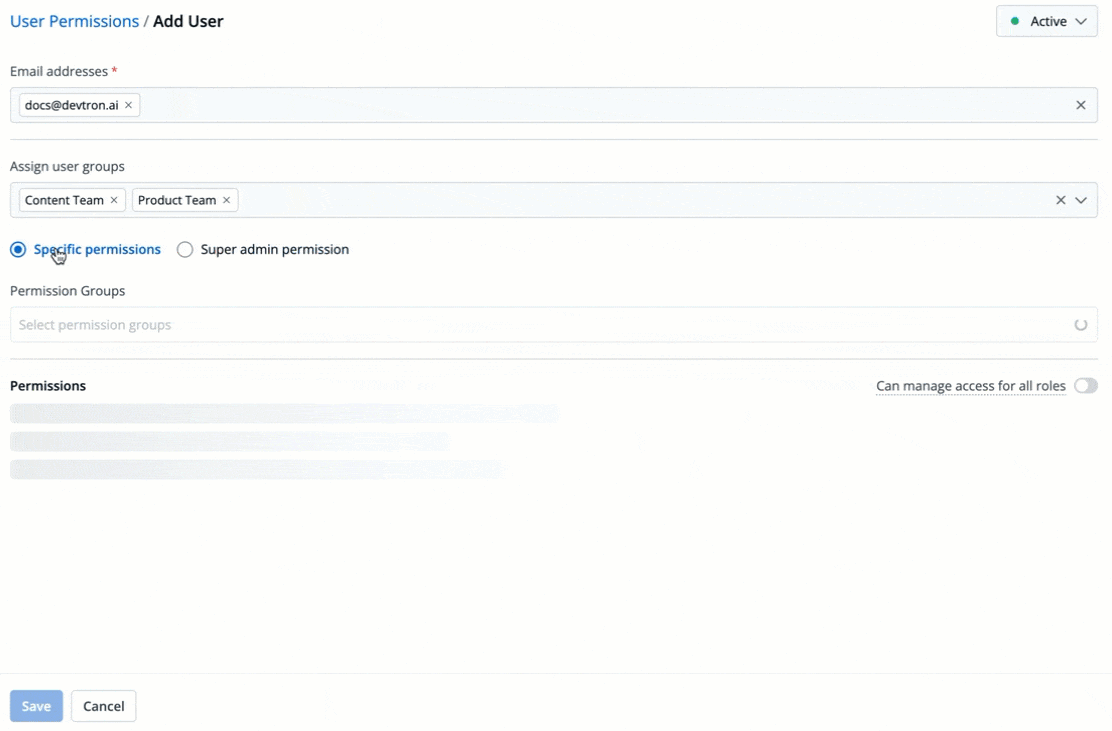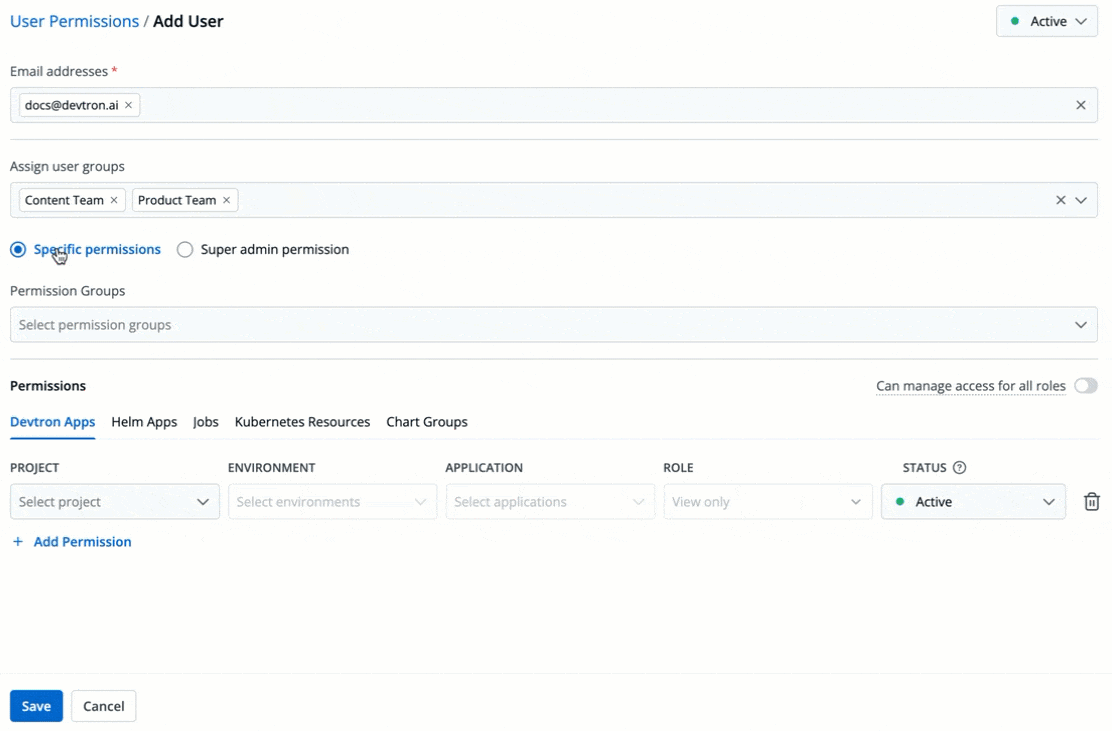
Figure 6: Granting Specific or Superadmin Access
6. Click **Save**. You have successfully added your user(s).
@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ Only managers and super-admins can add users.
## Grant Super Admin Permission
-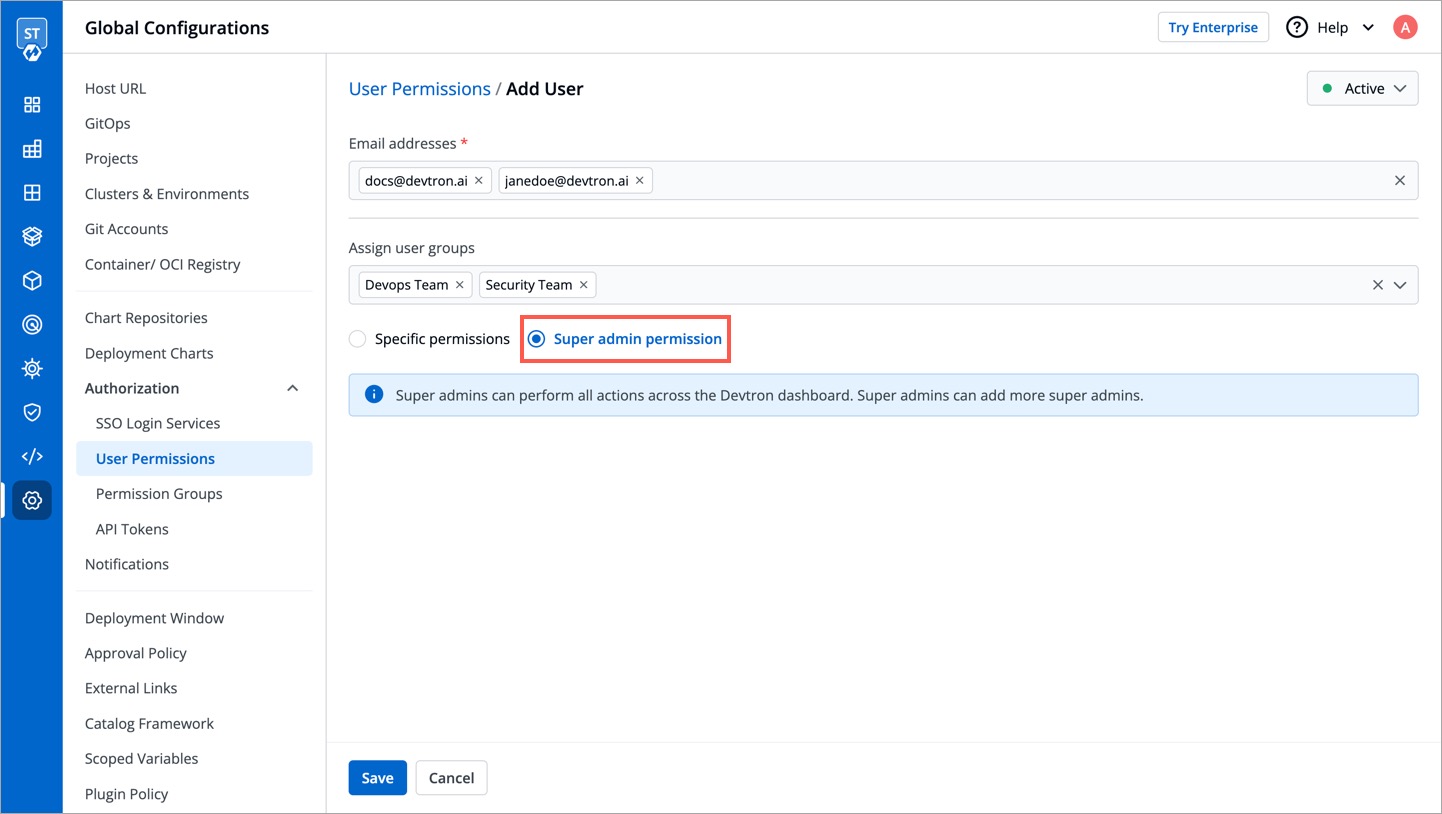
+
Figure 7: Granting Superadmin Access
Super-Admins have unrestricted access to all Devtron resources. They can create, modify, delete, and manage any resource, including user access, Git repositories, container registries, clusters, and environments. Before assigning this permission, please note:
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ Super-Admins have unrestricted access to all Devtron resources. They can create,
## Grant Specific Permissions
-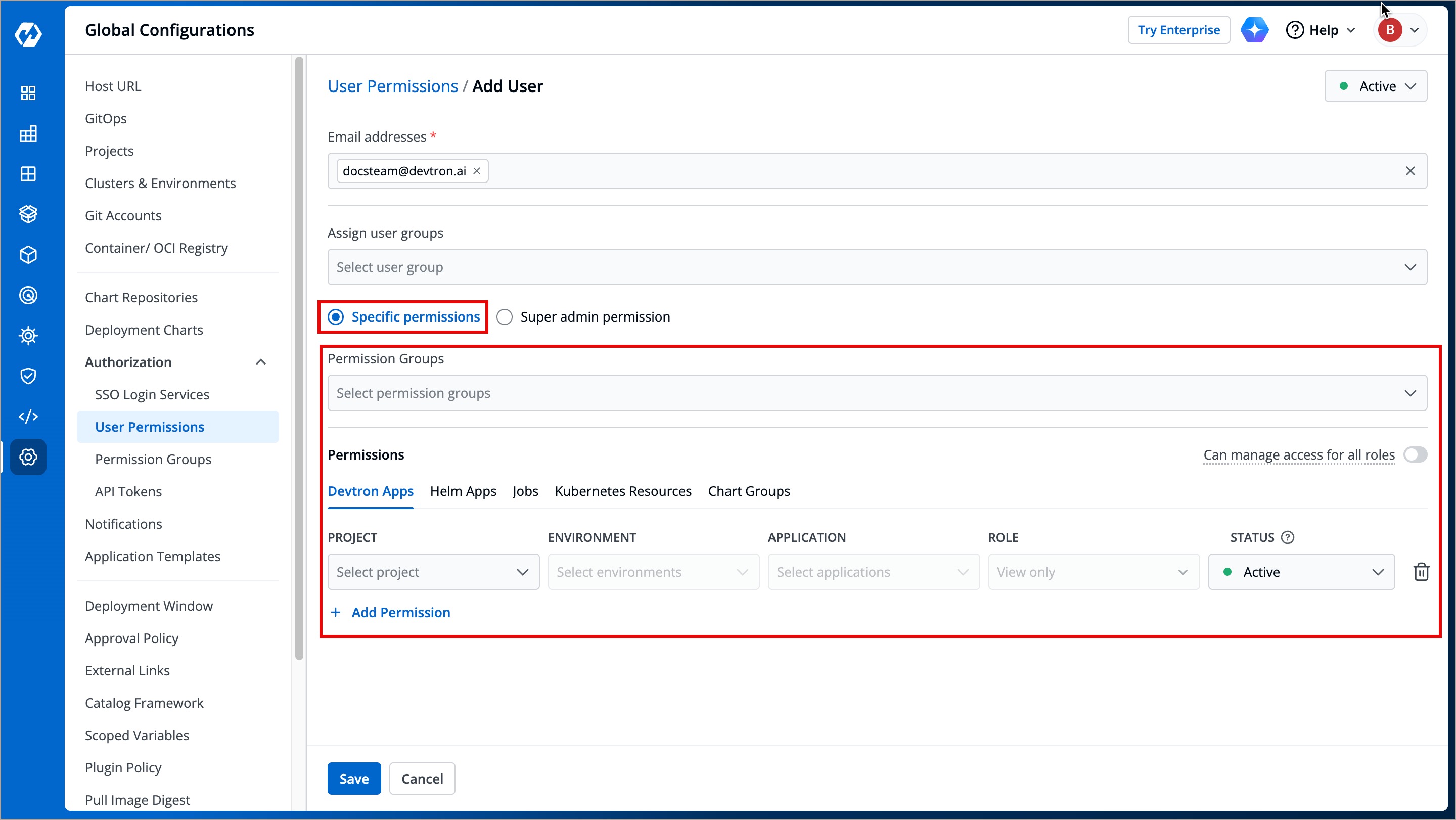
+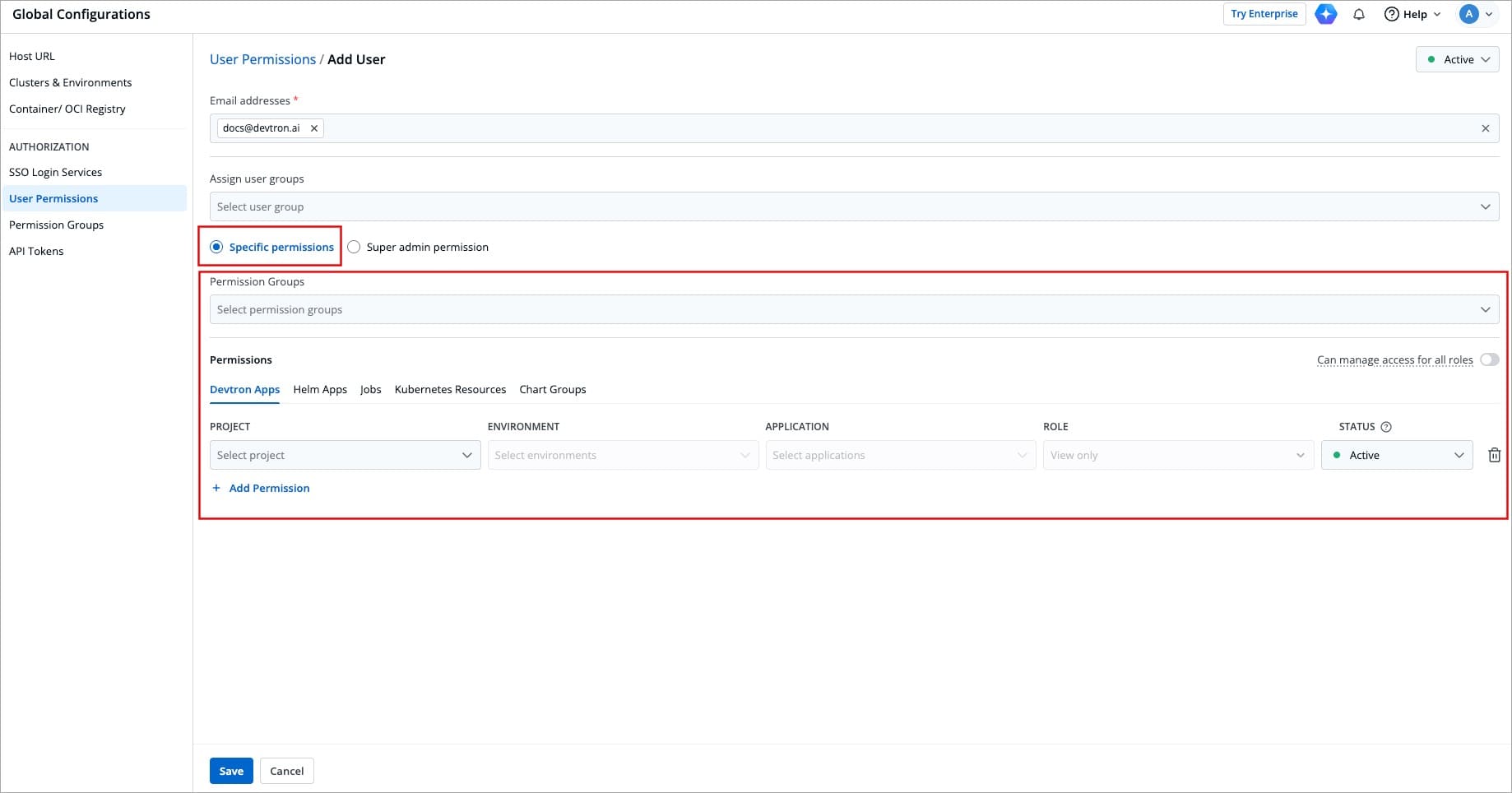
Figure 8: Granting Specific Access
### Permission Groups
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ Super-Admins have unrestricted access to all Devtron resources. They can create,
The **Permission Groups** drop-down box allows you to select from a list of permission groups already created in the [Permission Groups](../authorization/permission-groups.md) page.
-
+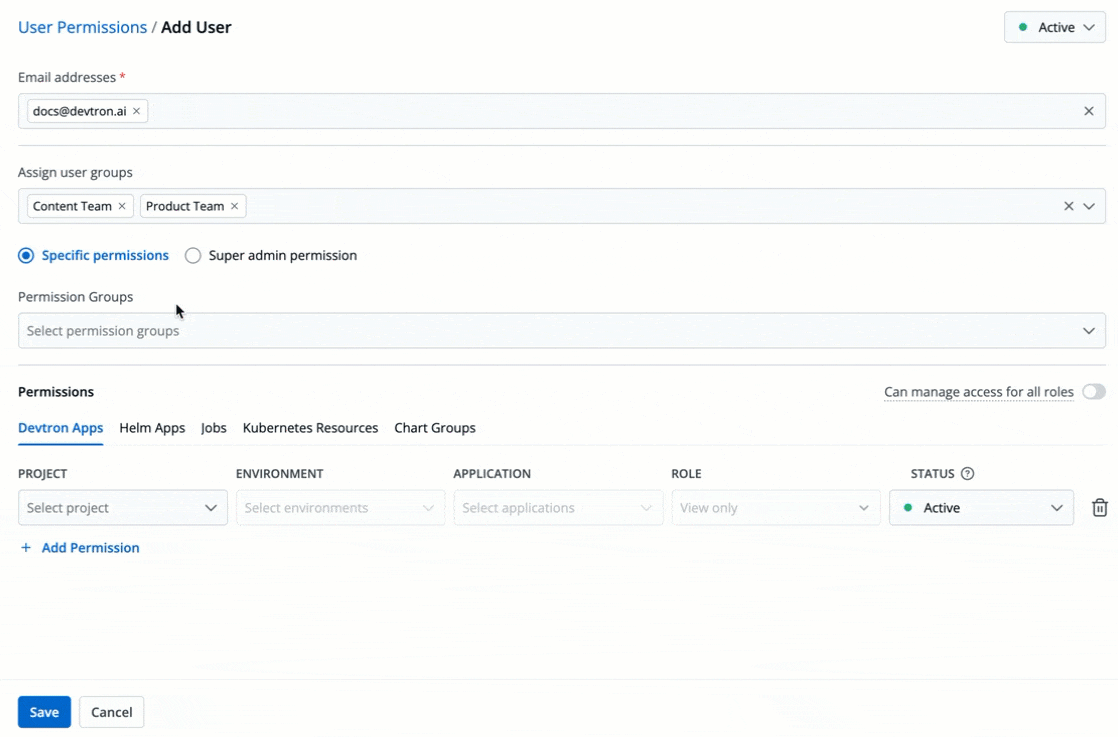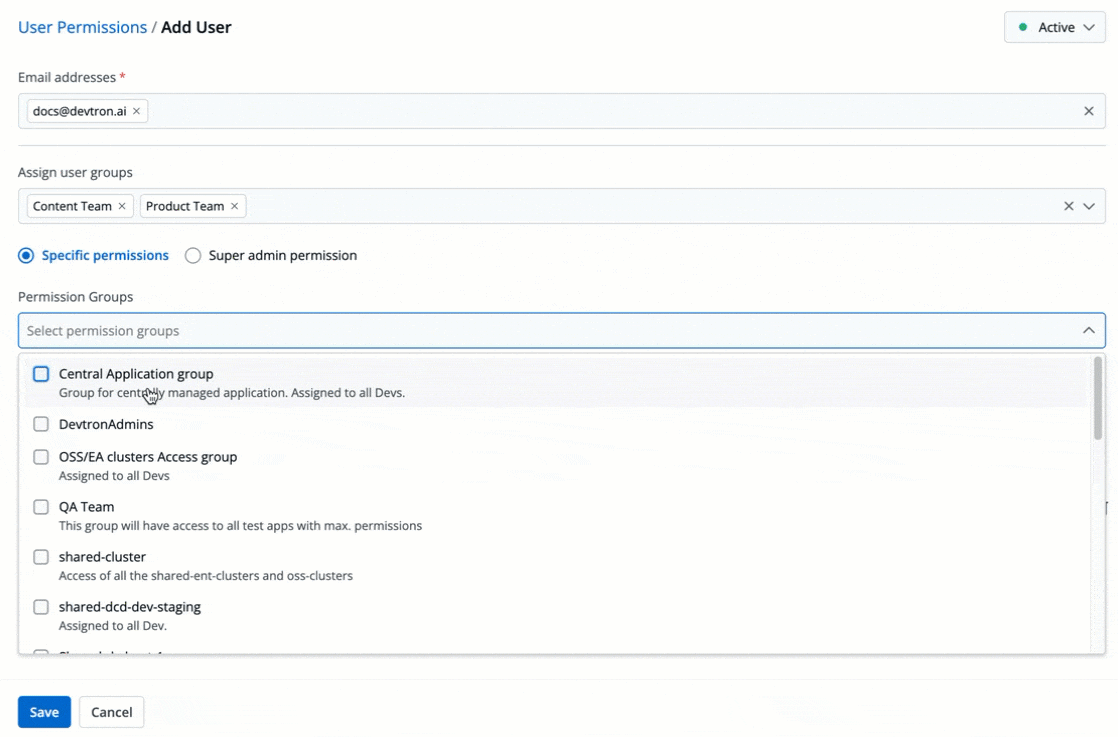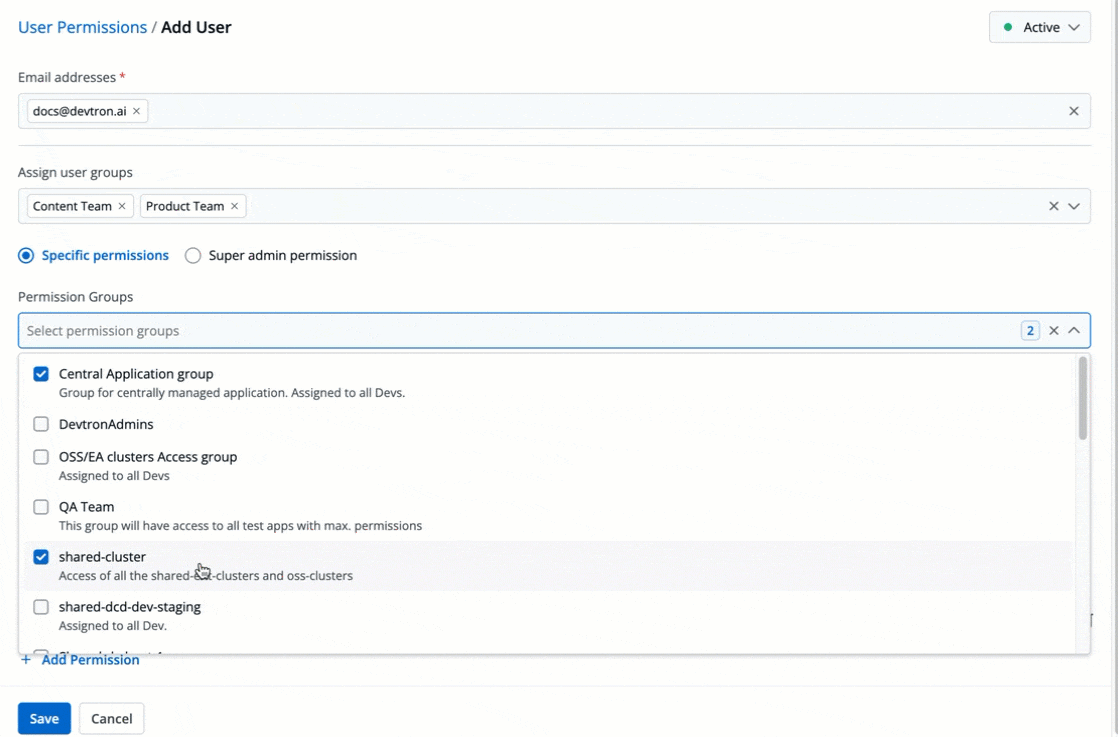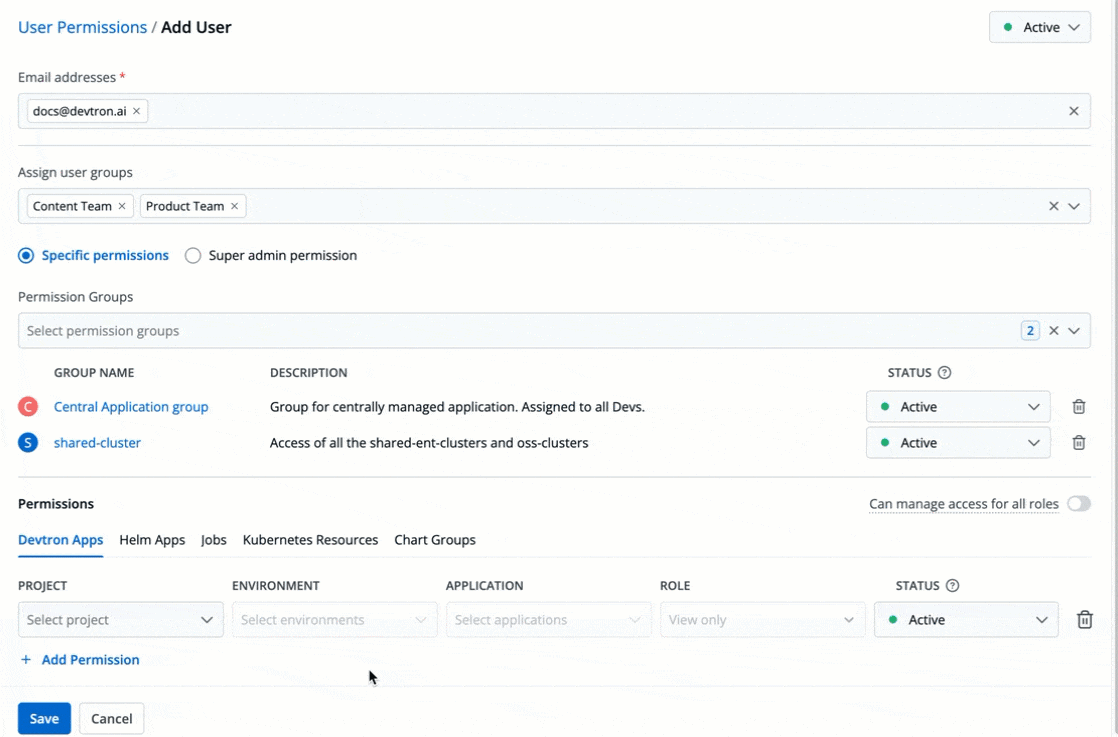
Figure 9: Permission Groups
You can select one or more permission groups, and the user will automatically inherit all the permissions to the projects and resources defined for those groups. Once you select permission group(s), assigning direct permissions can be skipped (unless you wish to grant additional permissions).
@@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ The **Devtron Apps** tab is displayed only when the [Build and Deploy (CI/CD)](.
The **Devtron Apps** tab allows you to grant user permissions for Devtron applications.
-
+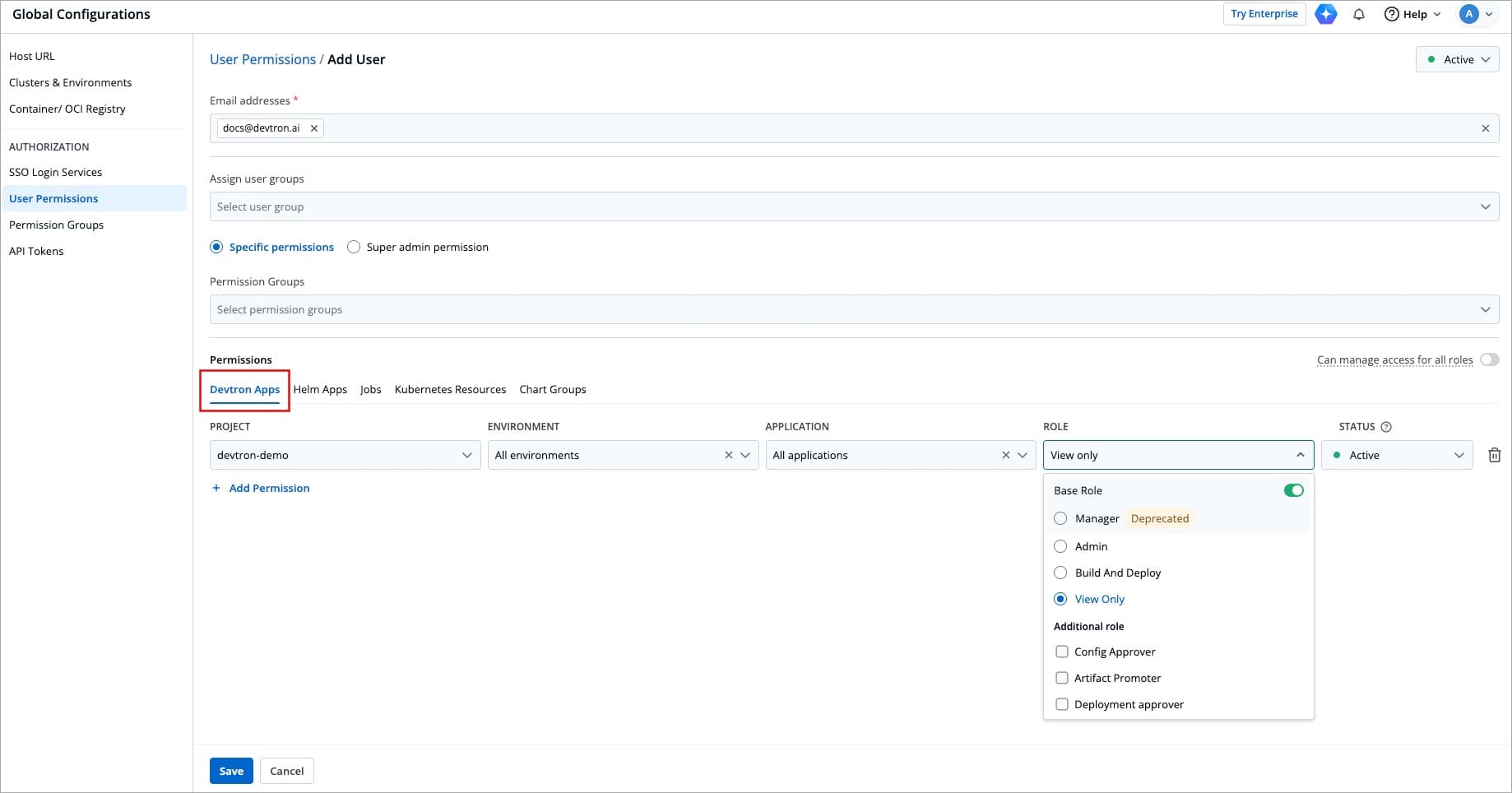
Figure 10: Granting Devtron Apps Permissions
| Field | Description |
@@ -162,7 +162,7 @@ You also have the provision of granting Access Manager role to a user. Refer [Ac
Here you can grant your user the permissions for Helm apps deployed from Devtron or outside Devtron.
-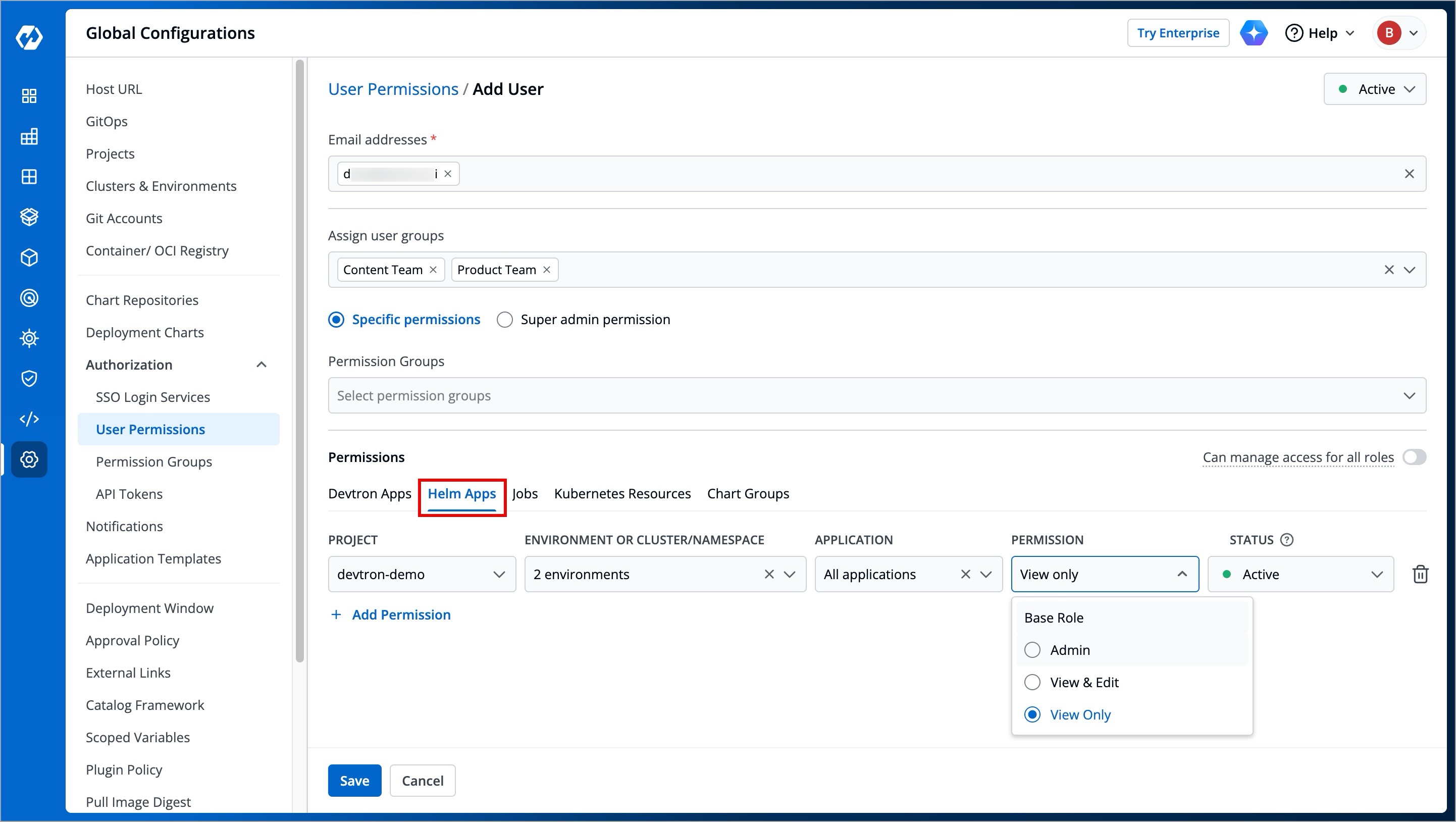
+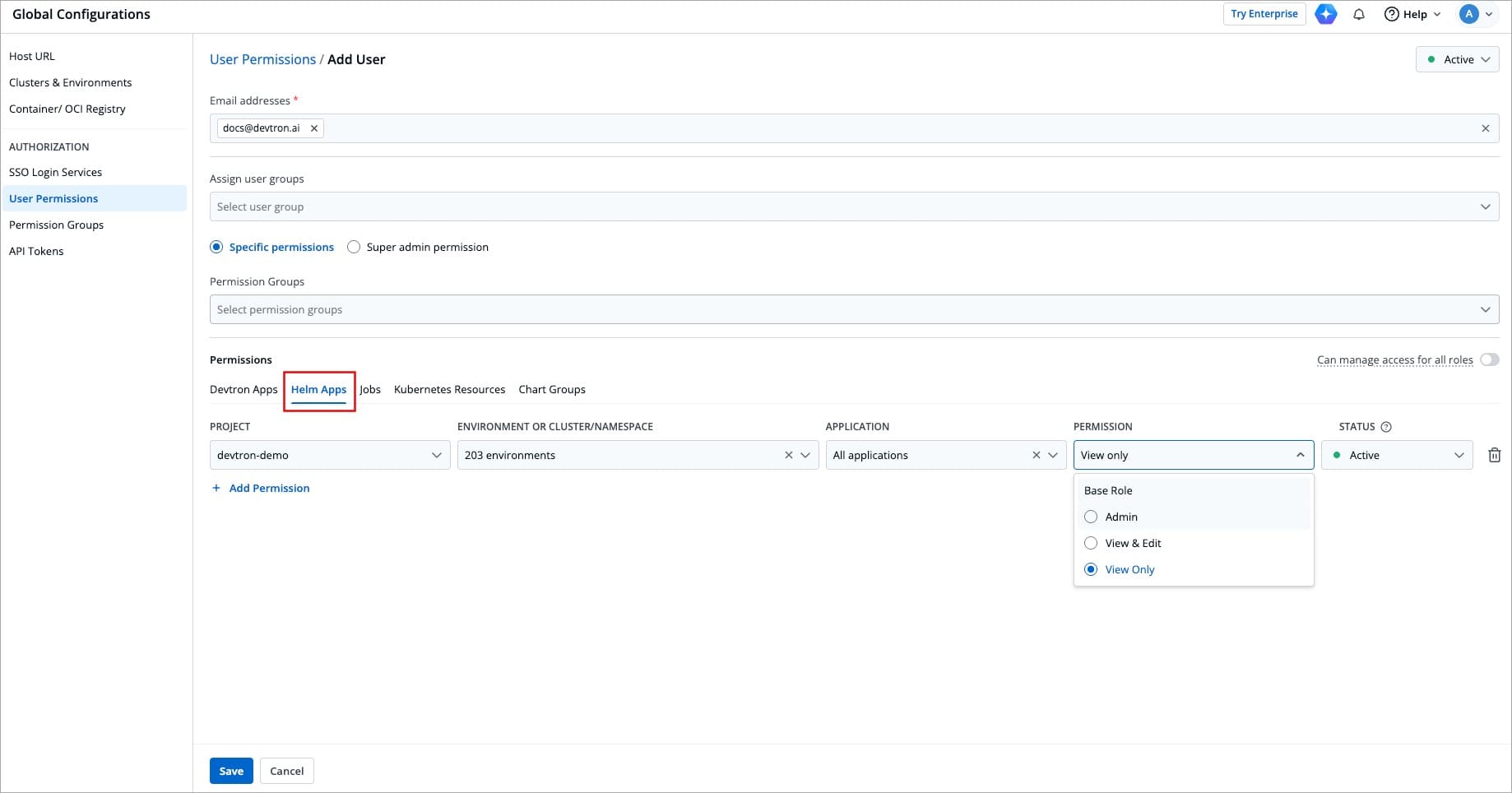
Figure 11: Granting Helm Apps Permissions
| Field | Description |
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ There are three role-based access levels for Helm Apps:
Here you can grant your user the permissions to access the jobs created in Devtron.
-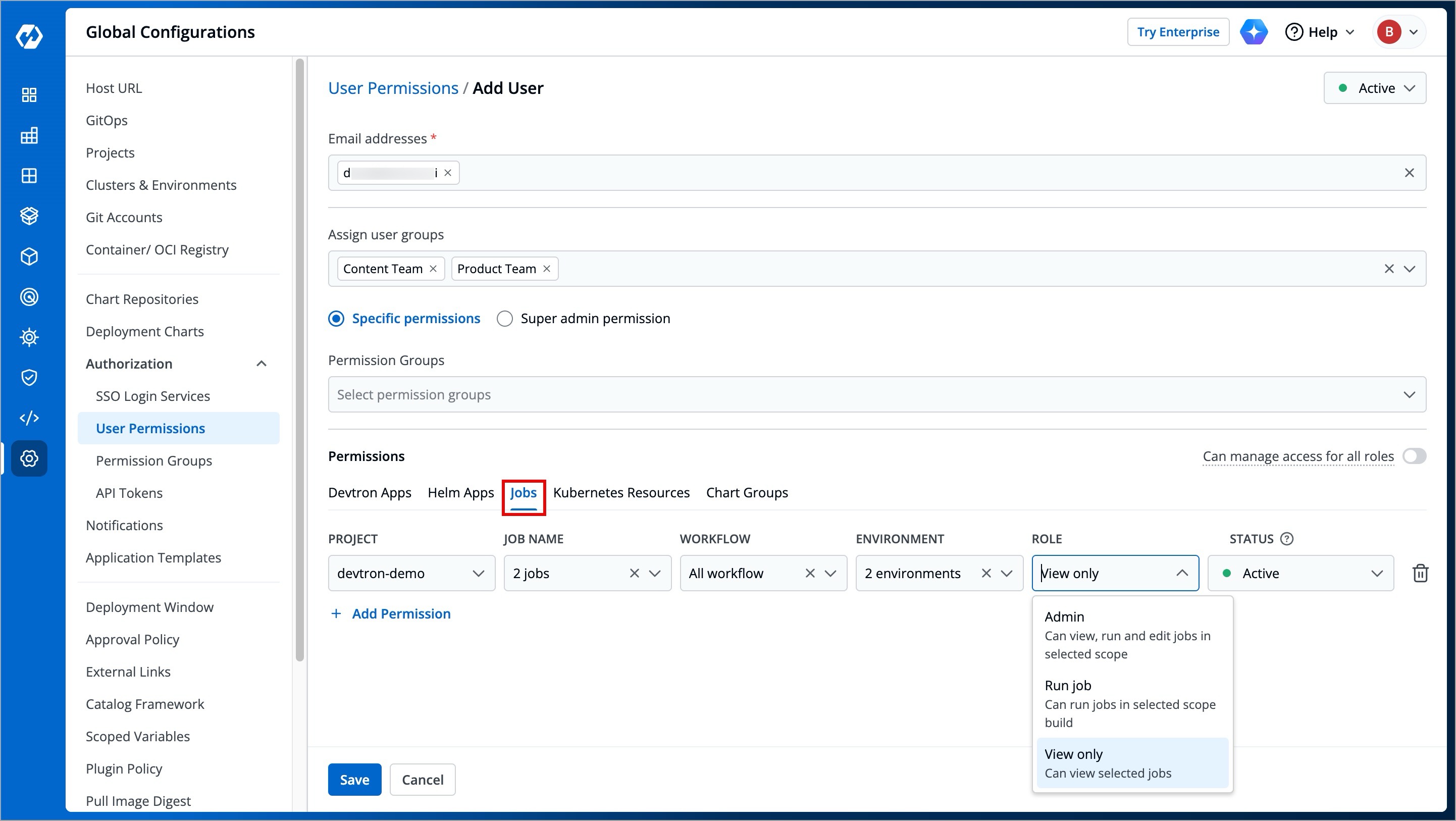
+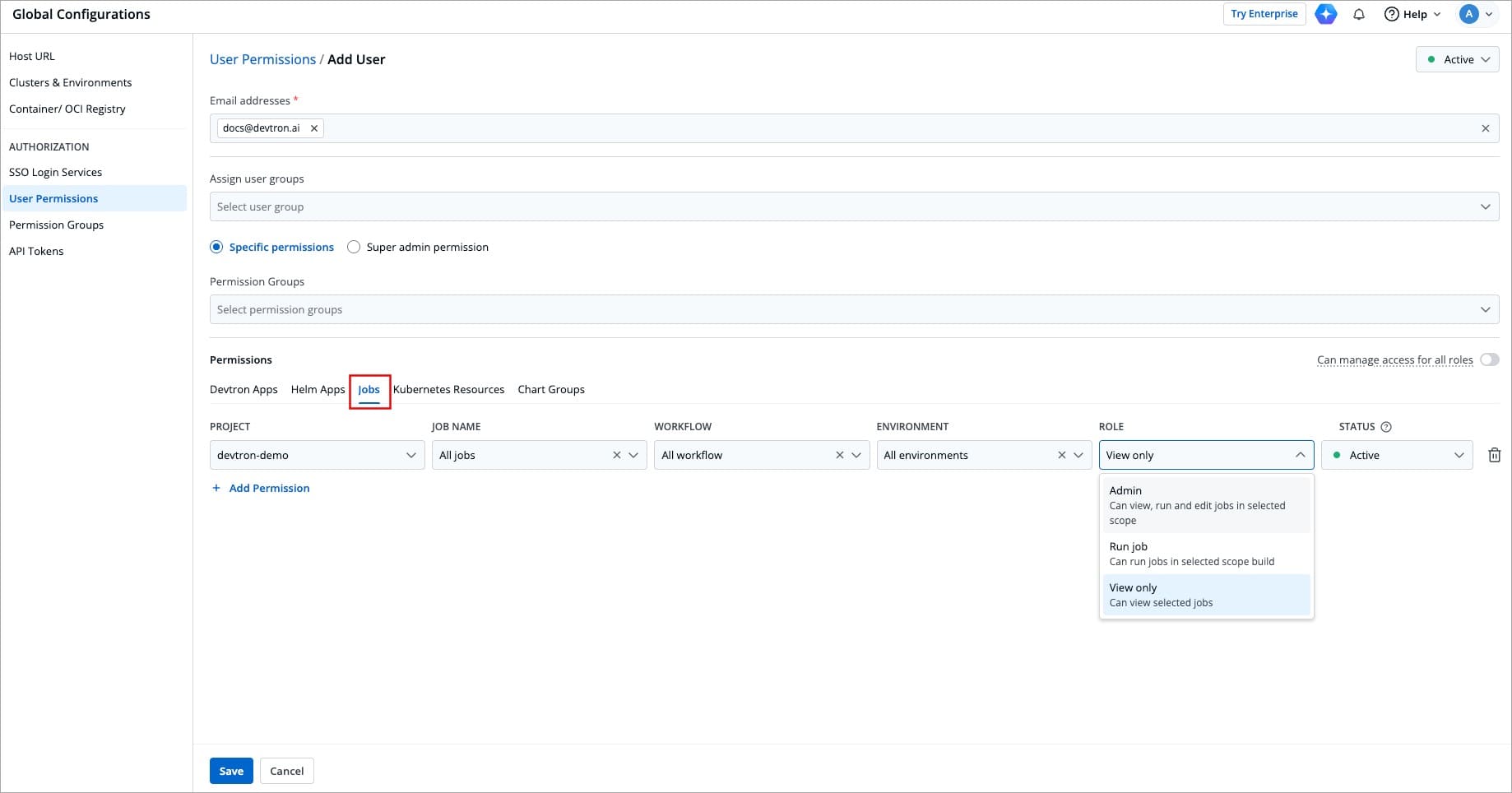
Figure 12: Granting Jobs Permissions
| Field | Description |
@@ -231,11 +231,11 @@ Here you can provide permission to view, inspect, manage, and delete resources i
To grant Kubernetes resource permission, click **Add permission**.
-
+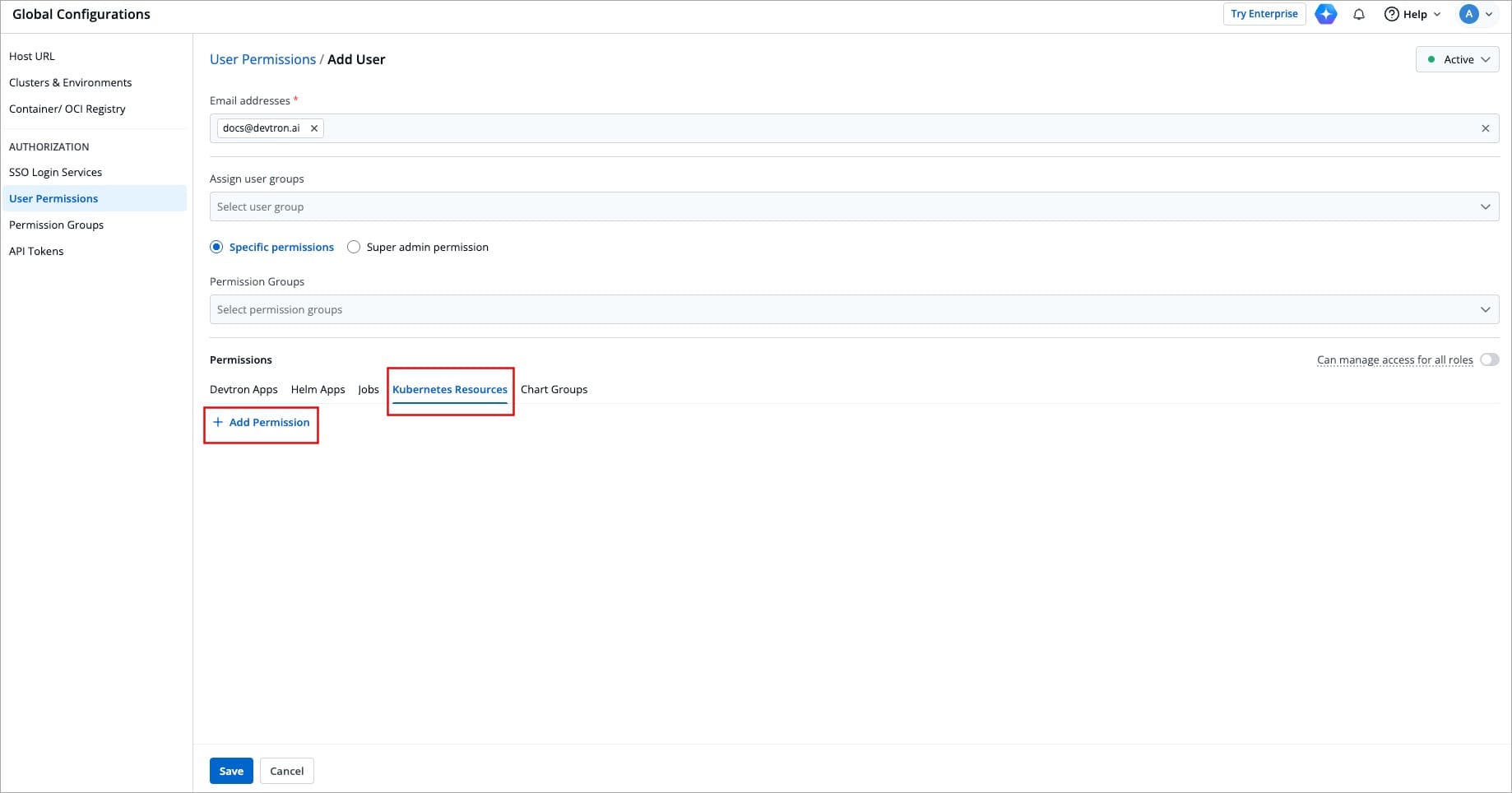
Figure 13a: Adding Permissions for Kubernetes Resources
Figure 13b: Granting Permissions for Kubernetes Resources
| Field | Description |
@@ -269,7 +269,7 @@ The 'Chart Groups' tab will be available only if the [CI/CD module](../../integr
Here you can grant your user the permissions for accessing Chart Groups. Note that you can only give users the permission to either create chart groups or edit them, but not both.
-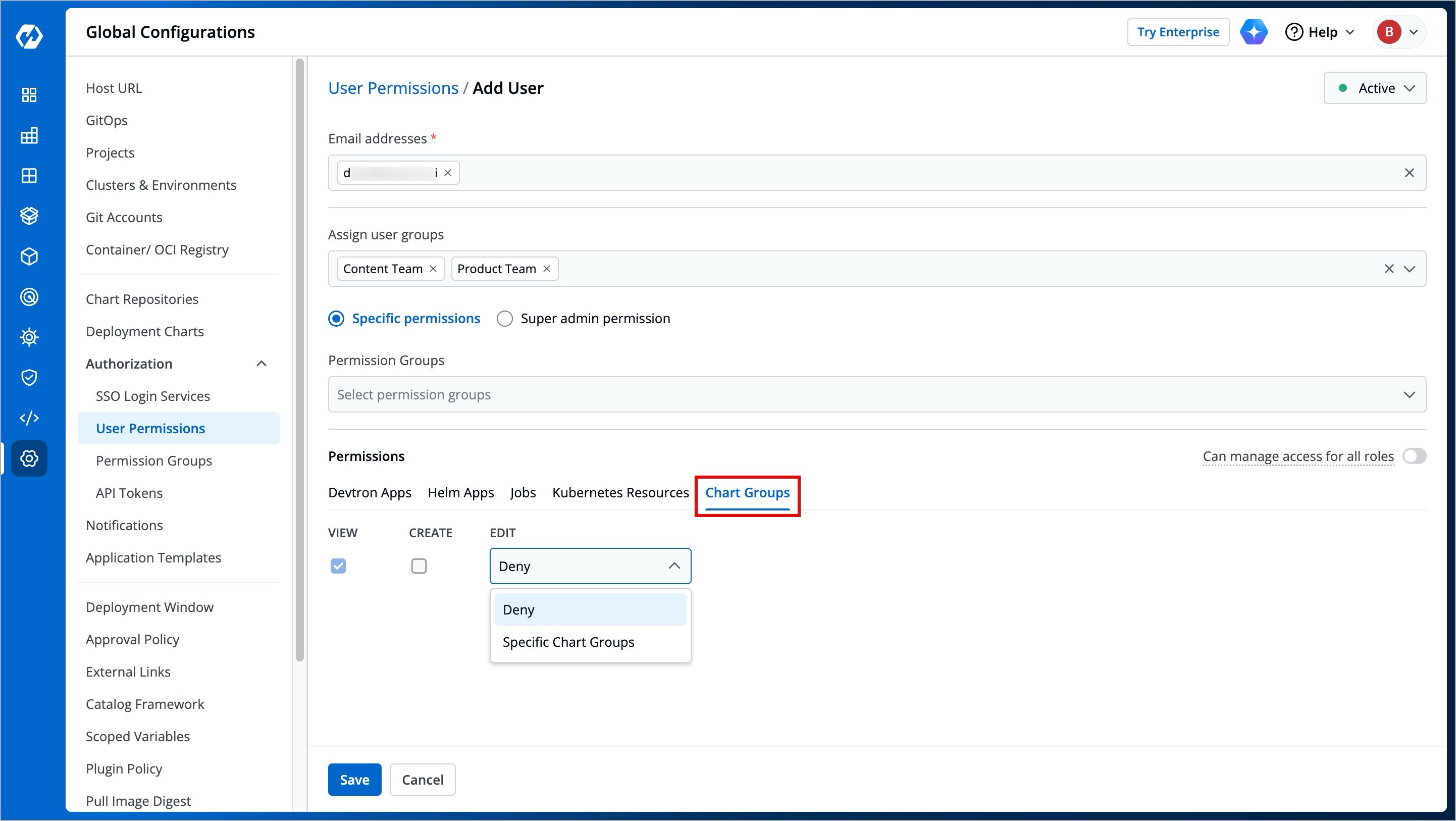
+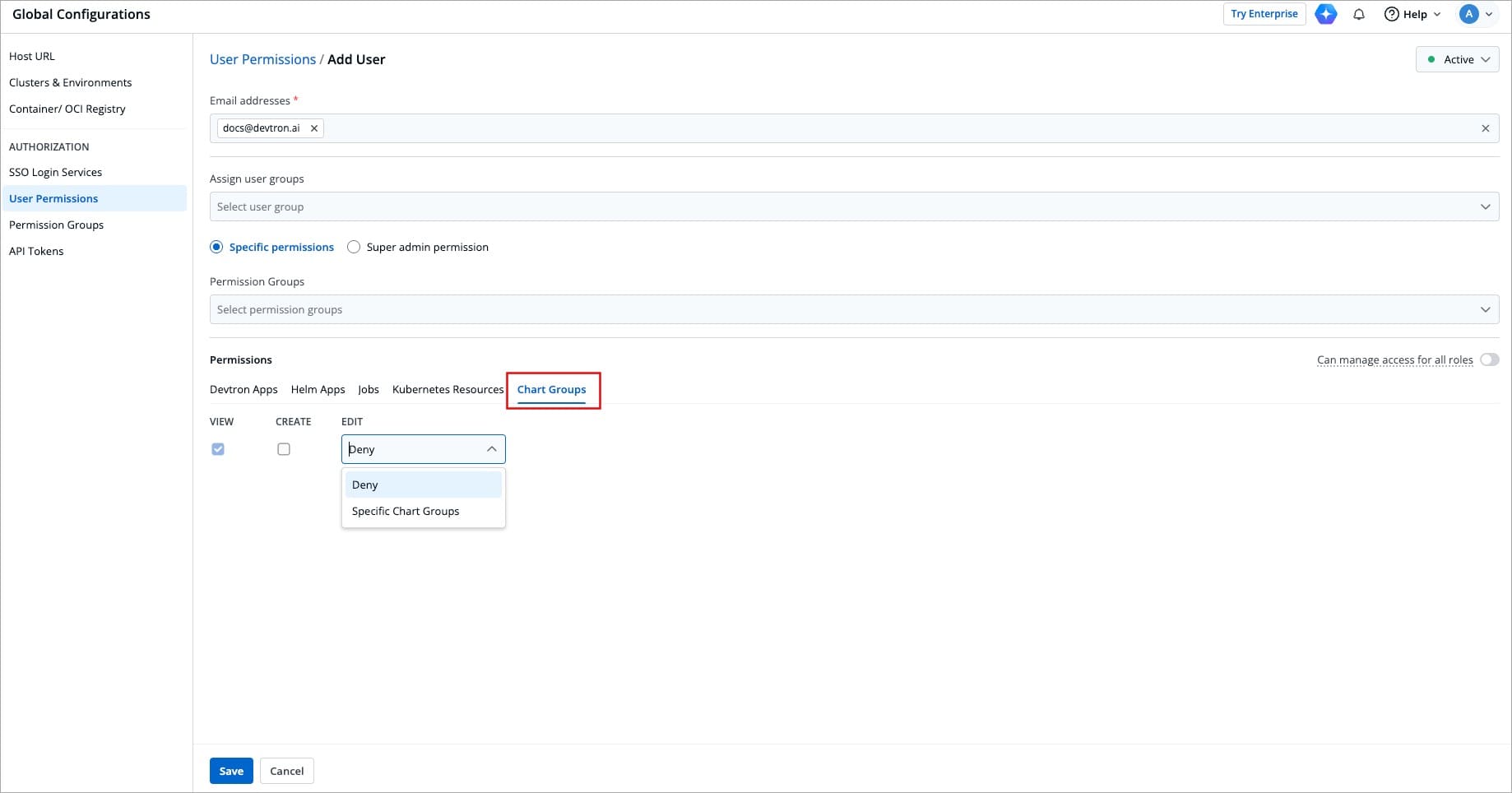
Figure 14: Granting Chart Group Permissions
| Action | Permissions |
@@ -302,7 +302,7 @@ Only a [Super Admin](#grant-super-admin-permission) can enable the **Can manage
:::
-
+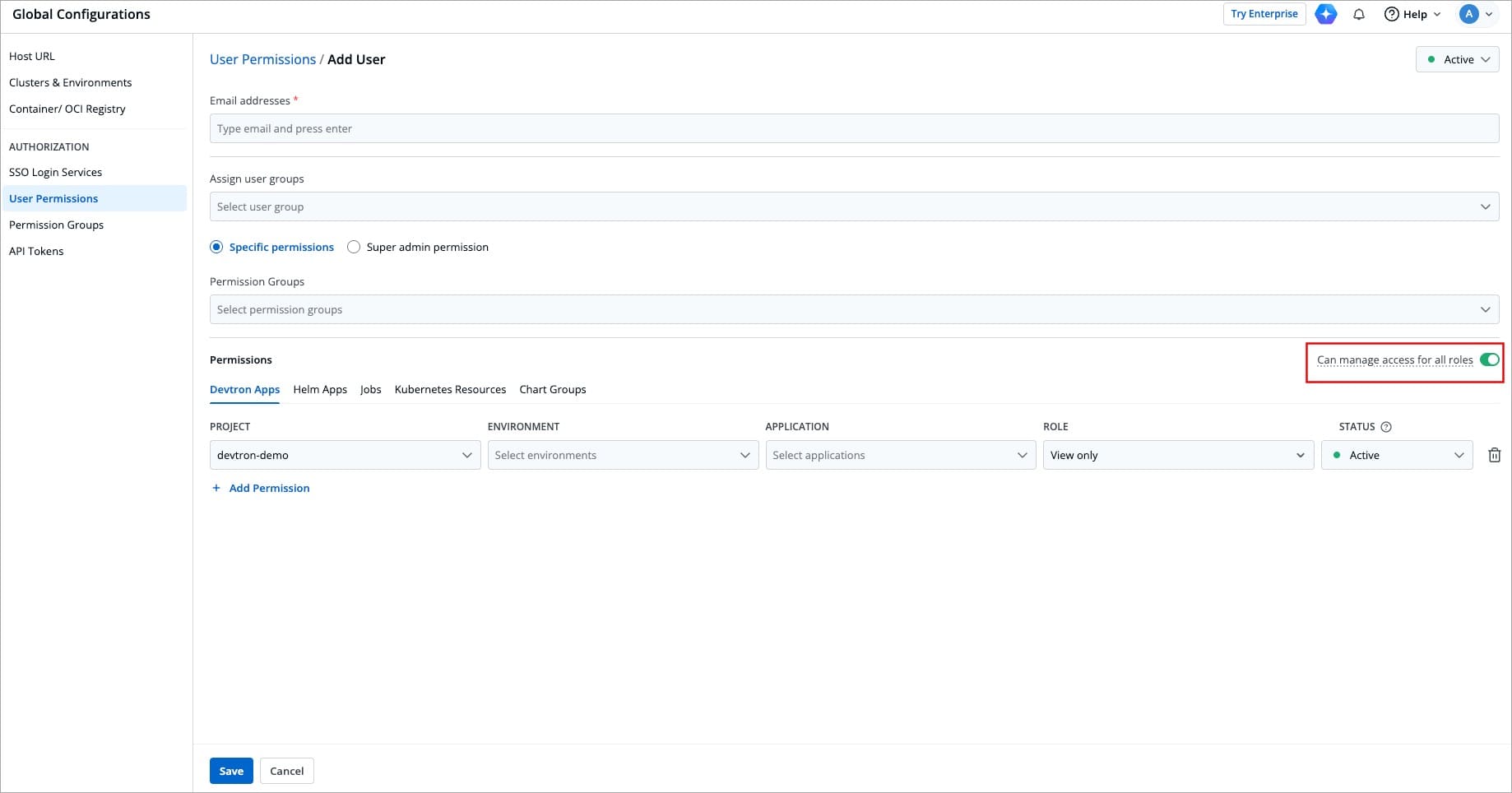
Figure 15: 'Can manage access for all roles' Toggle
By enabling the **Can manage access for all roles** toggle, you can grant a user the permission to manage access for all roles across Devtron apps, Helm Apps, Jobs, Kubernetes Resources, and Chart Groups. However, they cannot create new users.
@@ -321,7 +321,7 @@ Only [Super-Admins](#grant-super-admin-permission) can grant an **Access Manager
:::
-
+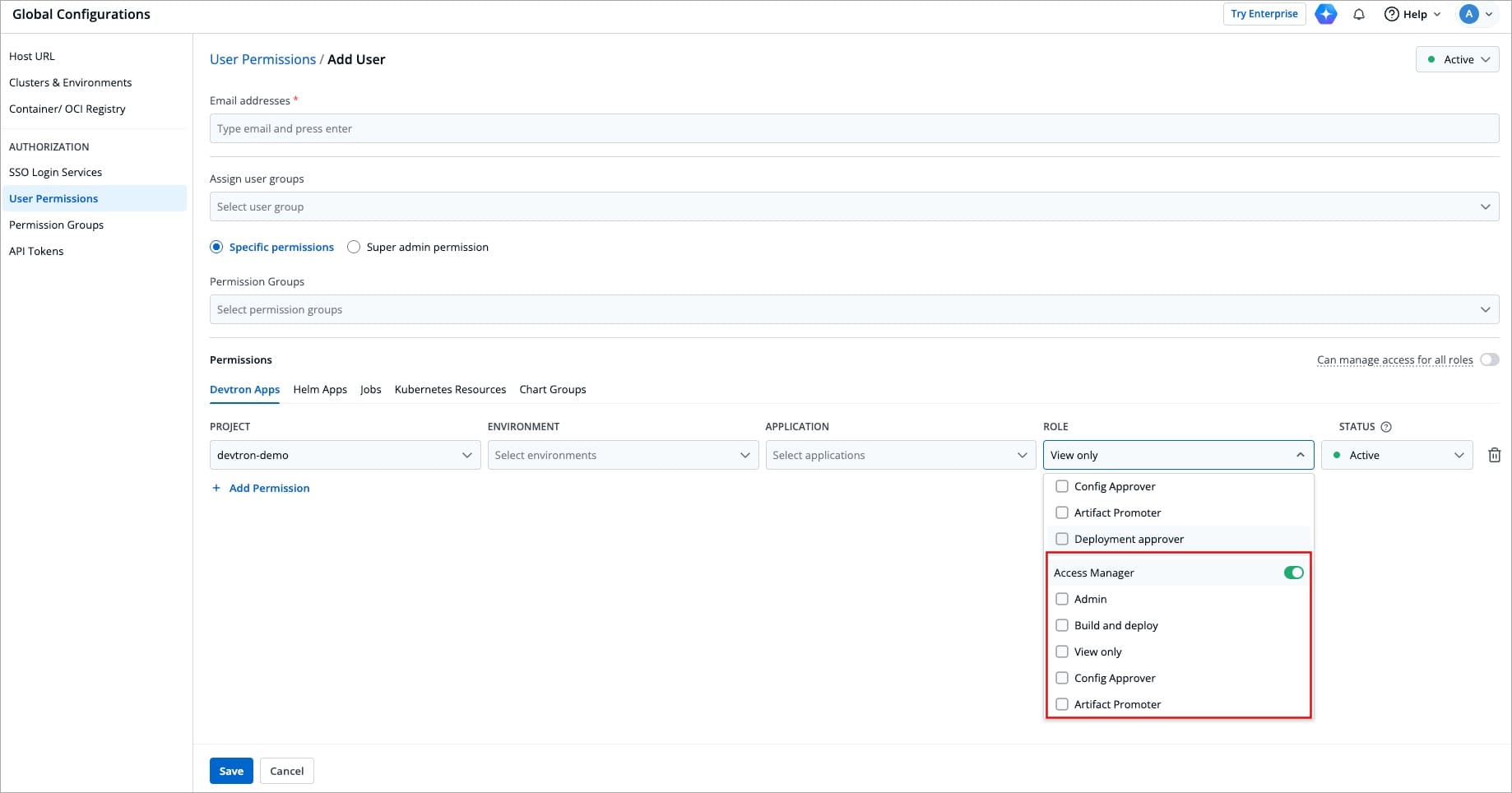
Figure 16: Access Manager
Enabling **Access Manager** for a user allows that user to further grant or change permissions of existing users.
@@ -388,7 +388,7 @@ The following permissions are currently available in the Access Manager role:
When working with multiple collaborators in Devtron, you may need to deactivate users who no longer require access and reactivate them when needed. This applies to users of Devtron Apps, Helm Apps, Jobs, and Kubernetes Resources.
-
+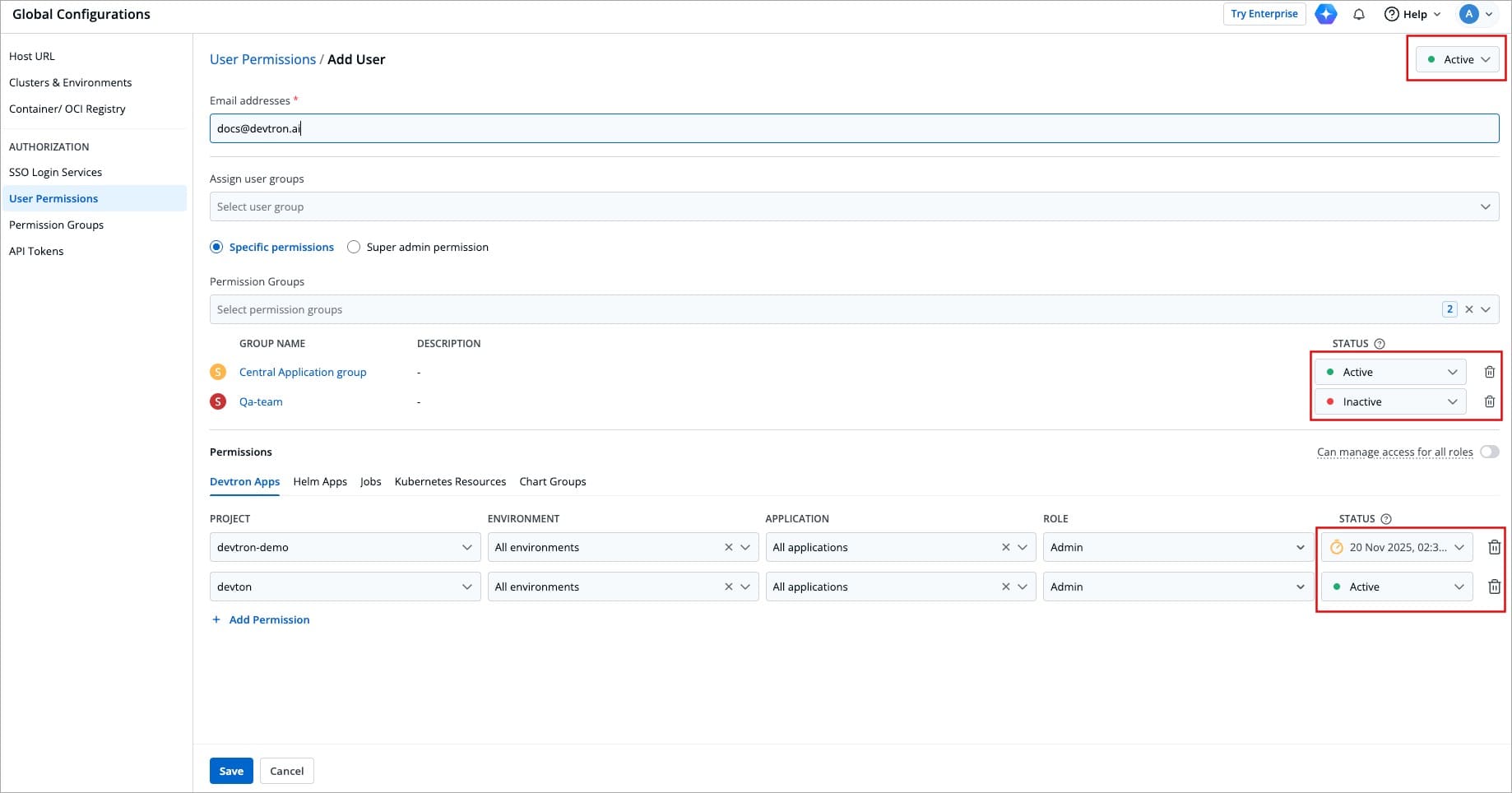
Figure 17: Active/Inactive Options
You can manage a user's active status at three levels:
@@ -399,7 +399,7 @@ You can manage a user's active status at three levels:
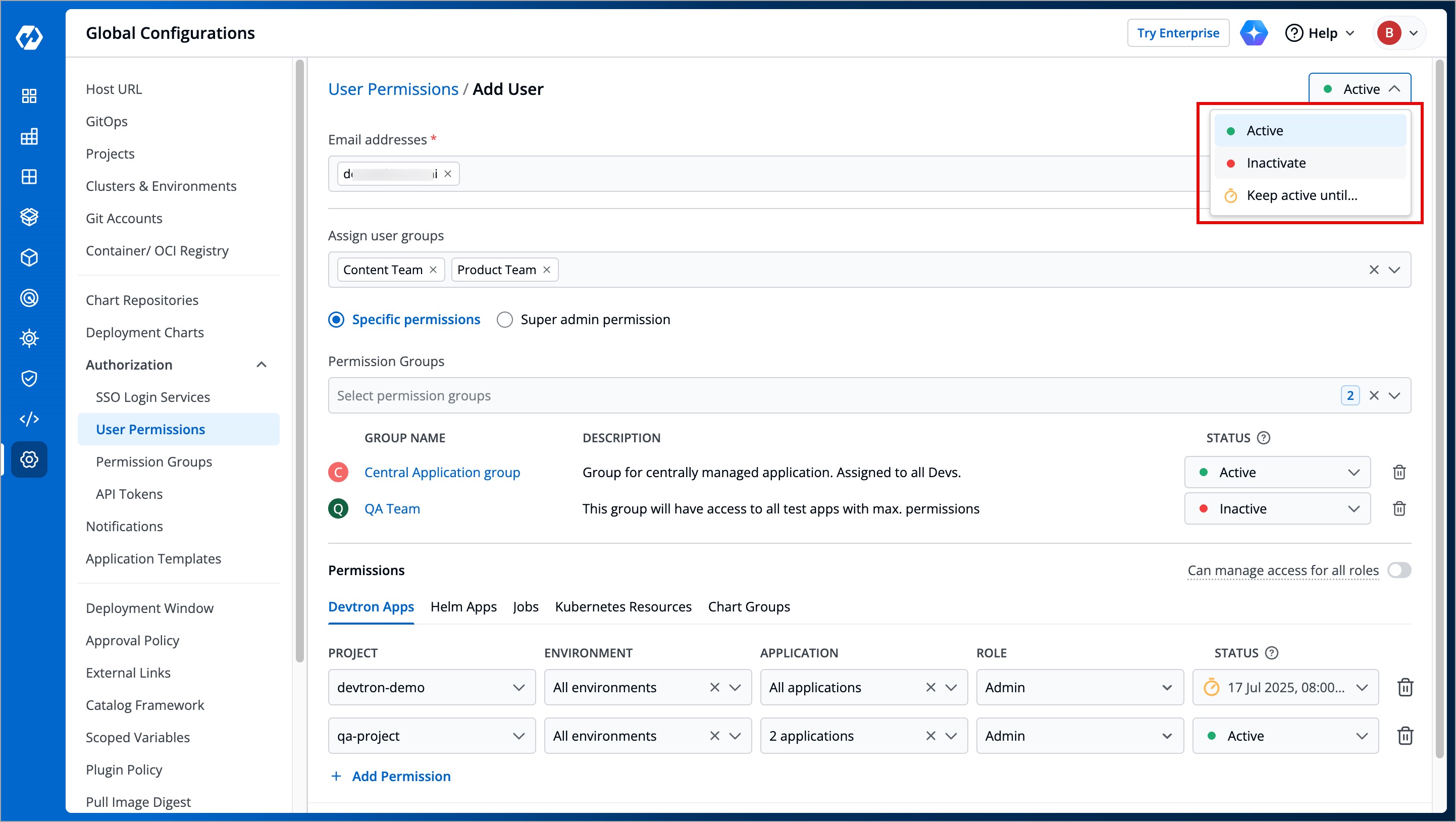
### At User level
-
+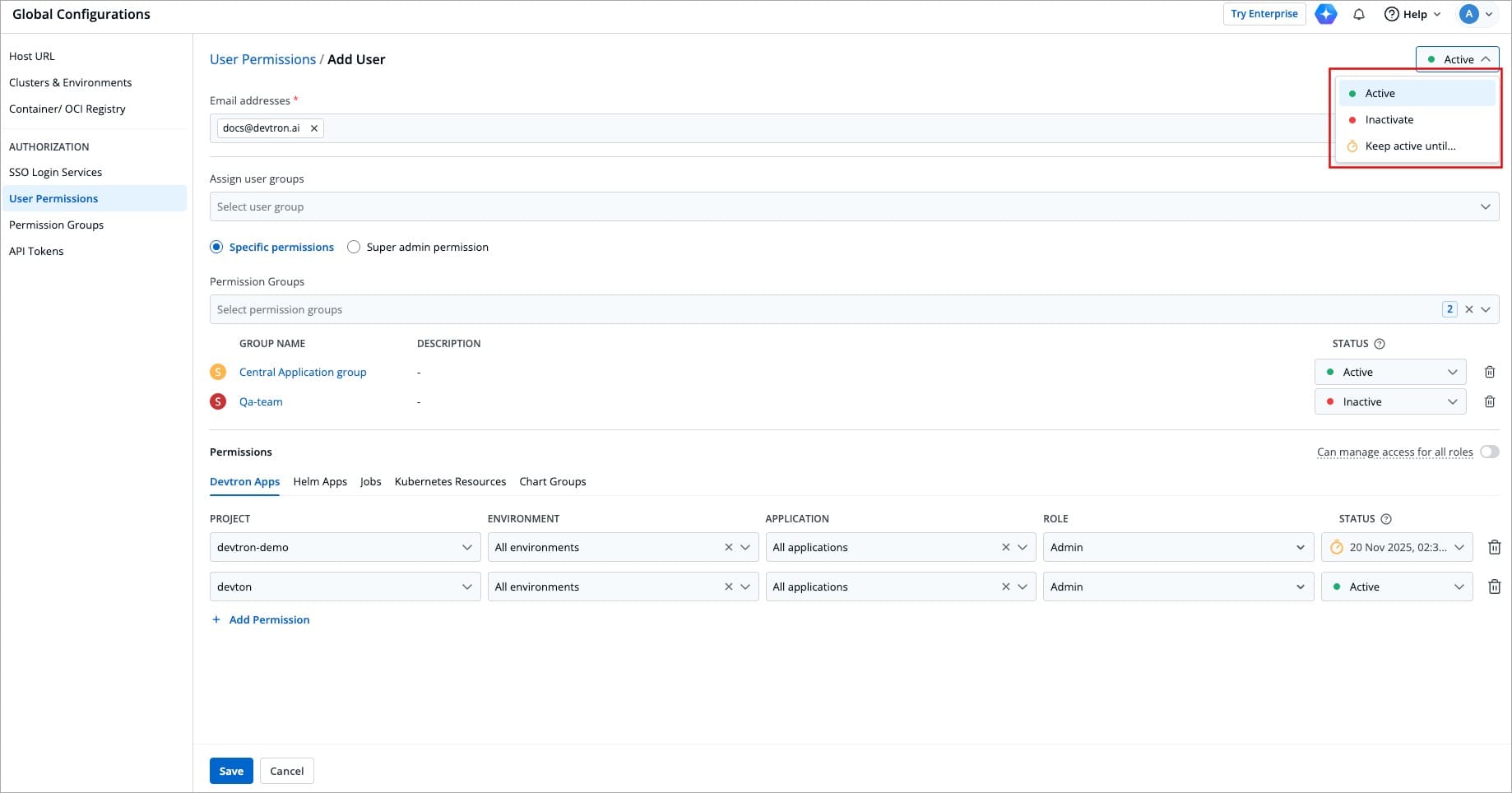
Figure 18: Active/Inactive User
* **Active/Activate** - Use this option to activate a deactivated user while retaining their previous roles and permissions.
@@ -408,7 +408,7 @@ You can manage a user's active status at three levels:
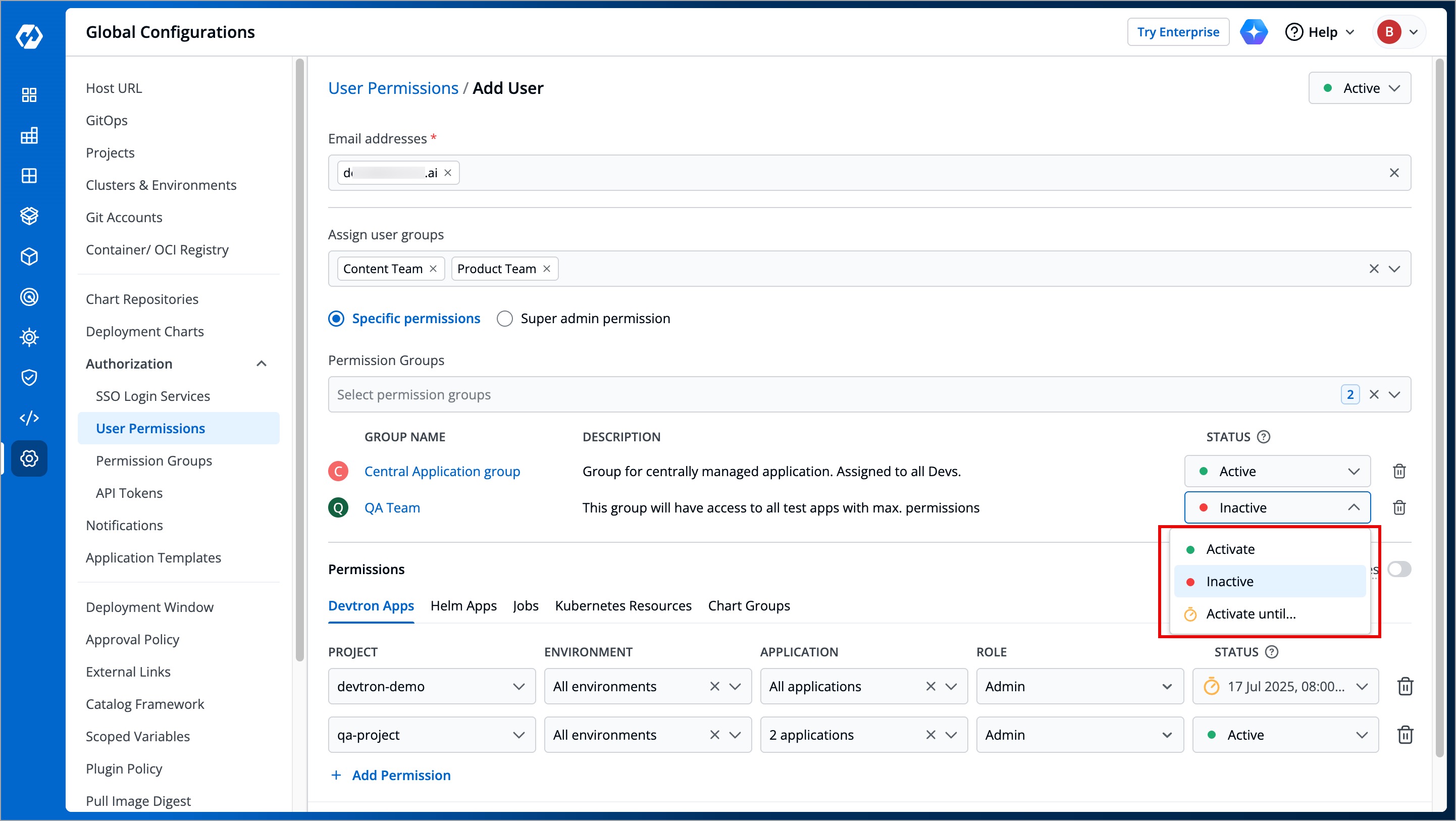
### At Permission Group level
-
+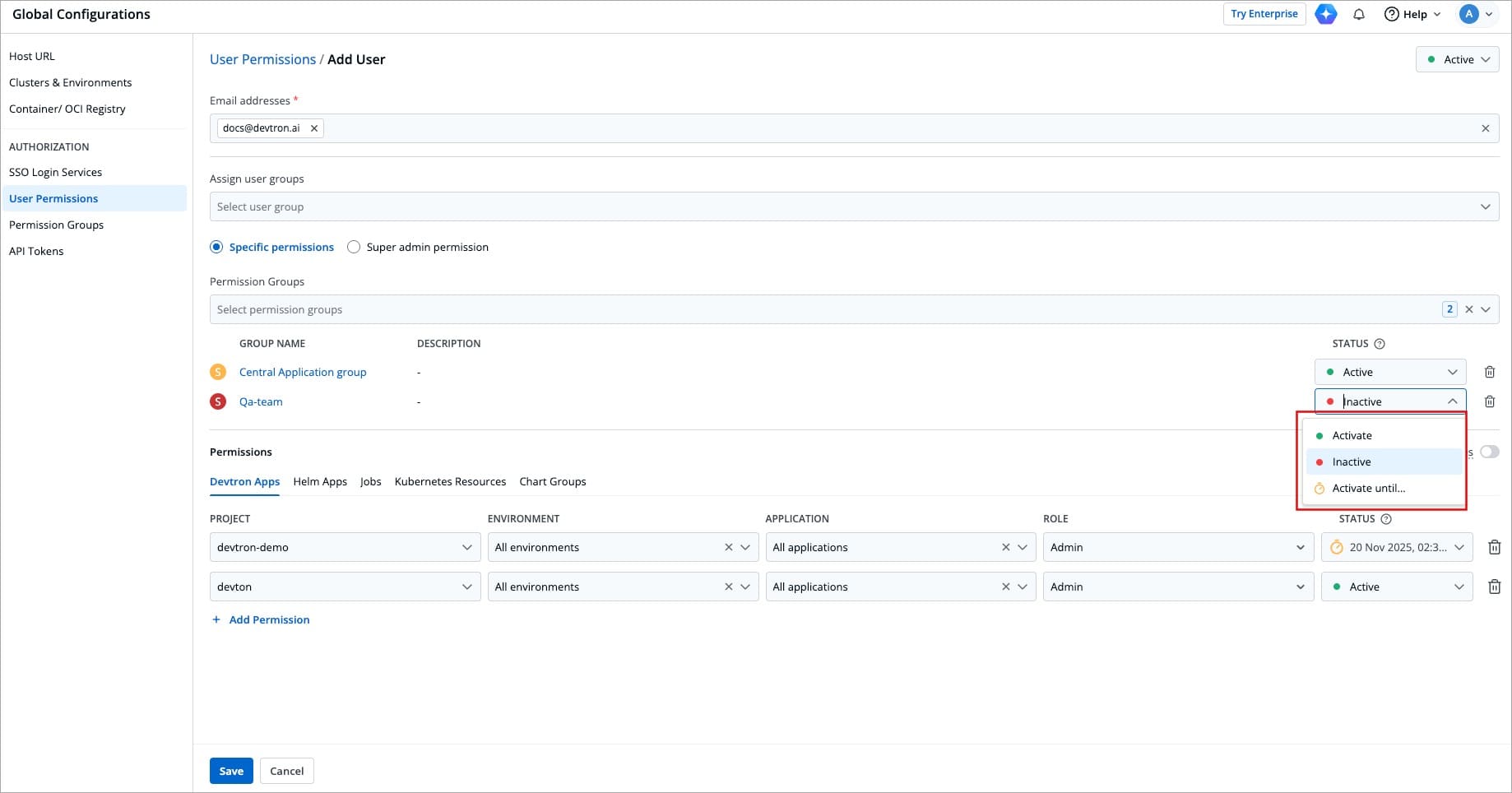
Figure 19: Active/Inactive User from Permission Group
* **Active/Activate** - Use this option to allow permissions from the group to take effect for the user.
@@ -417,7 +417,7 @@ You can manage a user's active status at three levels:
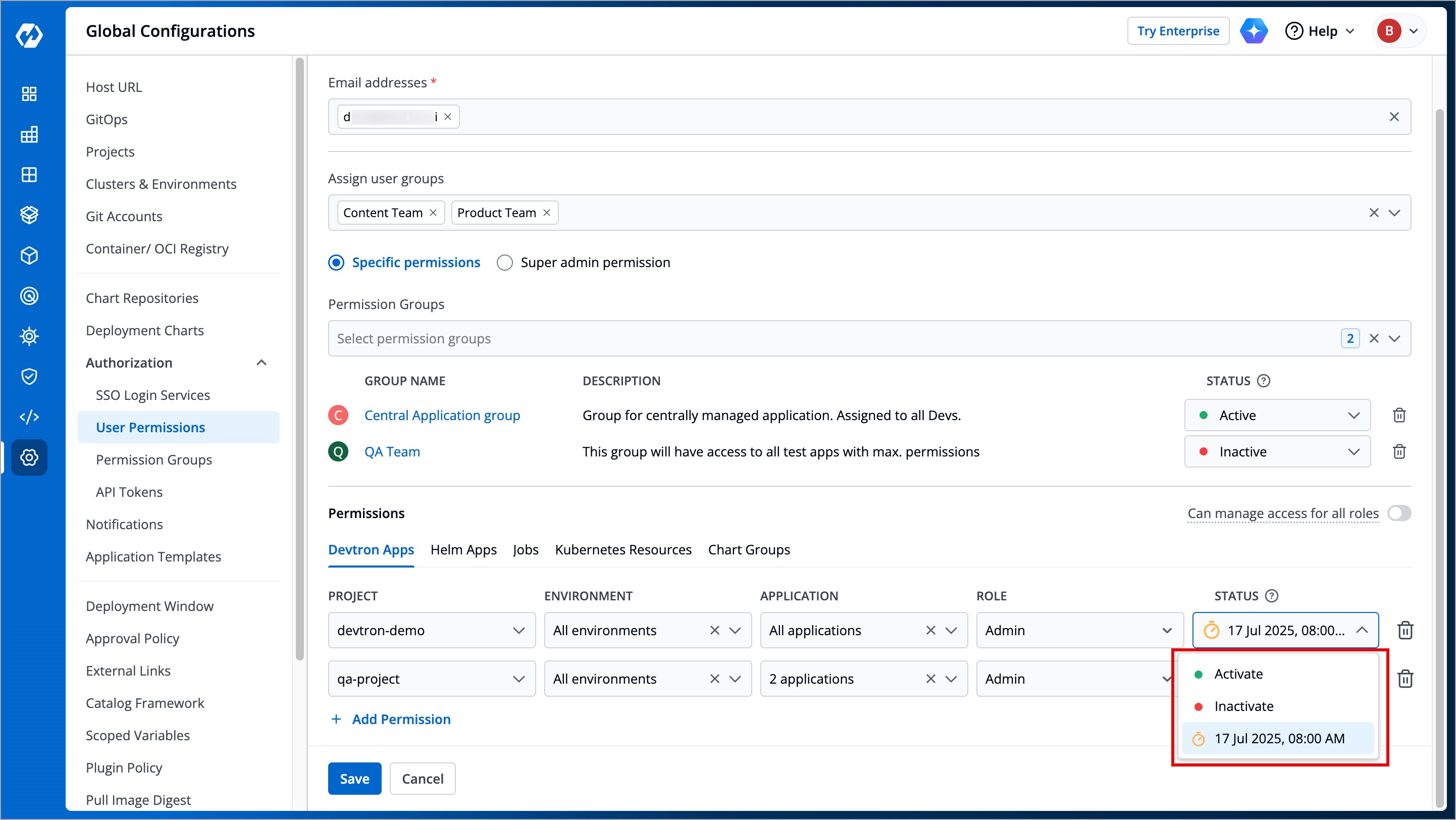
### At Direct Permissions level
-
+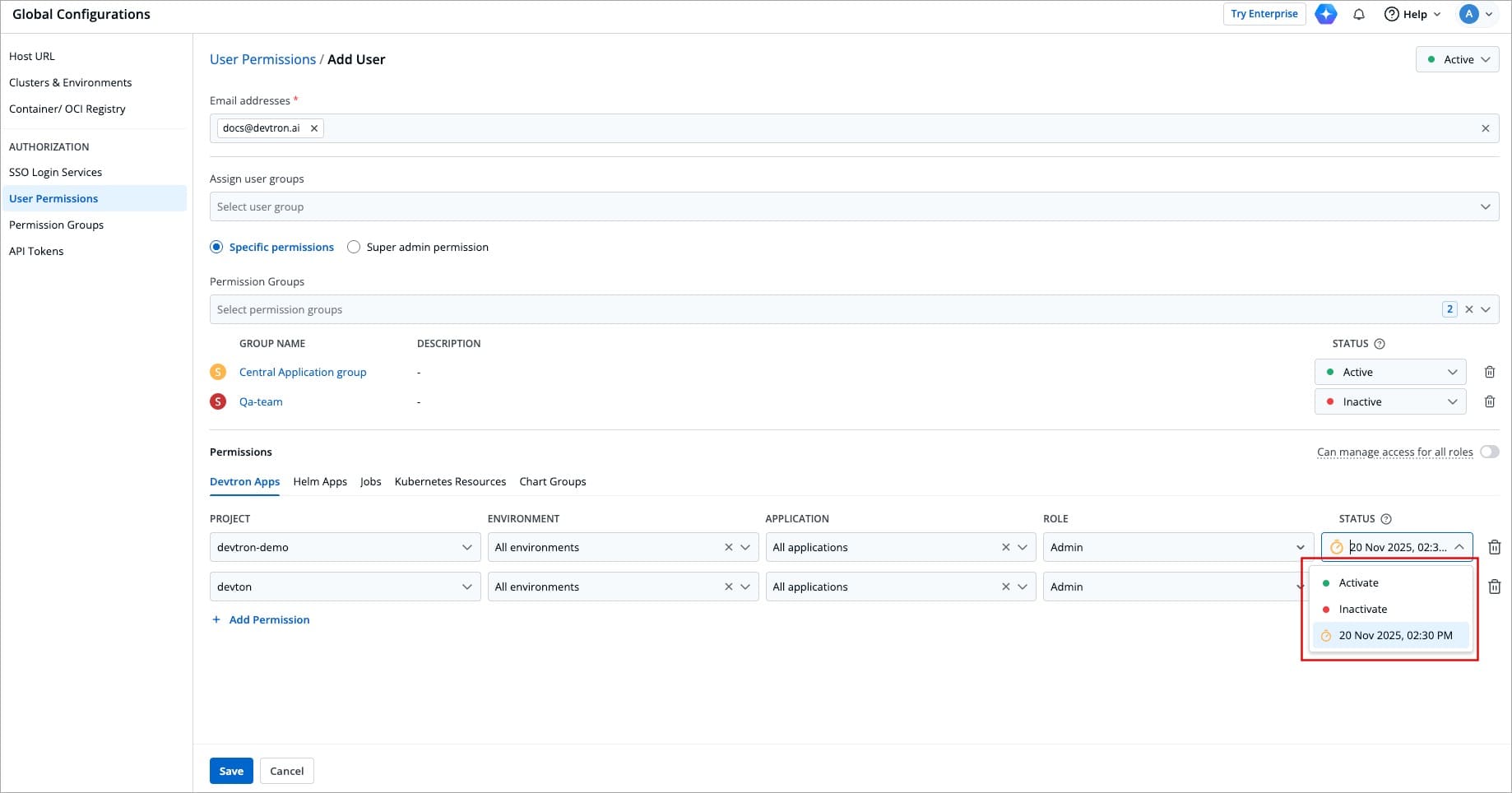
Figure 20: Active/Inactive User for Project Access
* **Active/Activate** - Use this option to grant the project/resource access to the user.
@@ -439,7 +439,7 @@ Direct user permissions cannot be edited if you're using [LDAP](./sso/ldap.md)/[
You can edit the user permissions by clicking the edit icon. Click **Save** after editing the permissions.
-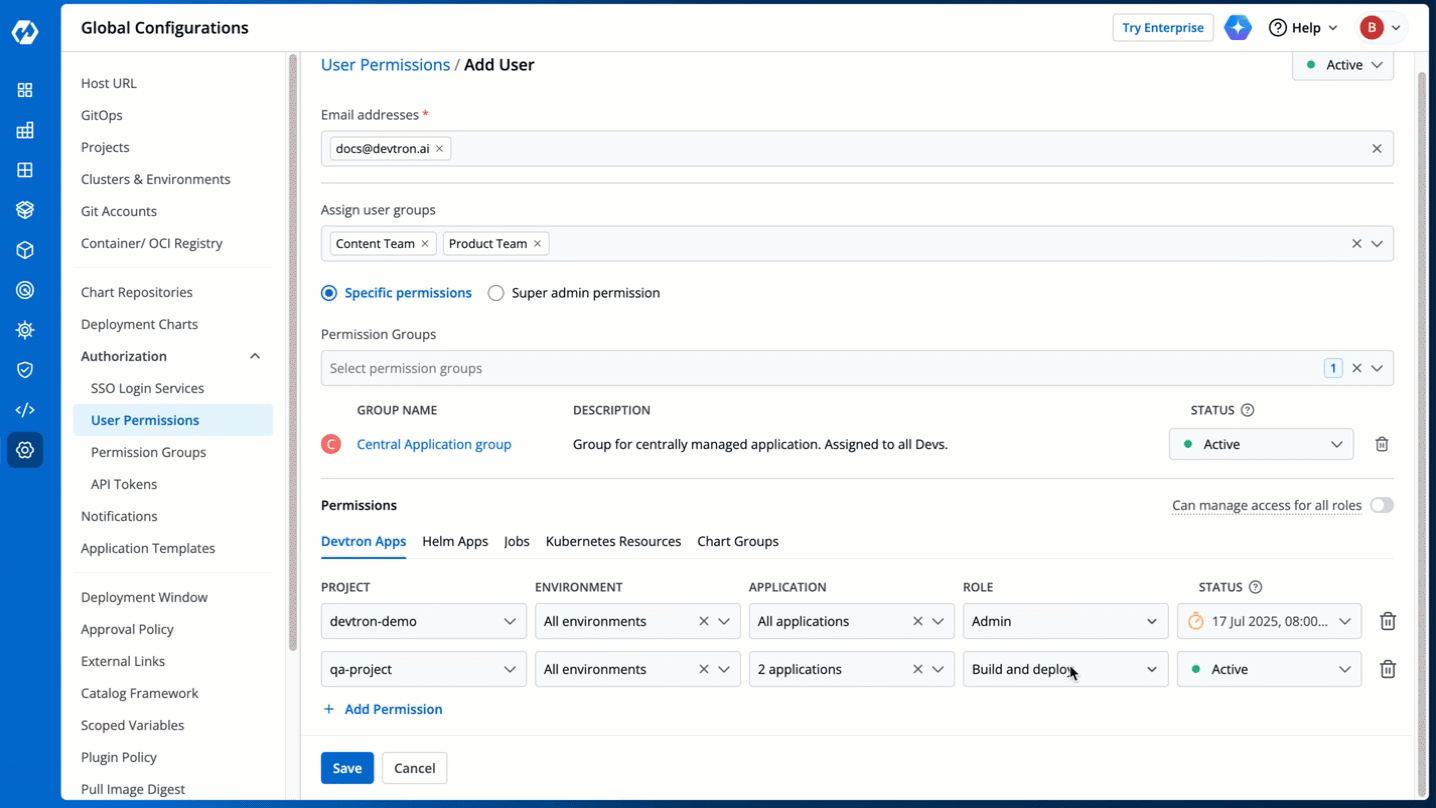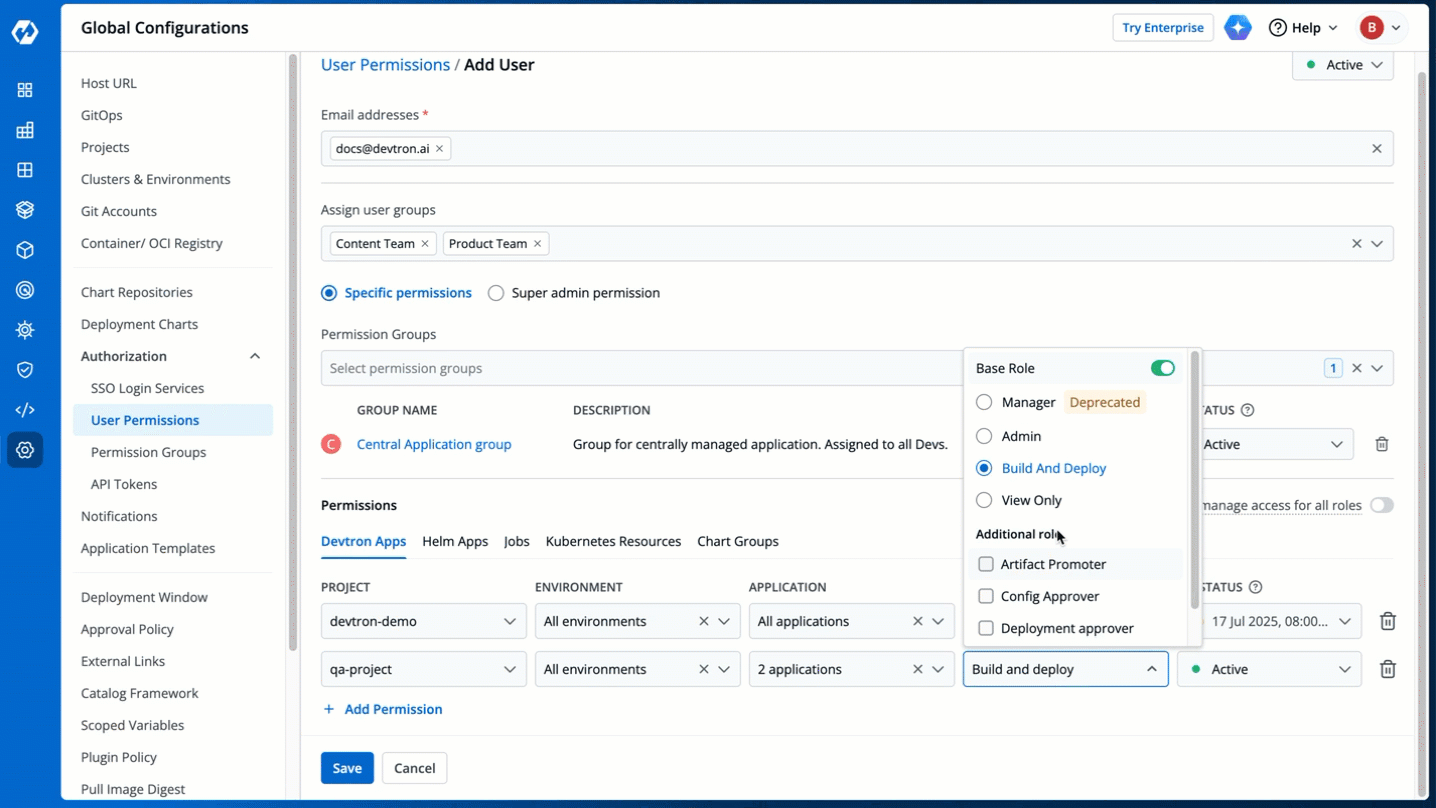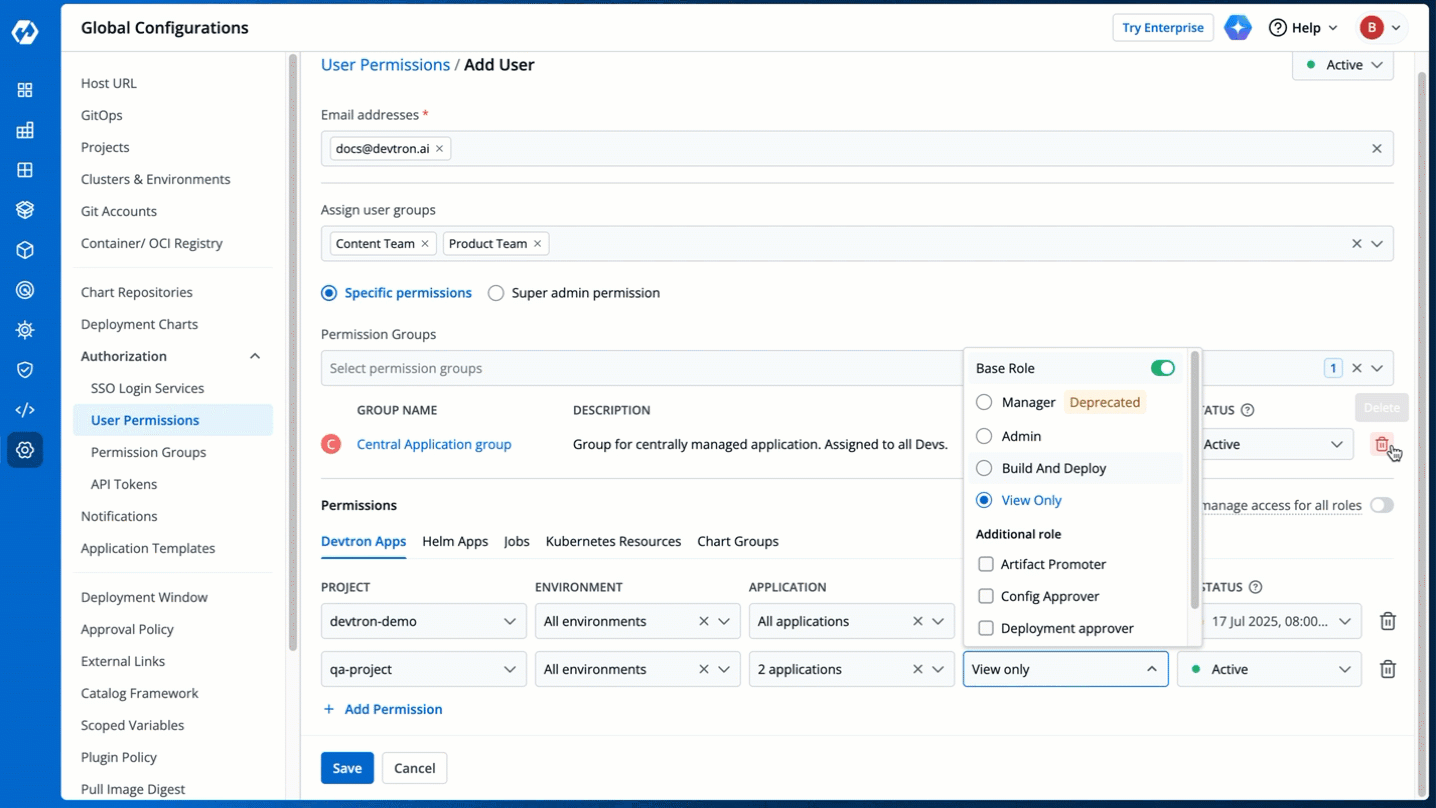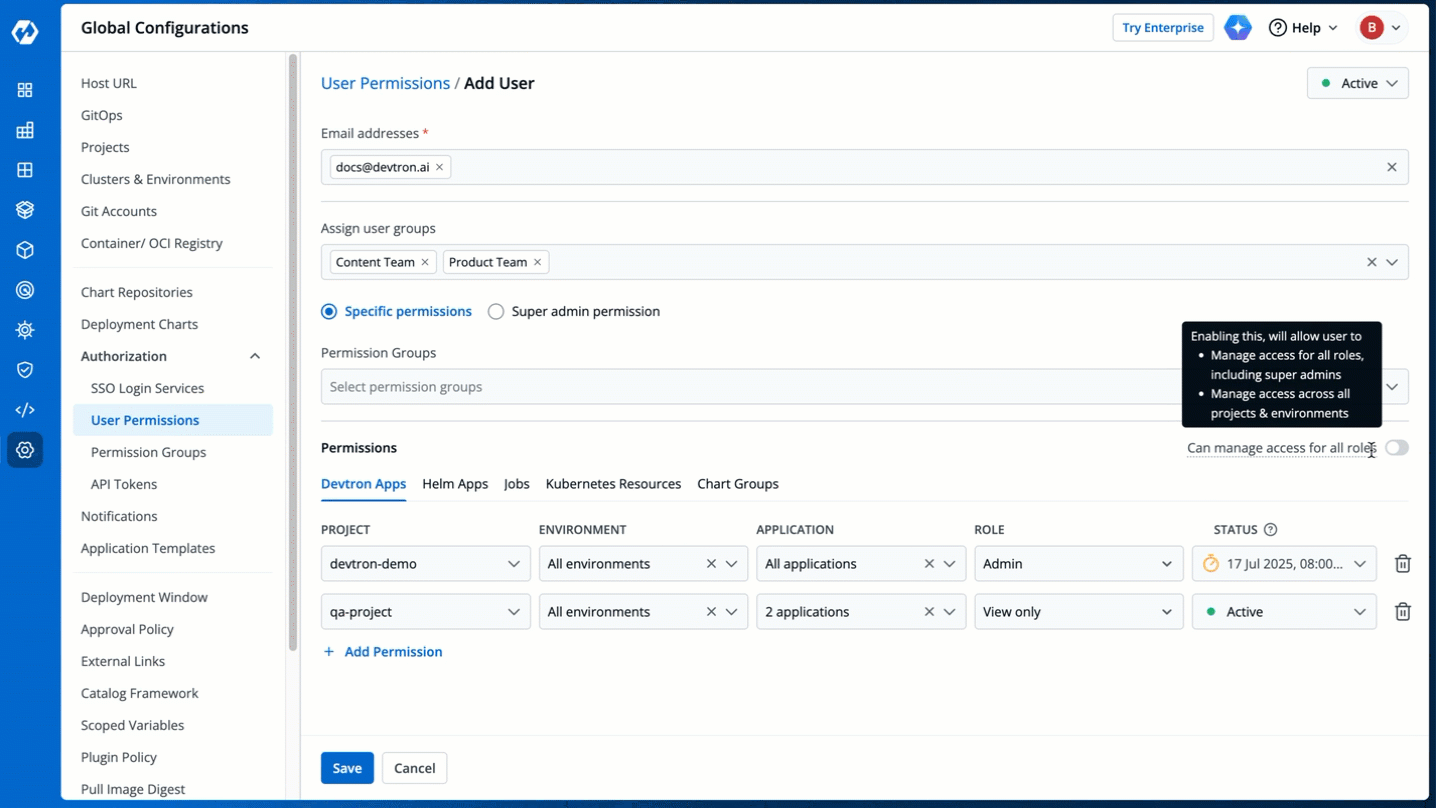
+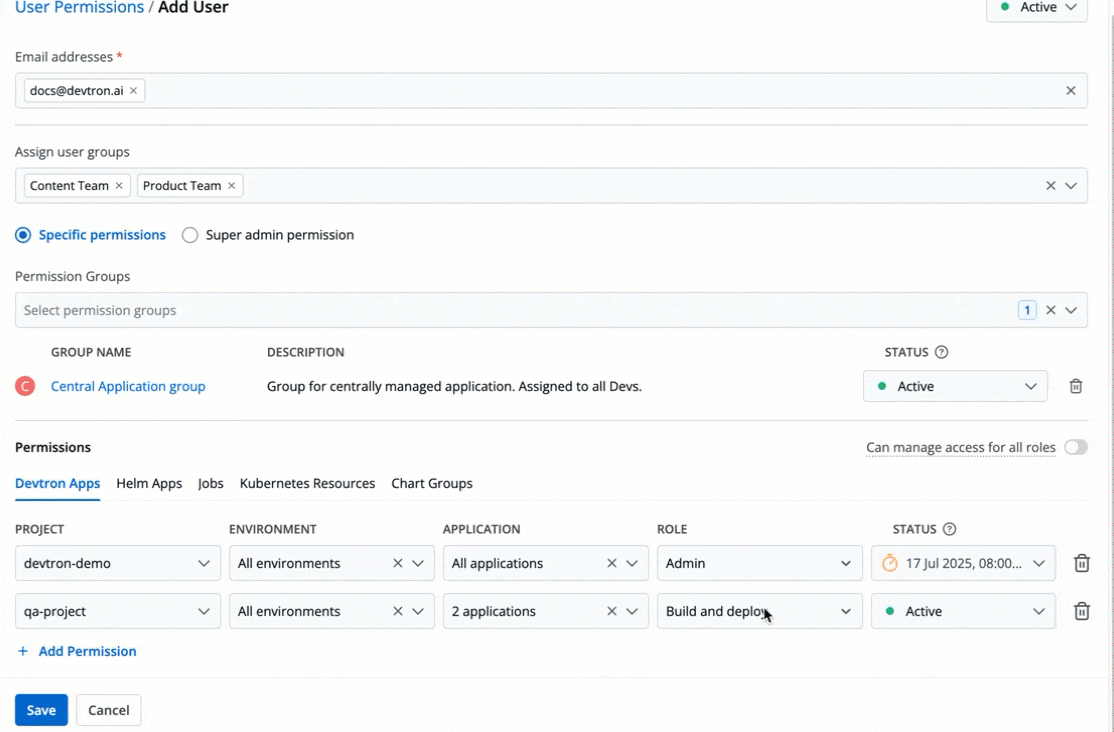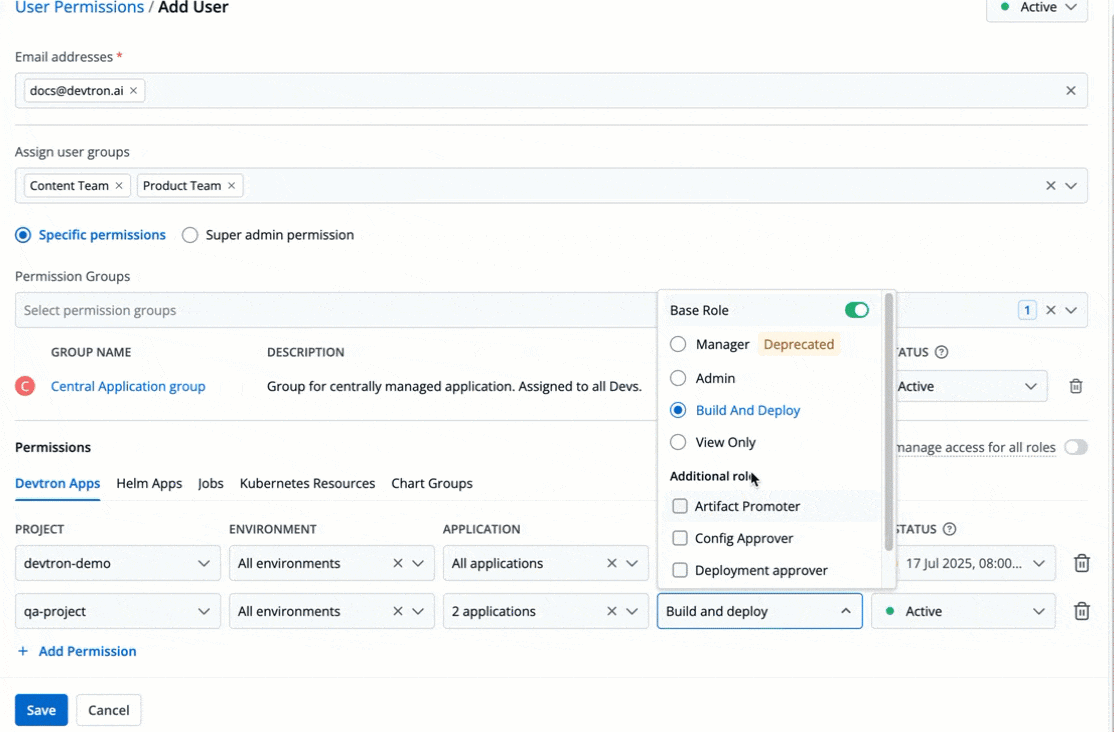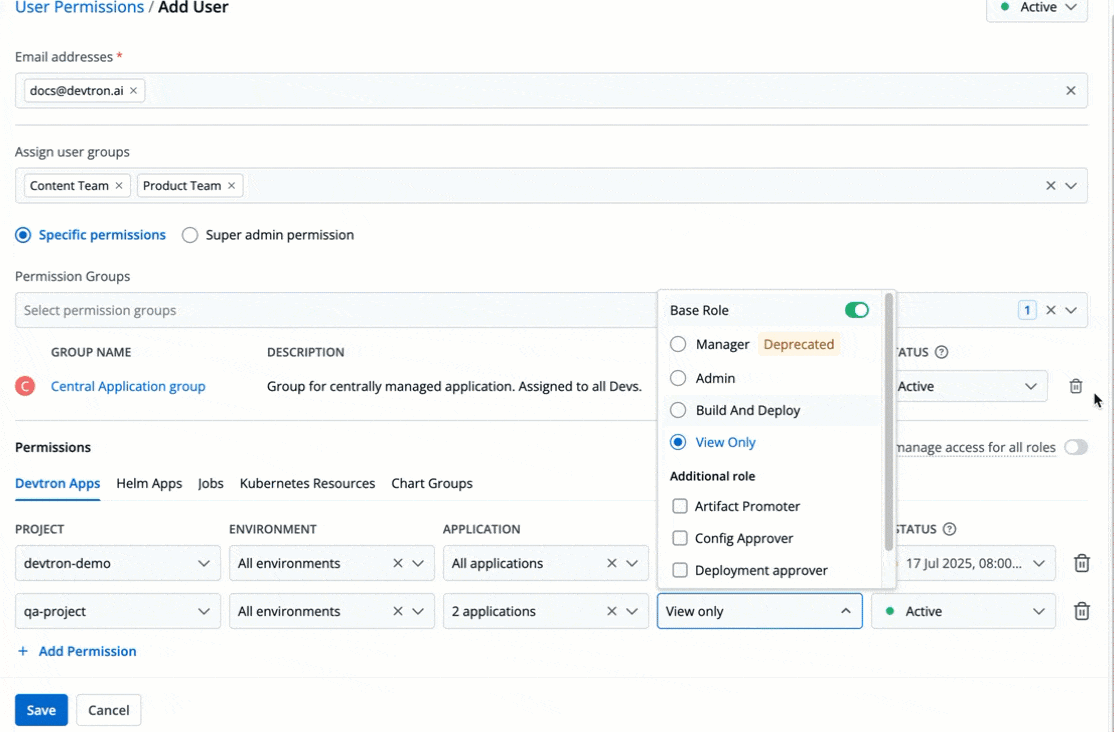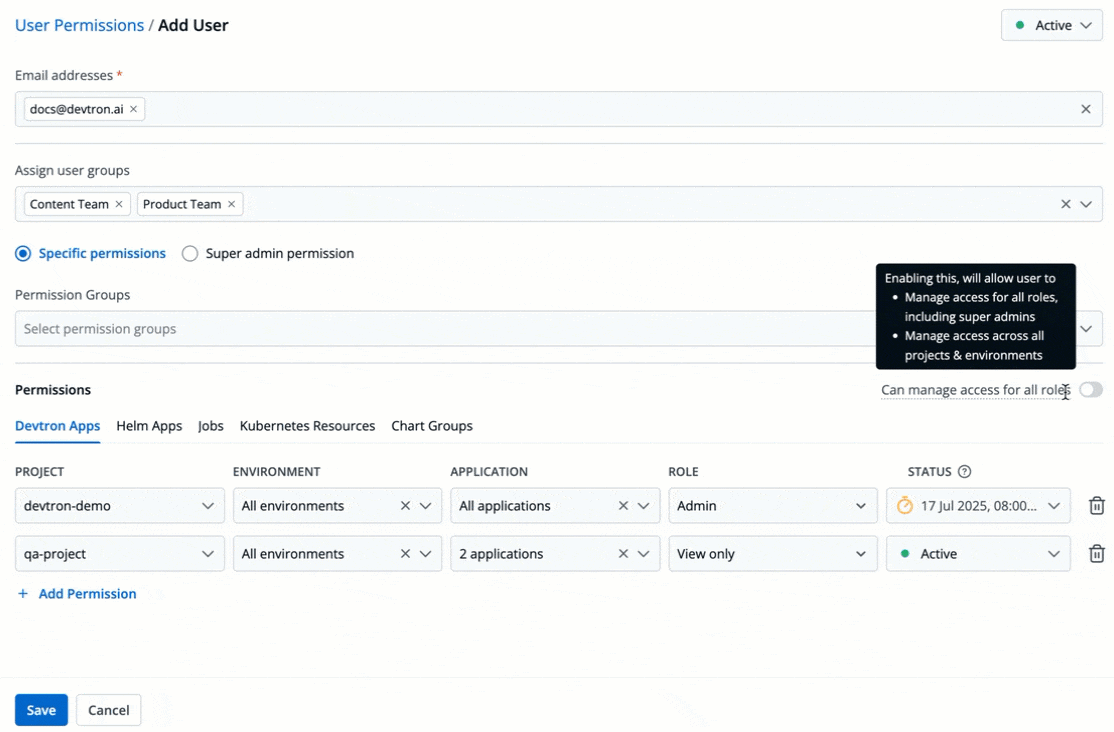
Figure 21: Editing User Permissions
---
@@ -455,7 +455,7 @@ You may download the user data of current users and deleted users in a CSV forma
* Role
* Timestamps for User Addition, Updation, and Deletion
-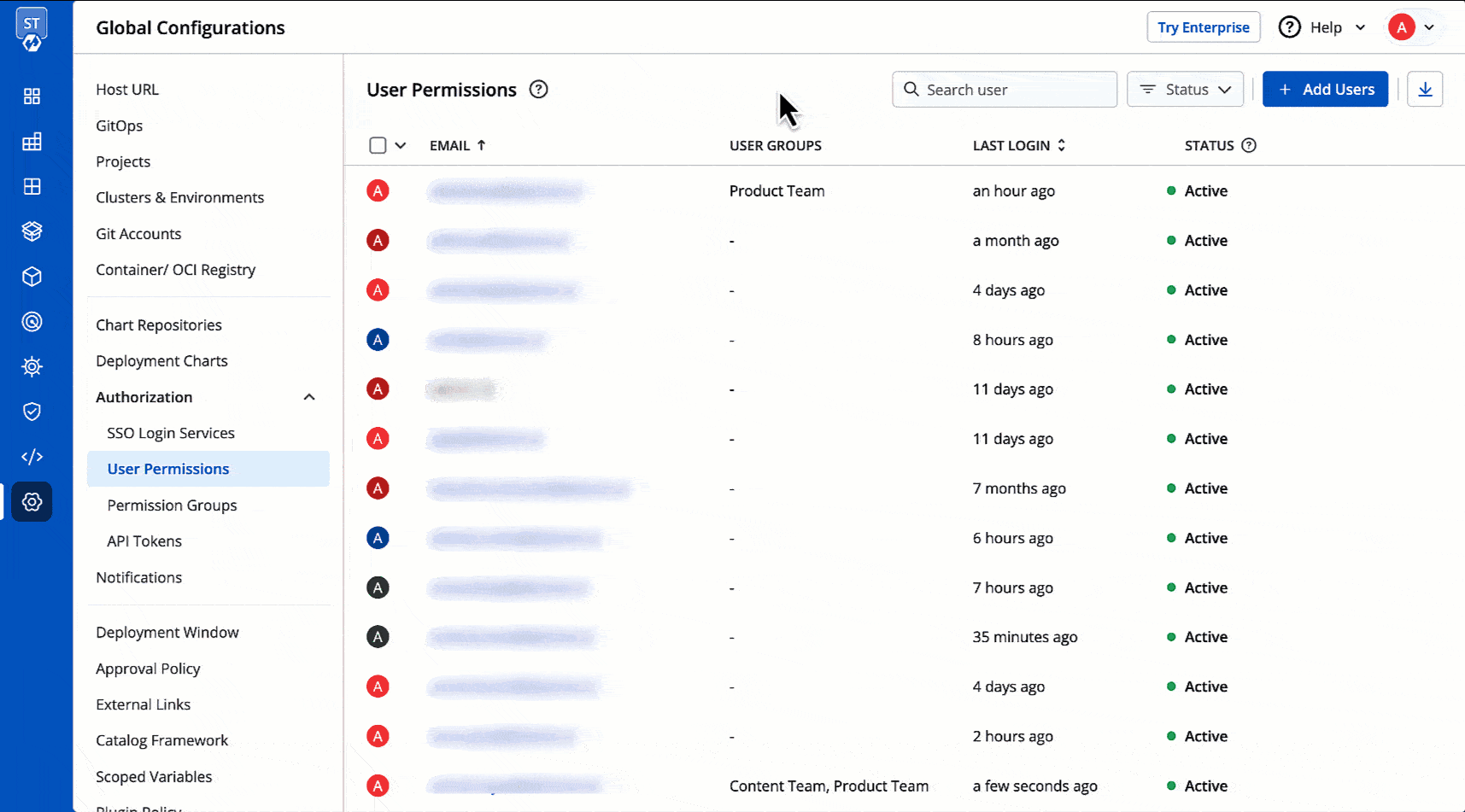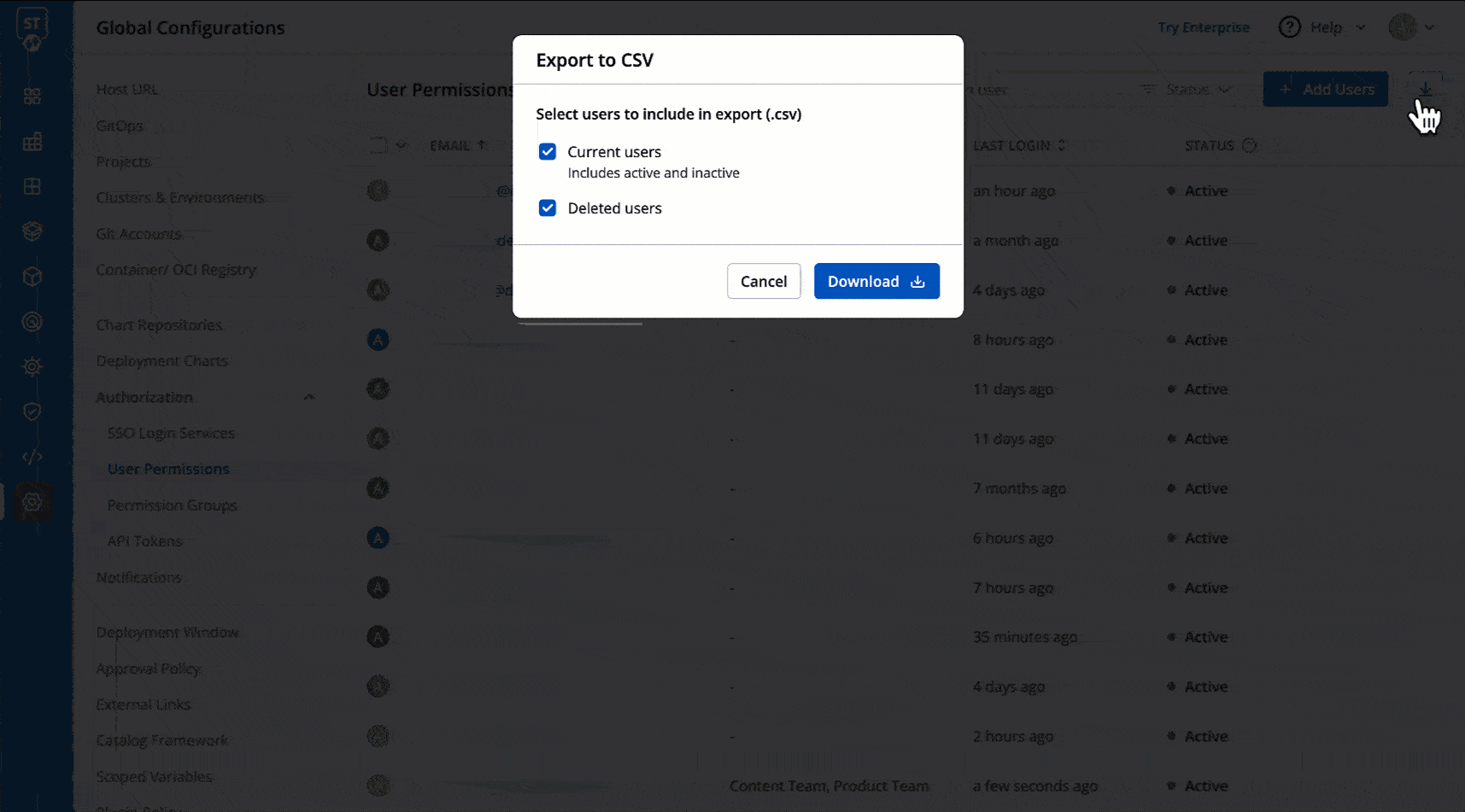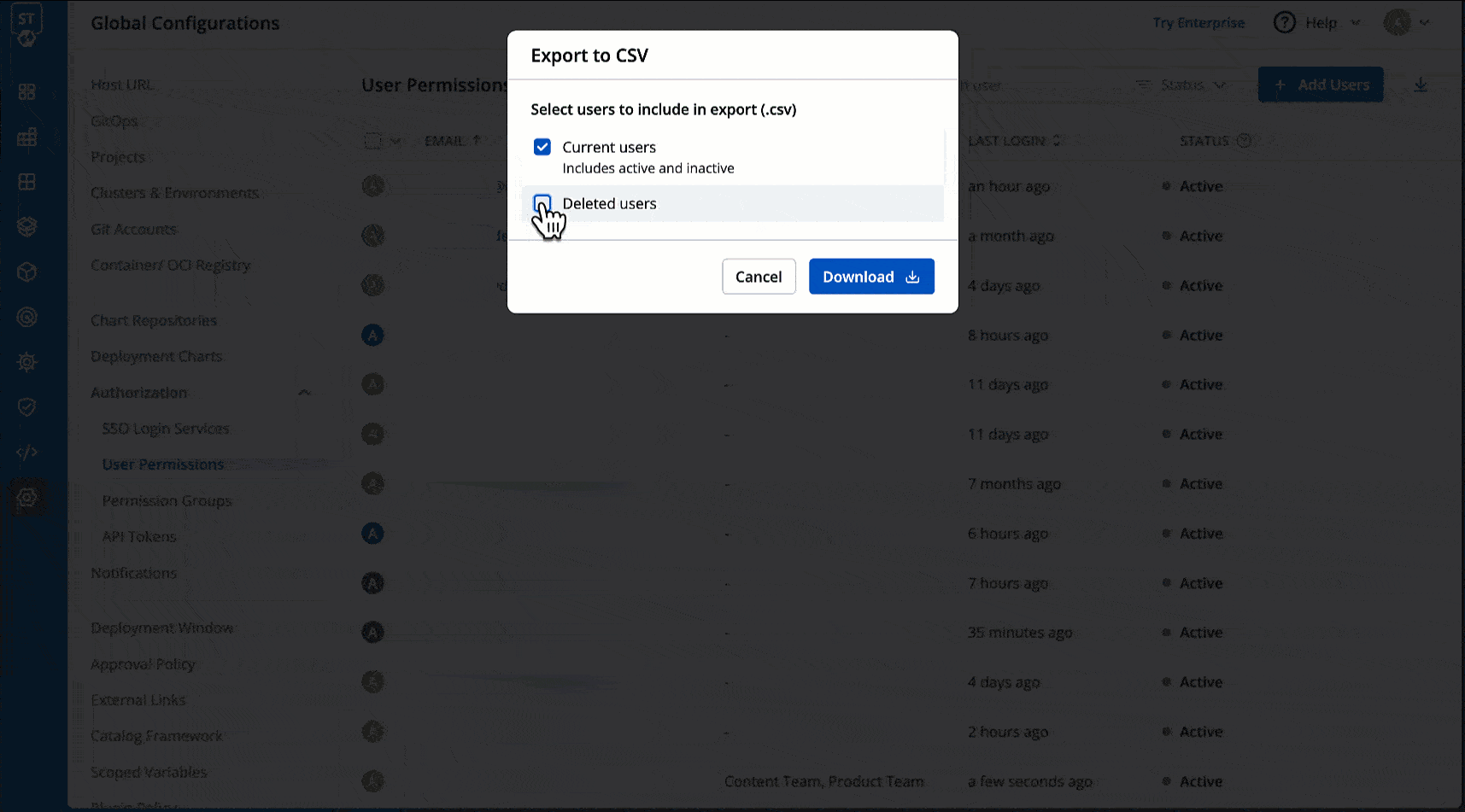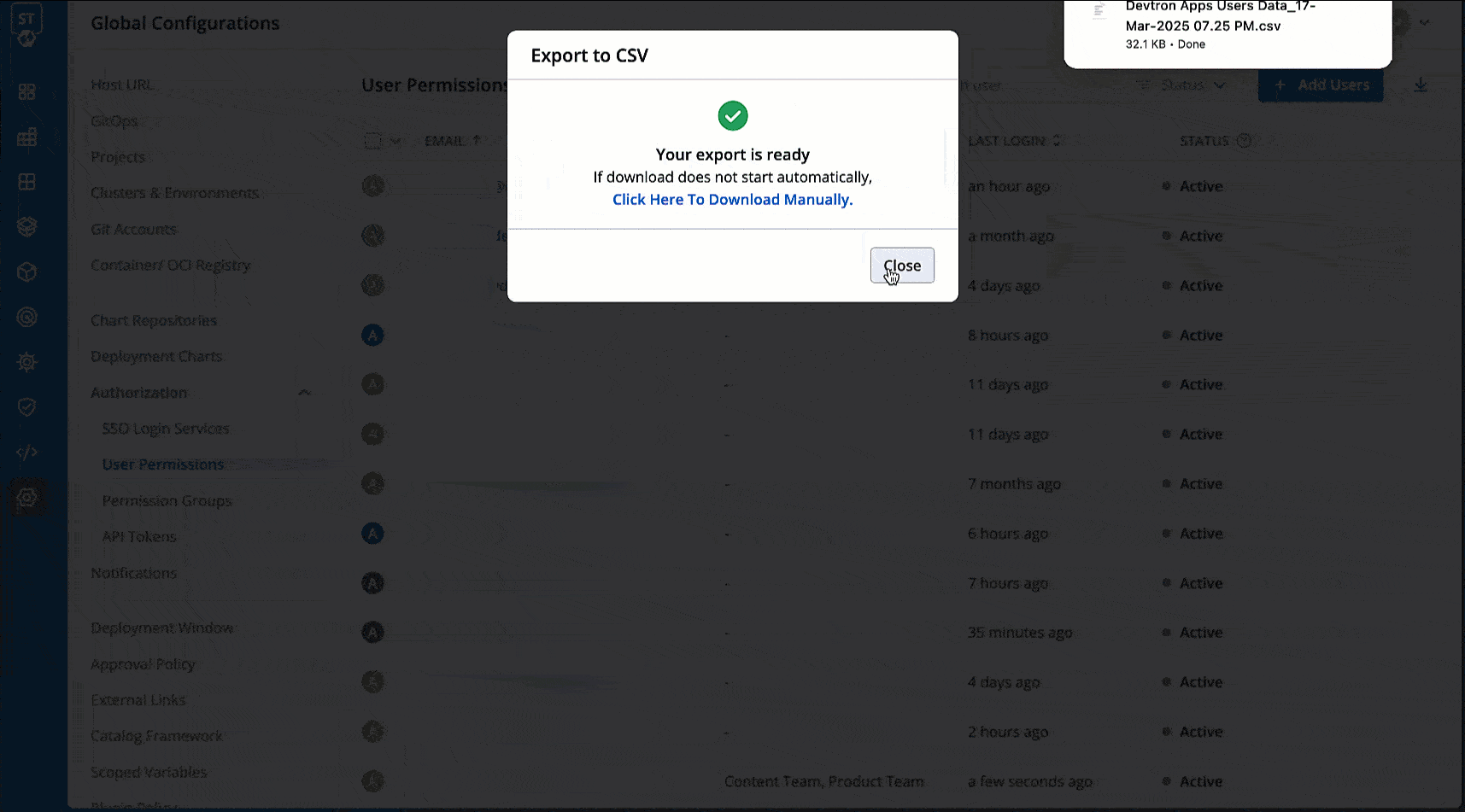
+
Figure 22: Exporting User Data
---
@@ -469,7 +469,7 @@ You may download the user data of current users and deleted users in a CSV forma
If you want to delete a user, click **Delete**.
-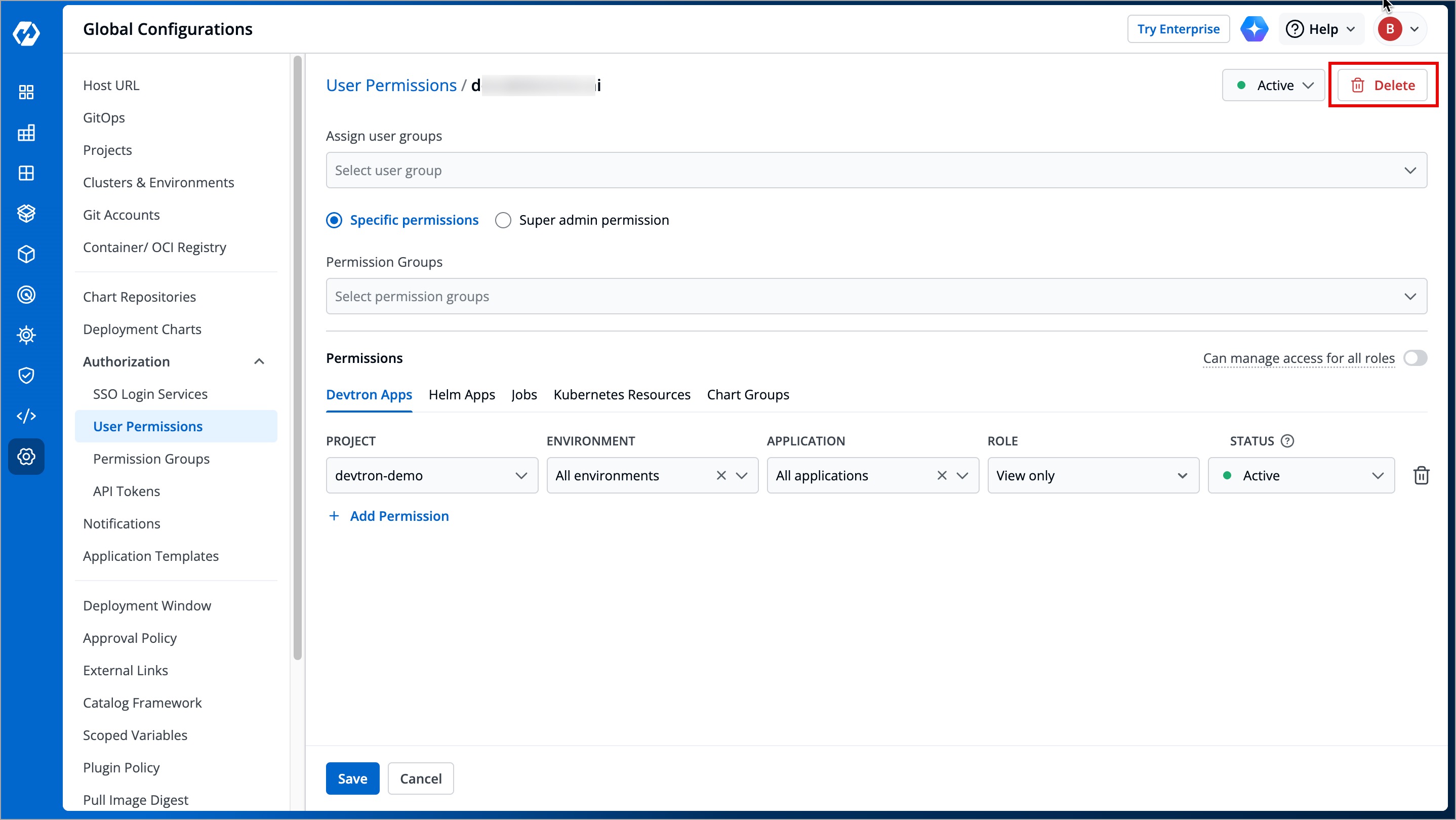
+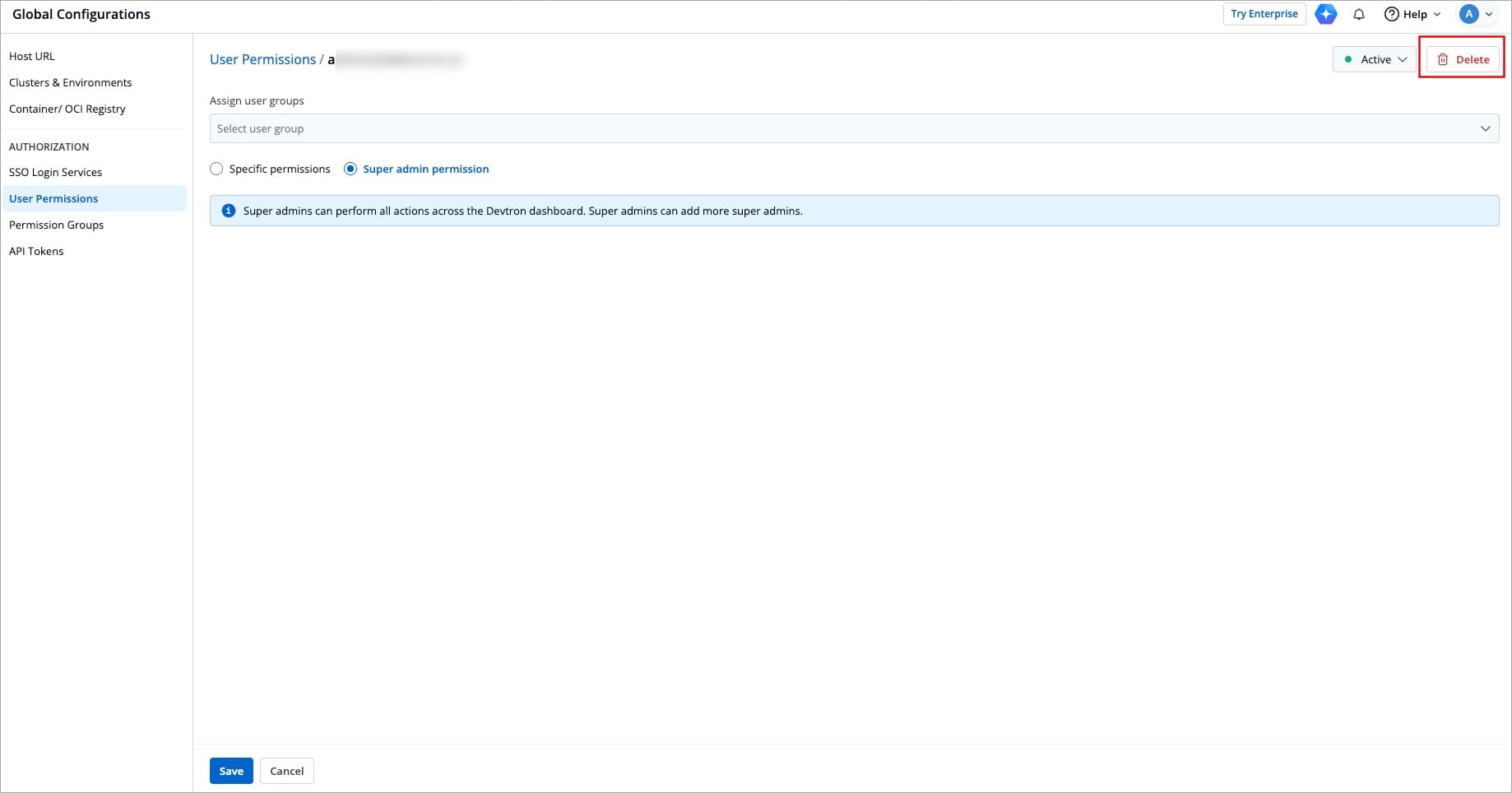
Figure 23: Deleting a User
This will remove the user from the system along with all the permissions granted earlier. The user will no longer be able to log in to Devtron unless added again.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/container-registries.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/container-registries.md
index 803e84444..4ce390f8a 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/container-registries.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/container-registries.md
@@ -14,12 +14,12 @@ You can configure a container registry using any registry provider of your choic
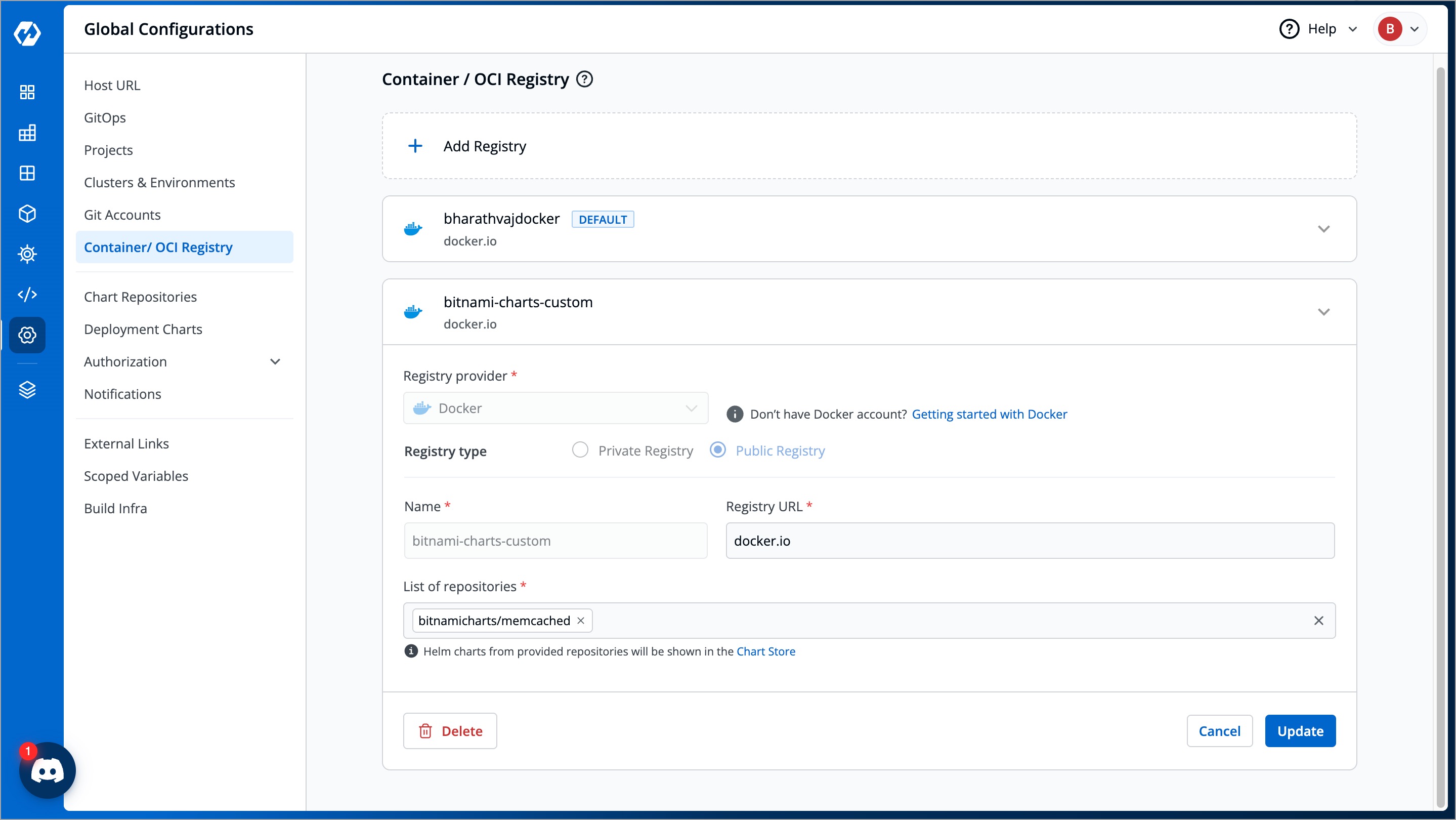
1. From the left sidebar, go to **Global Configurations** → **Container/OCI Registry**.
- 
+ 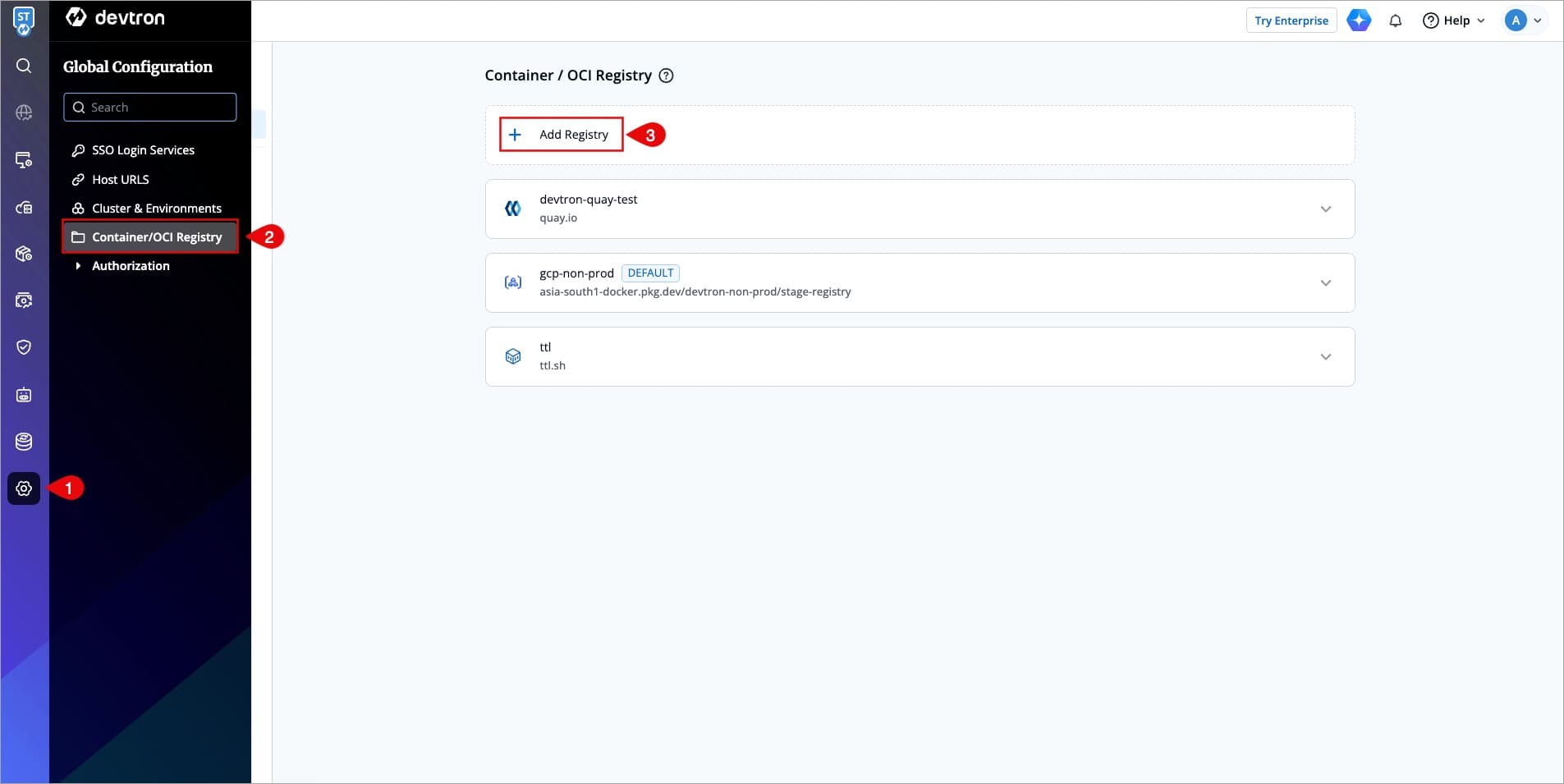
3. Choose a provider from the **Registry provider** dropdown. View the [Supported Registry Providers](#supported-registry-providers).
@@ -50,10 +50,10 @@ This is possible through [isolated clusters](../global-configurations/cluster-an
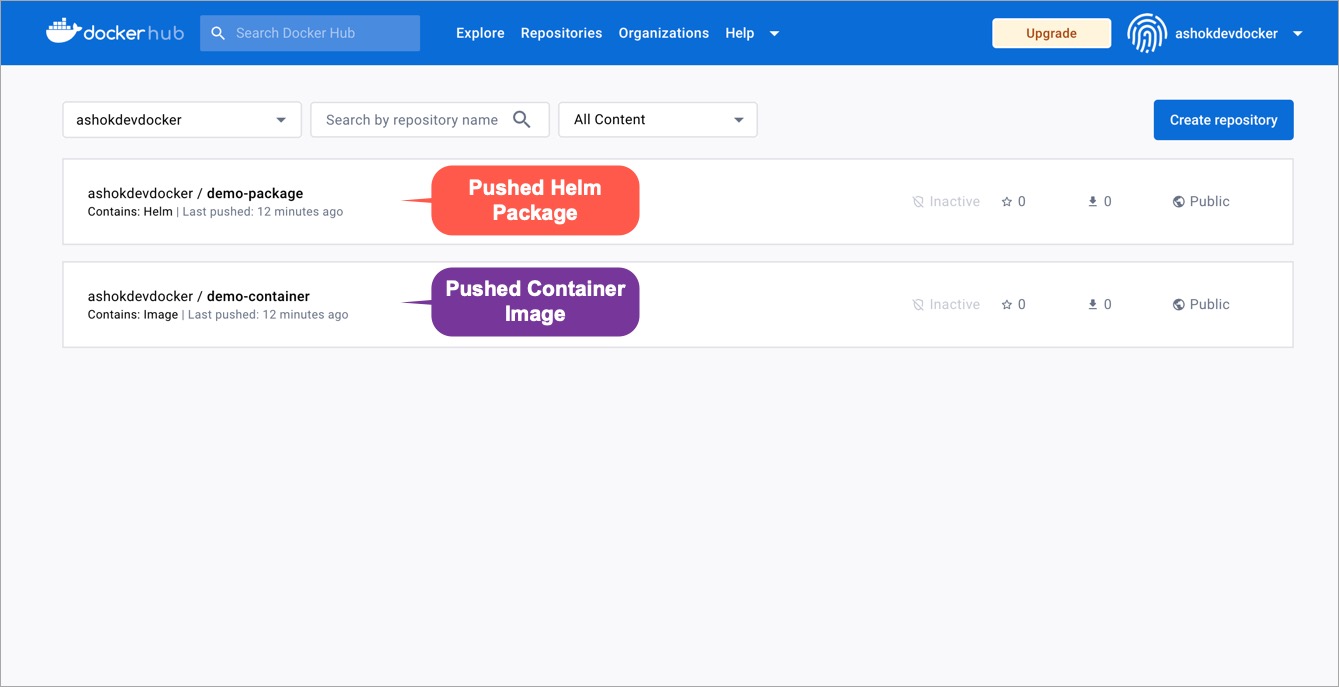
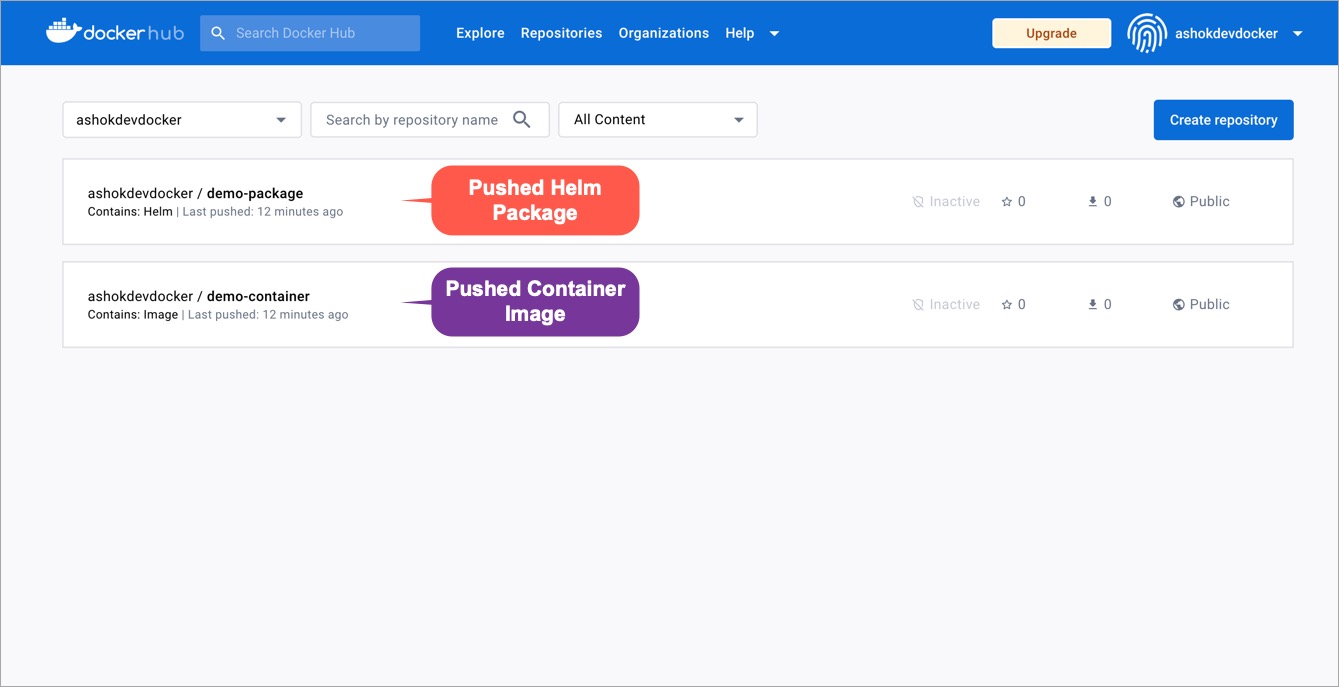
If you have [configured your CD pipeline](../creating-application/workflow/cd-pipeline.md) to push the helm package to your OCI registry, you can view the pushed helm package in your registry as shown below:
-
+
:::info Prerequisite
@@ -194,7 +194,7 @@ If you select **Use Registry Credentials**, the clusters will be auto-injected w
Click **Save**.
-
+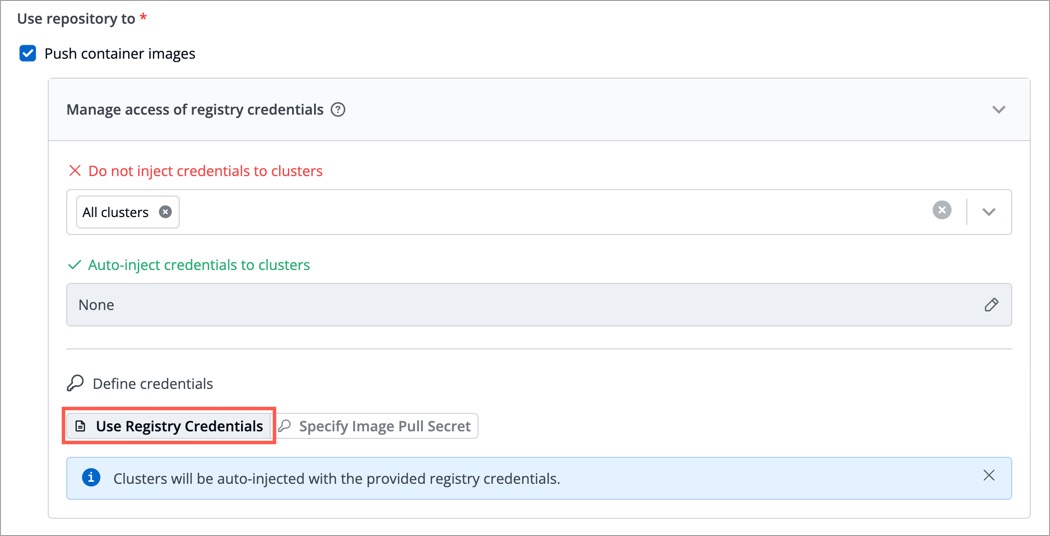
Figure 4: Using Registry Credentials
@@ -202,7 +202,7 @@ Click **Save**.
You can create a Secret by providing credentials on the command line.
-
+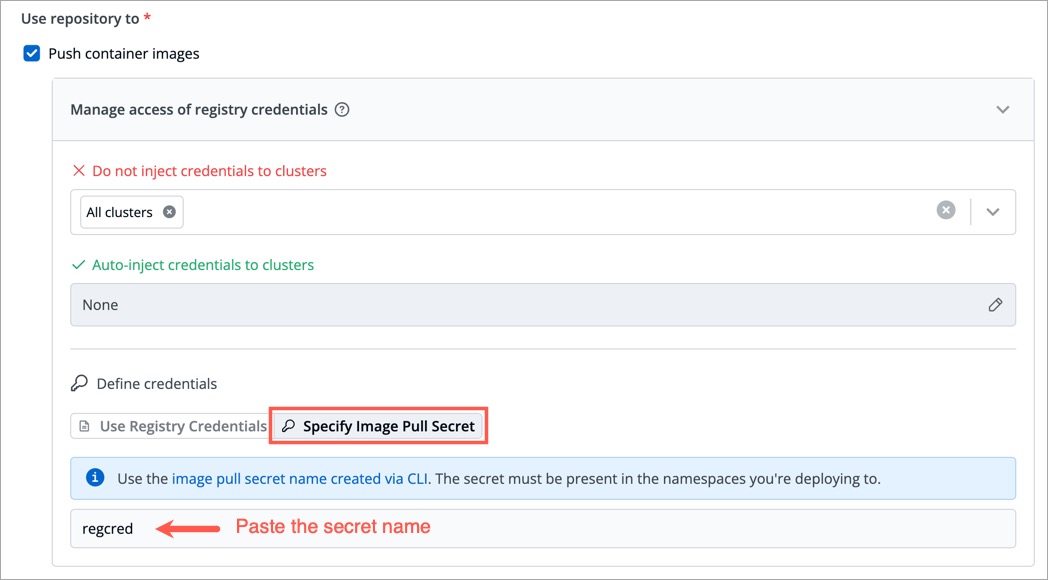
Figure 5: Using Image Pull Secret
Create this Secret and name it `regcred` (let's say):
@@ -233,7 +233,7 @@ If you prefer to delete an OCI registry, follow the instructions below:
1. Navigate back to **Container/OCI Registry** page.
- 
+ 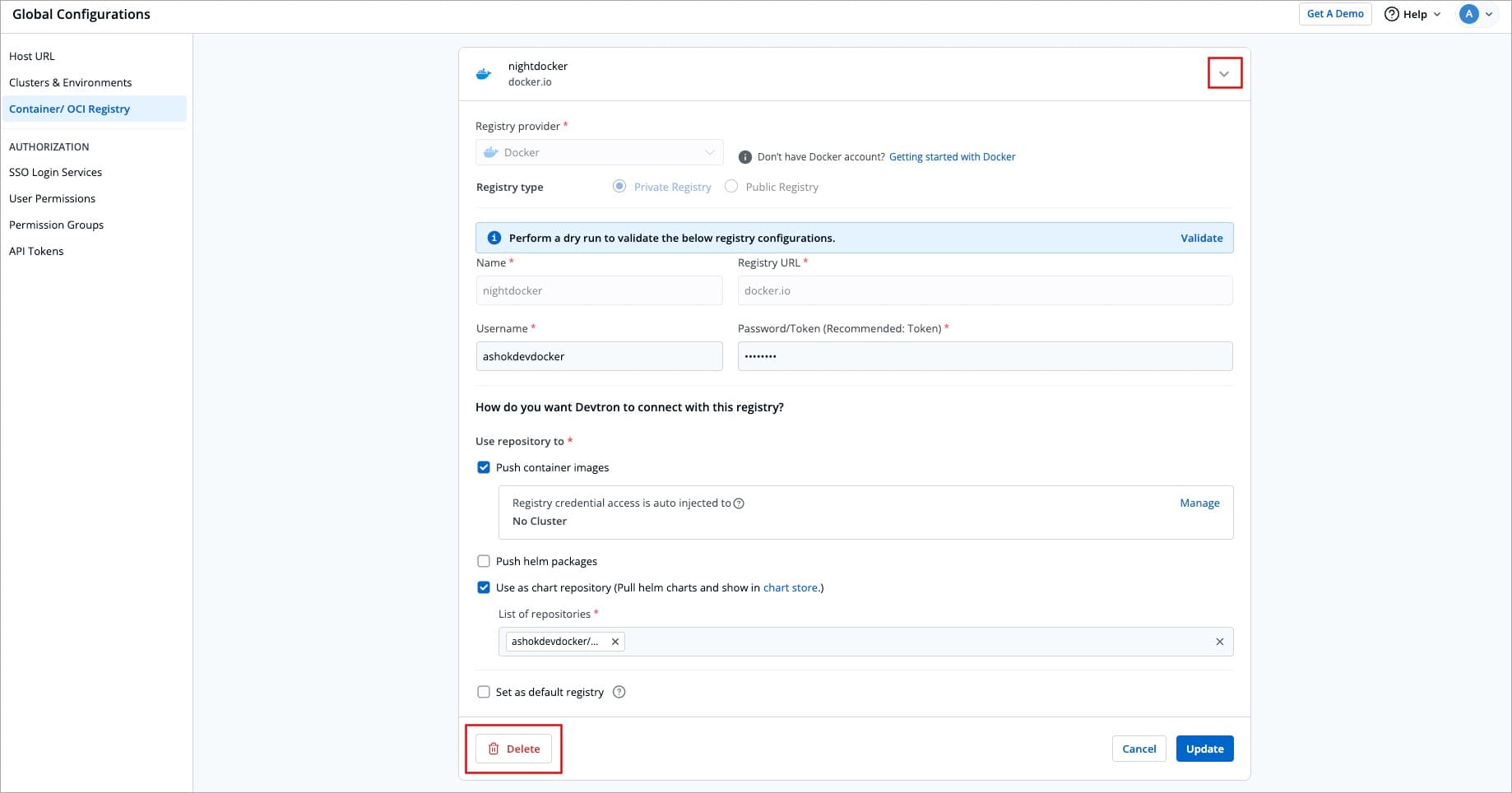
Figure 6: Delete an OCI Registry
2. Select your preferred OCI registry.
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/host-url.md b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/host-url.md
index f36cf100d..86d1e9580 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/host-url.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/global-configurations/host-url.md
@@ -10,8 +10,8 @@ Host URL is the domain address at which your devtron dashboard can be reached.
To add host URL, go to the `Host URL` section of `Global Configurations`.
-
-
On the **Host URL** page:
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-overview.md b/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-overview.md
index a0261fcb2..712646a2a 100644
--- a/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-overview.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-overview.md
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ By regularly reviewing this dashboard, you can proactively manage risks and main
This section provides a snapshot of the key vulnerability metrics in your environment.
-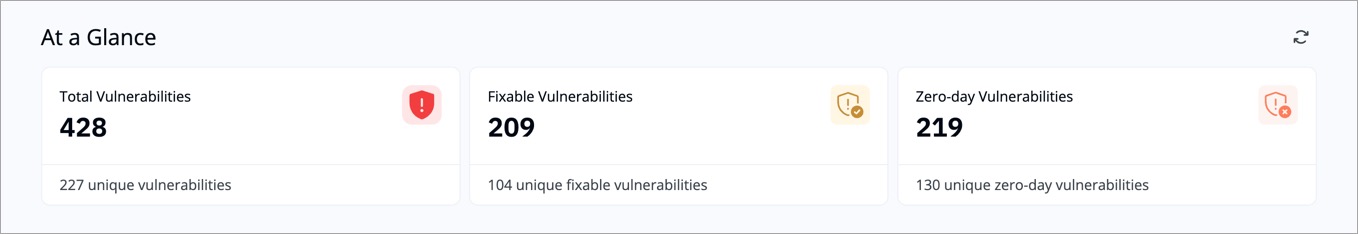
+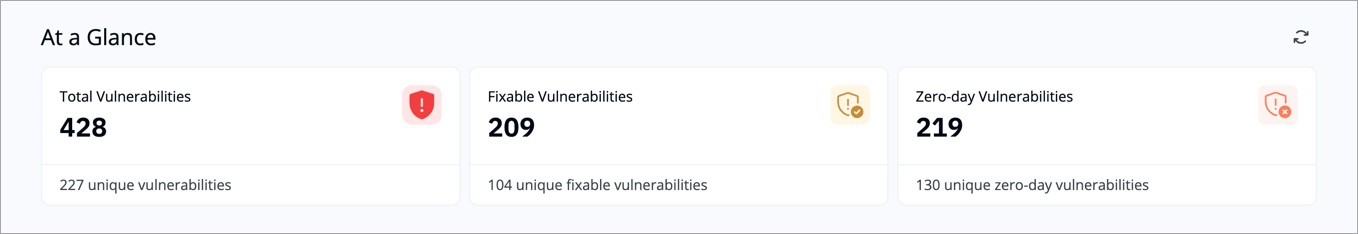
Figure 1: 'At a Glance' Section
| Metric | Description | Example |
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ Use this section to understand overall exposure and prioritize fixable items fir
The **Severity Insights** section helps you understand the nature and age of vulnerabilities in prod and non-prod deployments.
-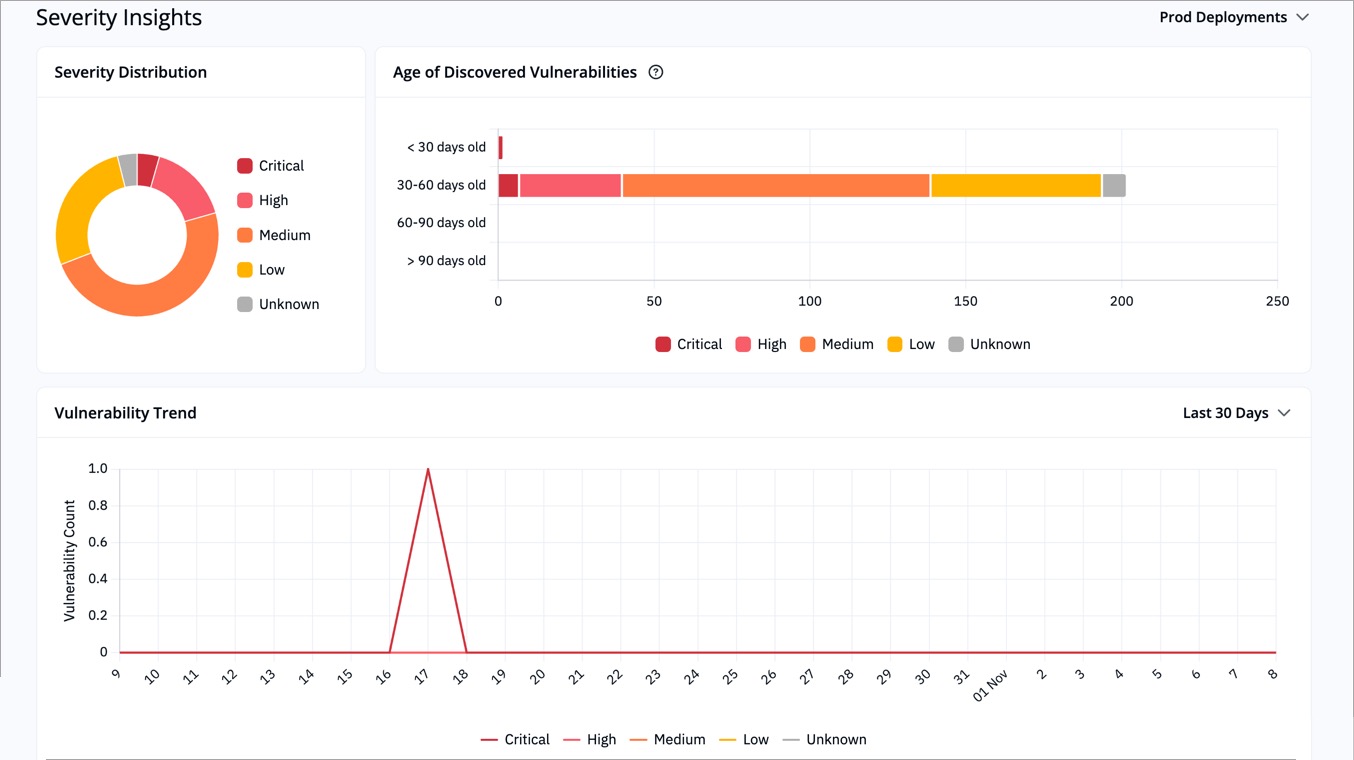
+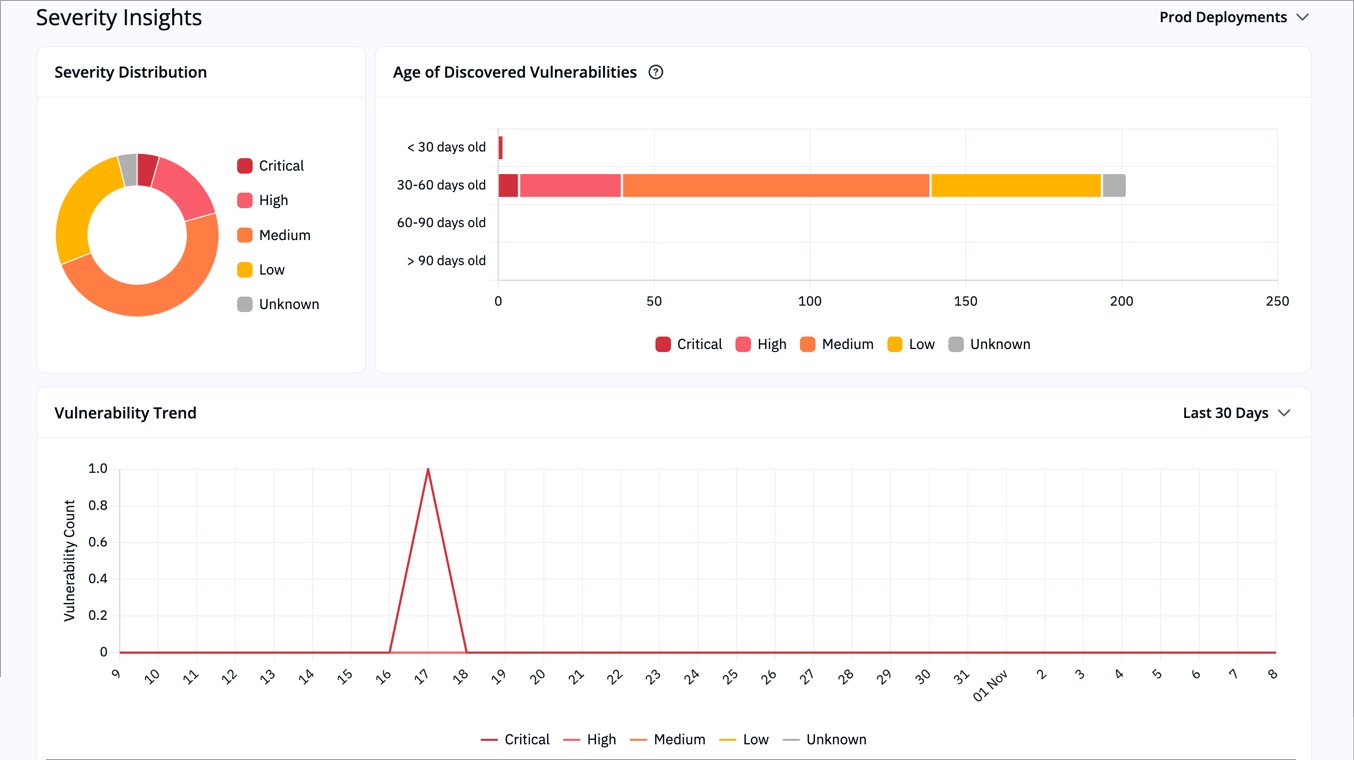
Figure 2: 'Severity Insights' Section
* **Severity Distribution:** Pie chart showing proportions of Critical, High, Medium, Low, and Unknown severity.
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ These visuals help you identify aging vulnerabilities, observe trends, and measu
The **Deployment Security Status** section highlights the current security health of your active deployments and pipelines.
-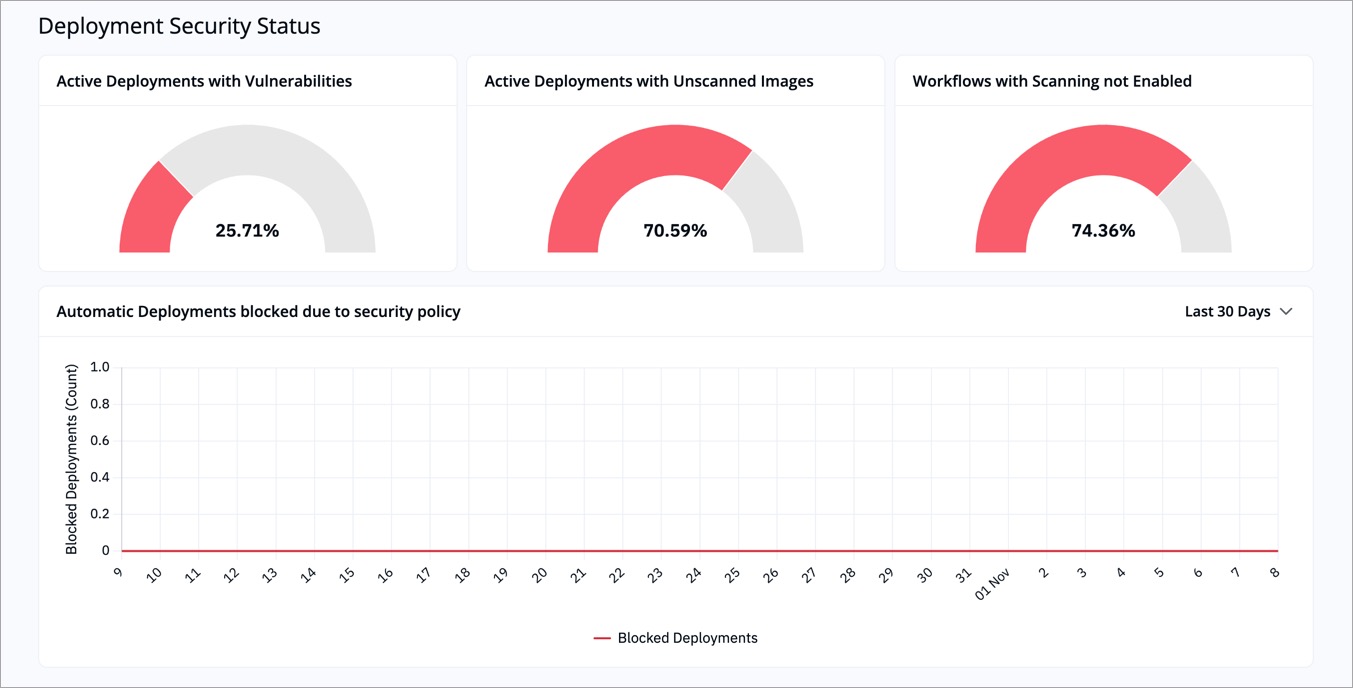
+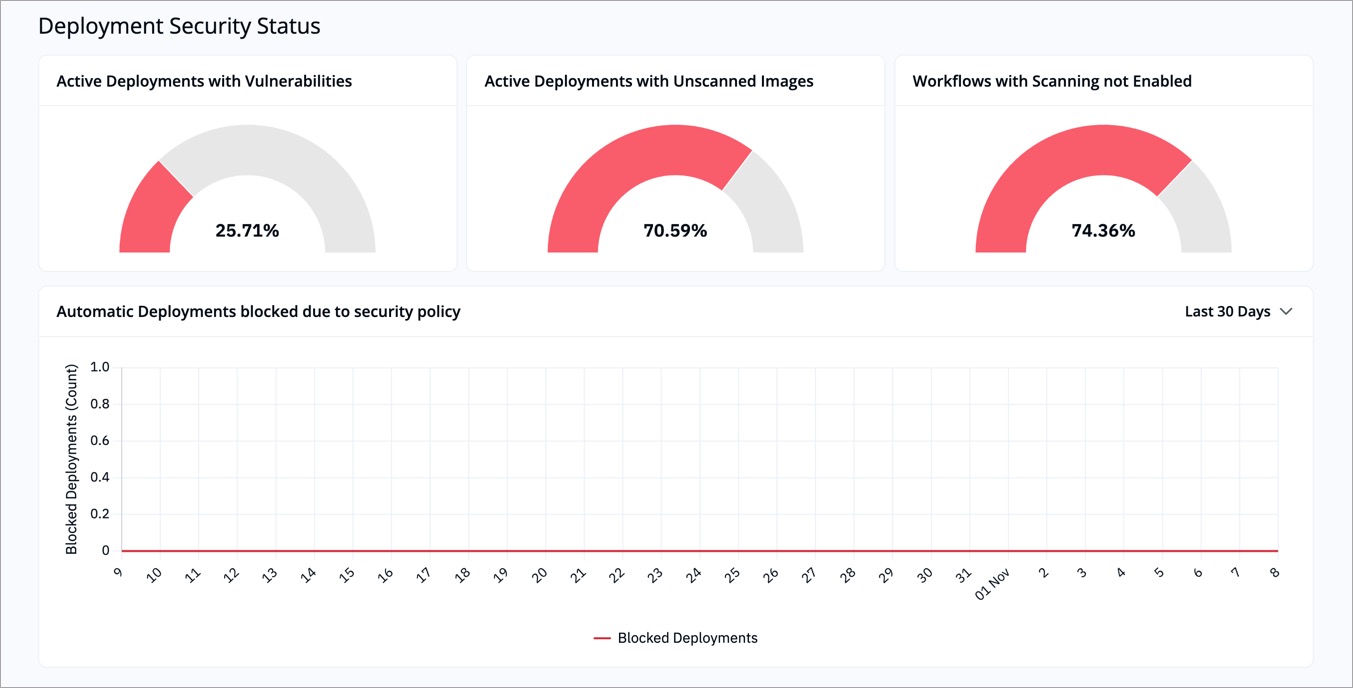
Figure 3: 'Severity Insights' Section
| Indicator | Description | Example |
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-policies.md b/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-policies.md
index 5dd7e4ffb..54516c9a9 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-policies.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-policies.md
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ You can define policies at the following levels:
* [Environment](#configure-environment-security-policy)
* [Application](#configure-application-security-policy)
-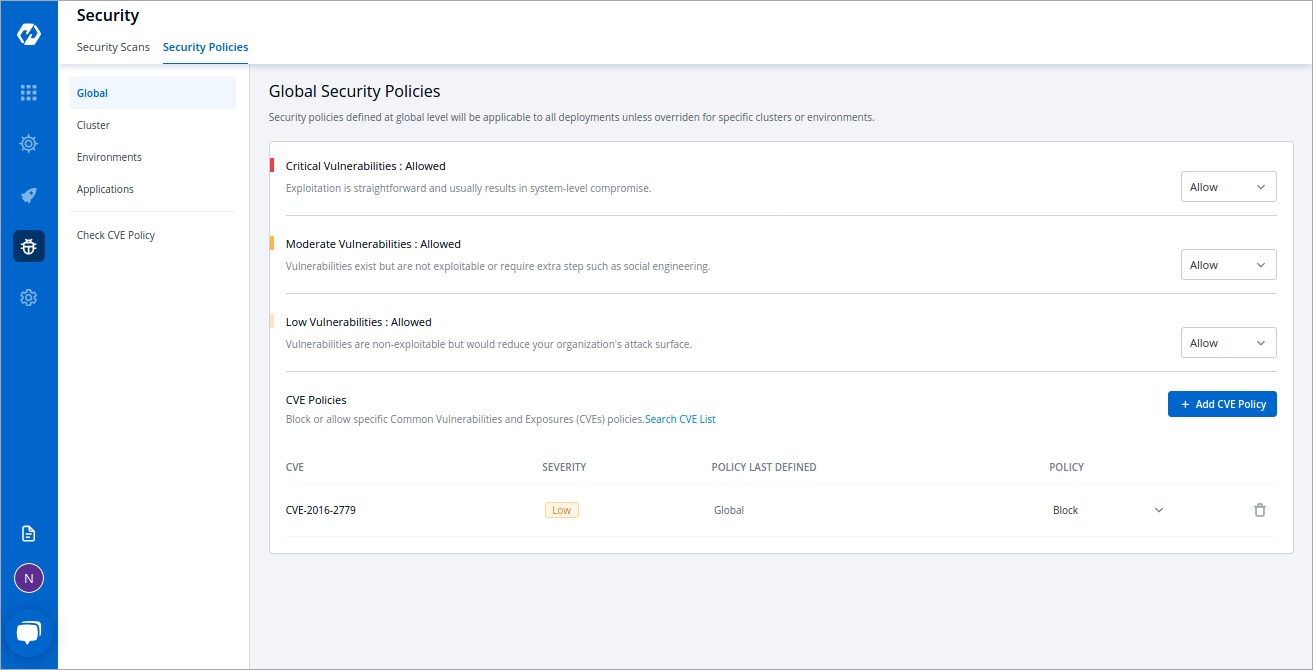
+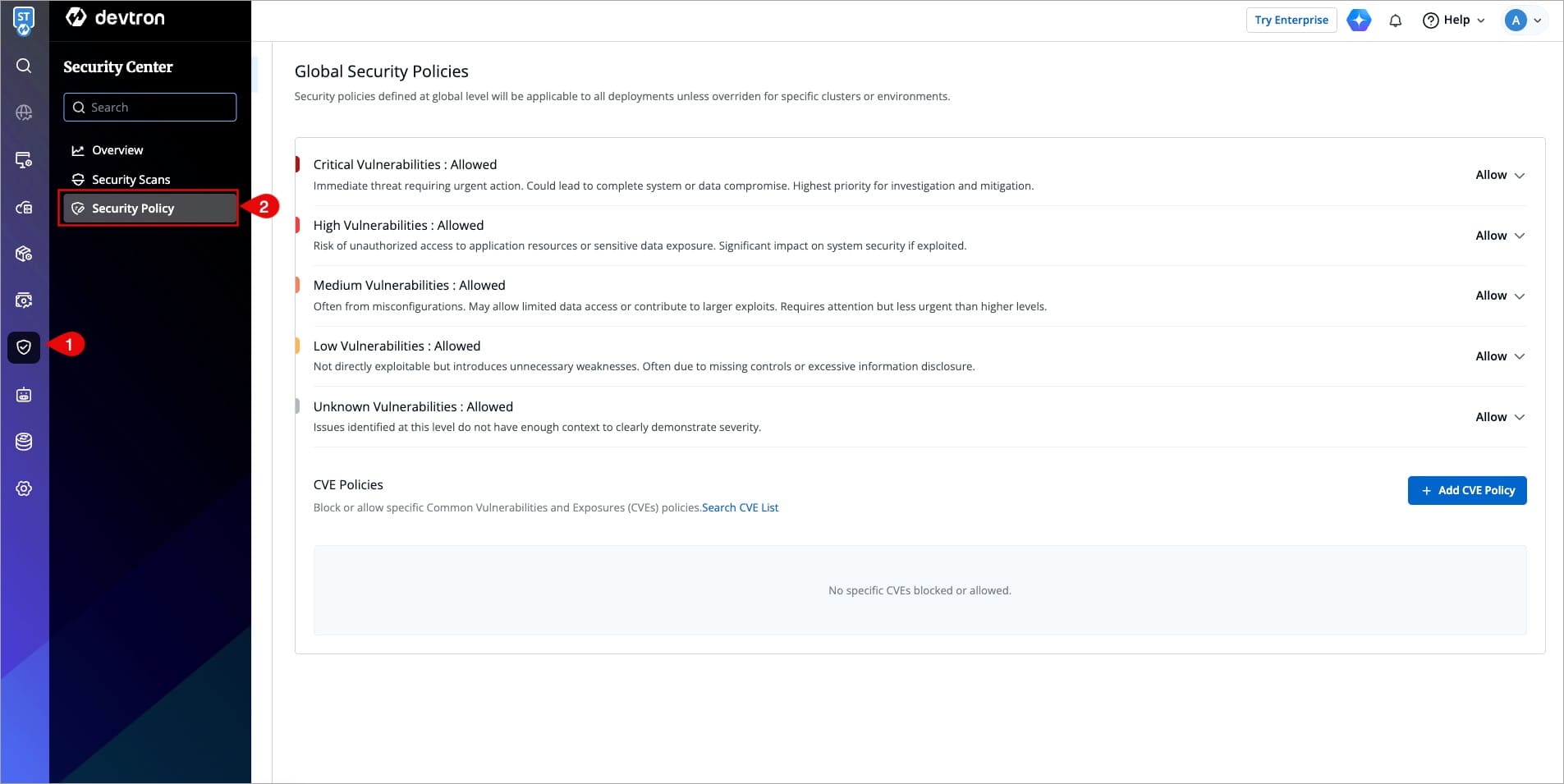
Figure 1: Security Policies
However, if you define policies at more than one level, the order of precedence would be as follows:
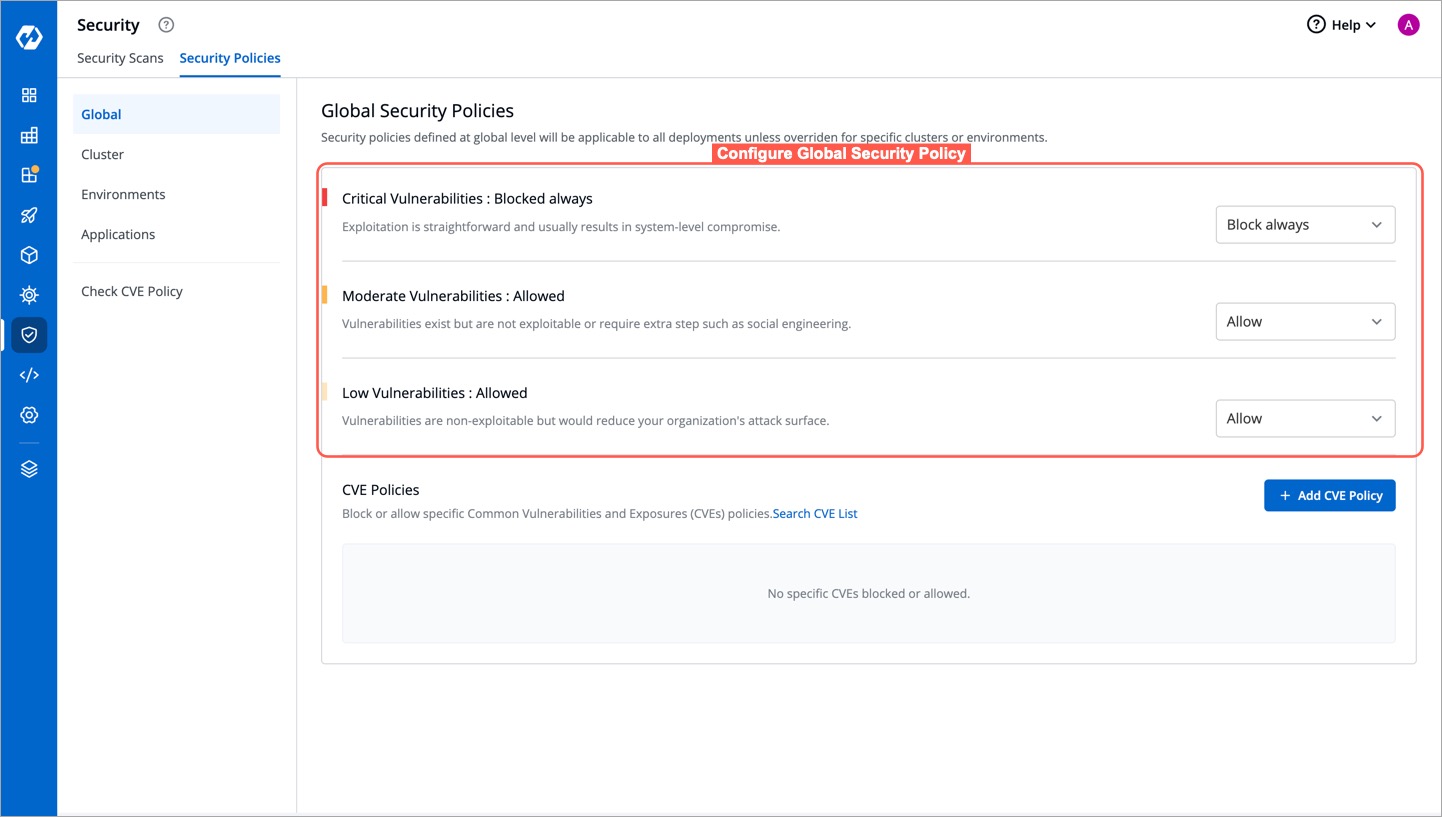
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ Within the Global Security Policies, there are three options available:
| Block if fix is available | Images containing vulnerabilities will be blocked if a fix is available and has not been applied |
| Allow | Images containing vulnerabilities will be allowed to be deployed regardless of whether a fix is available or not |
-
+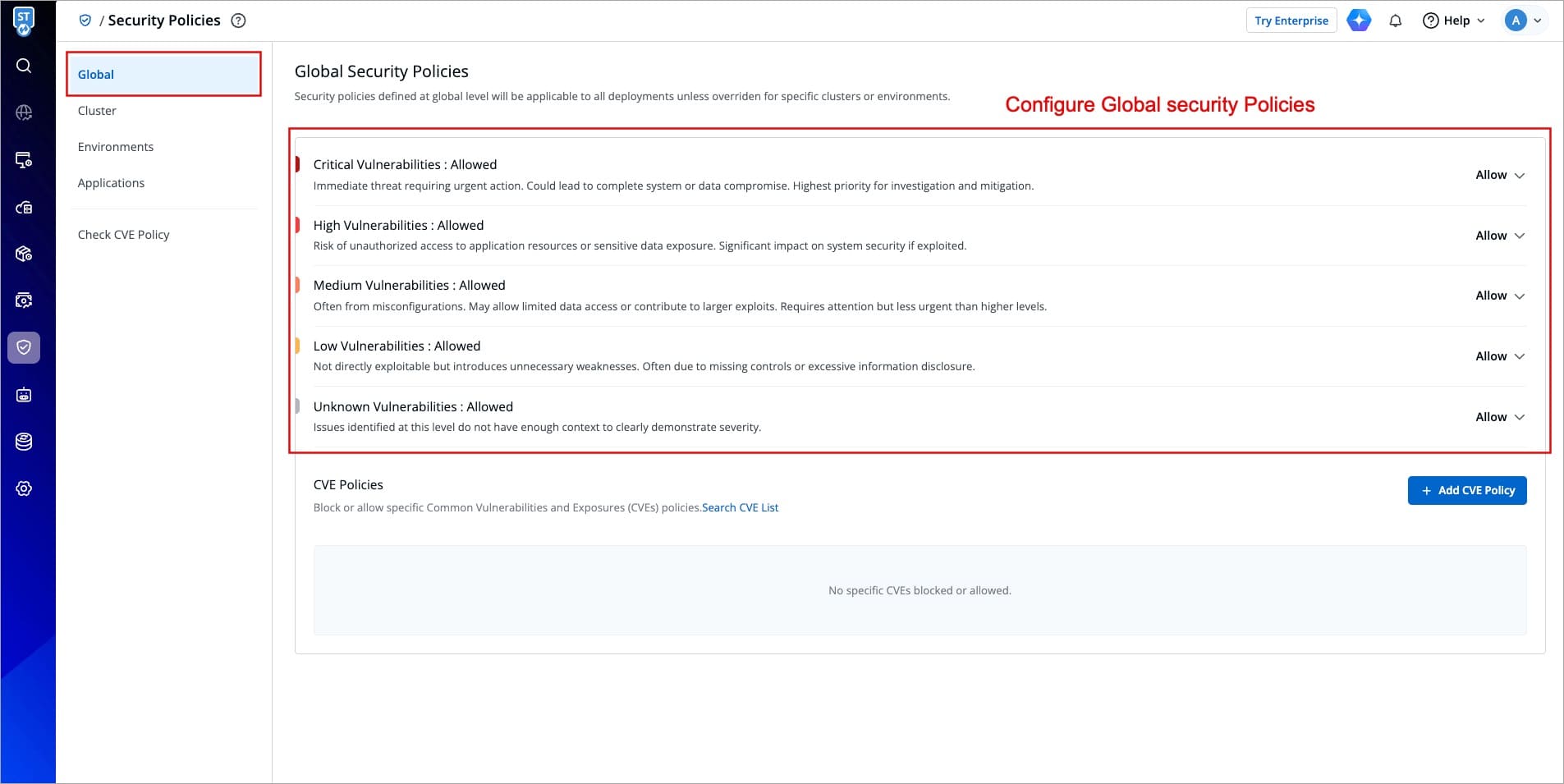
Figure 2: Configuring Global Security Policy
If critical severity levels are blocked in the Global Security Policy, the same blocking will be applied to the Cluster Security Policy. Likewise, allowing critical levels in the global policy automatically allows them in Cluster Security Policies.
@@ -71,8 +71,11 @@ However, users have the flexibility to explicitly modify these policies as desir
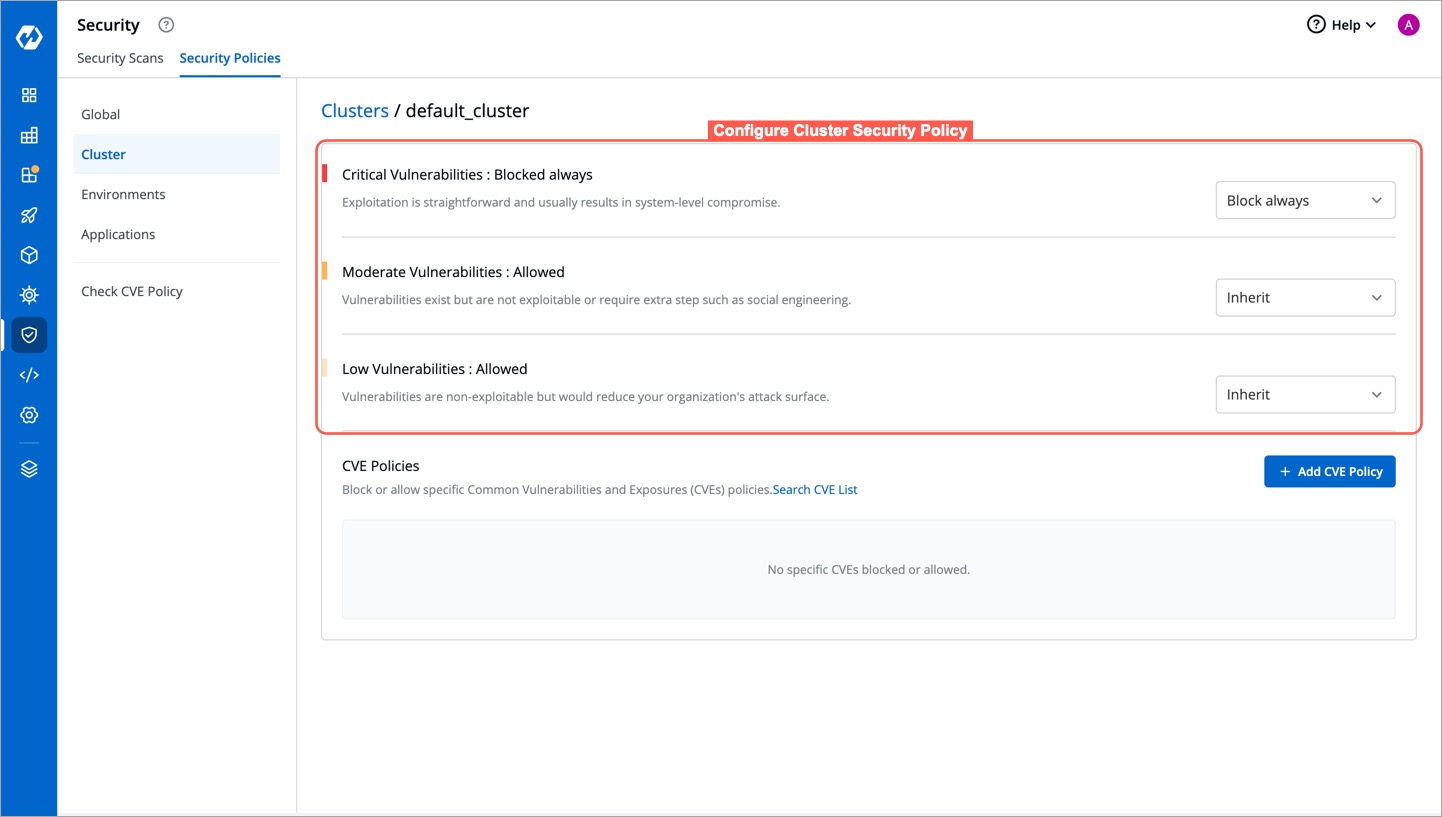
Cluster Security Policies offer the same three options as [Global Security Policies](#configure-global-security-policy) for handling vulnerabilities. However, an extra option called `Inherit` is available too.
-
-
When `Inherit` is selected, the policy adopts settings from higher-level options. For example, if critical severity levels are blocked globally, they will also be blocked in Cluster Security Policies. Changing the global policy to allow critical levels will also allow them in Cluster Security Policies. Explicit changes can be made to these policies.
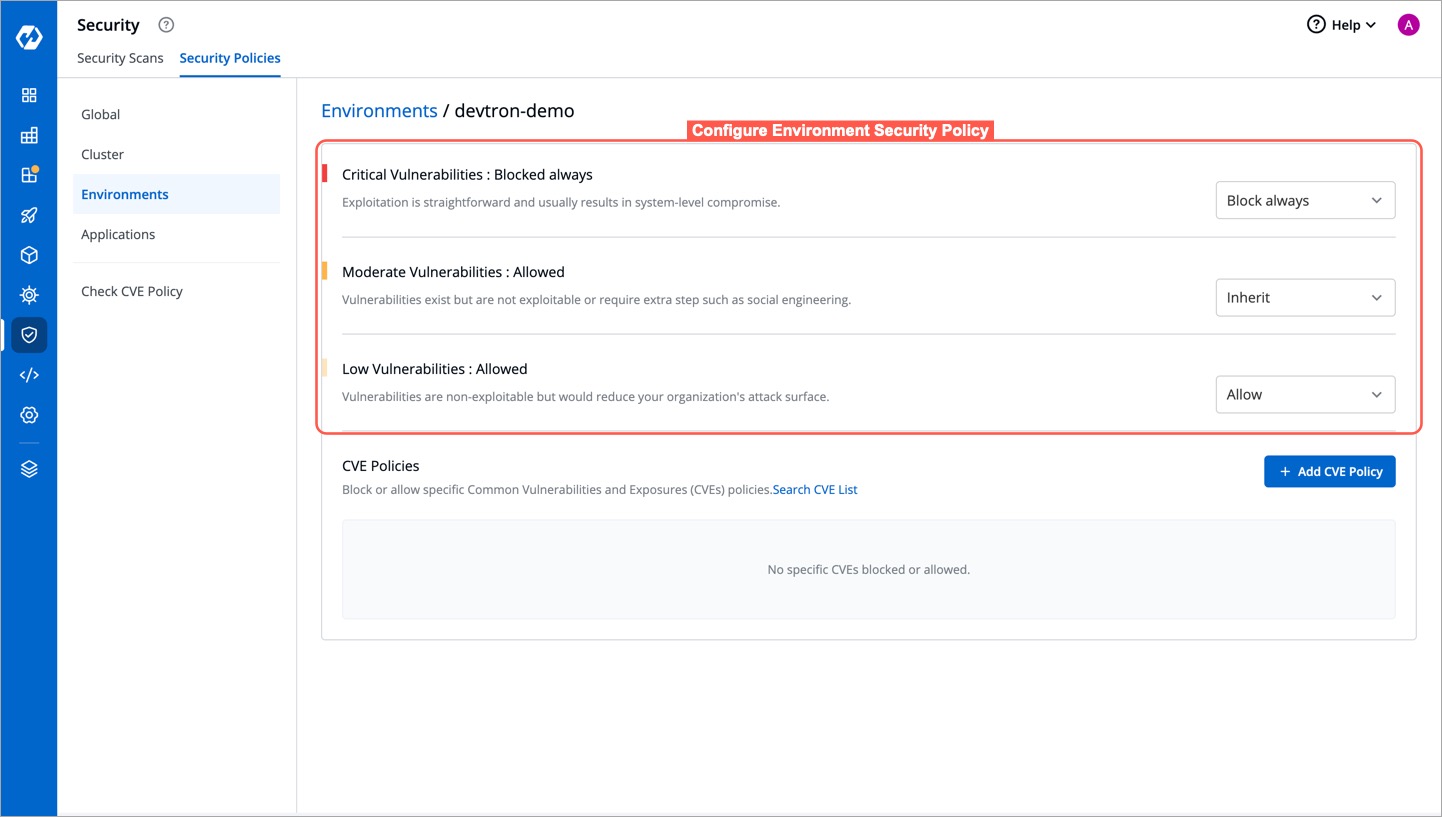
@@ -93,8 +96,11 @@ Environment Security Policies, like [Cluster Security Policies](#configure-clust
* Allow
* Inherit
-
-
The Environment Security Policy inherits its settings from the Cluster Security Policy, following a hierarchical structure where each level inherits the policy from its upper level.
@@ -117,37 +123,40 @@ However, in the Application Security Policy, the policy is determined by both: A
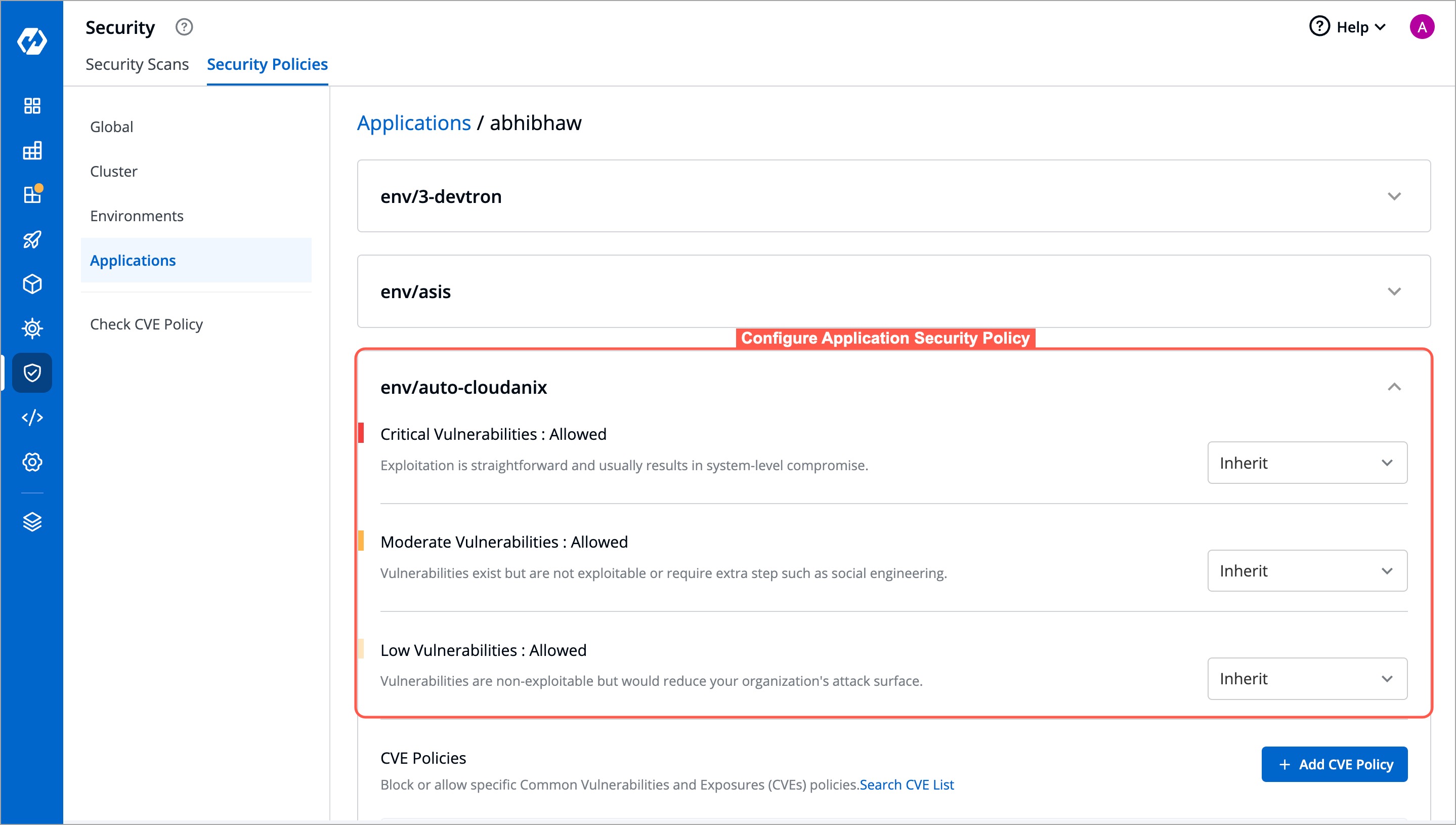
First, choose an application from the list.
-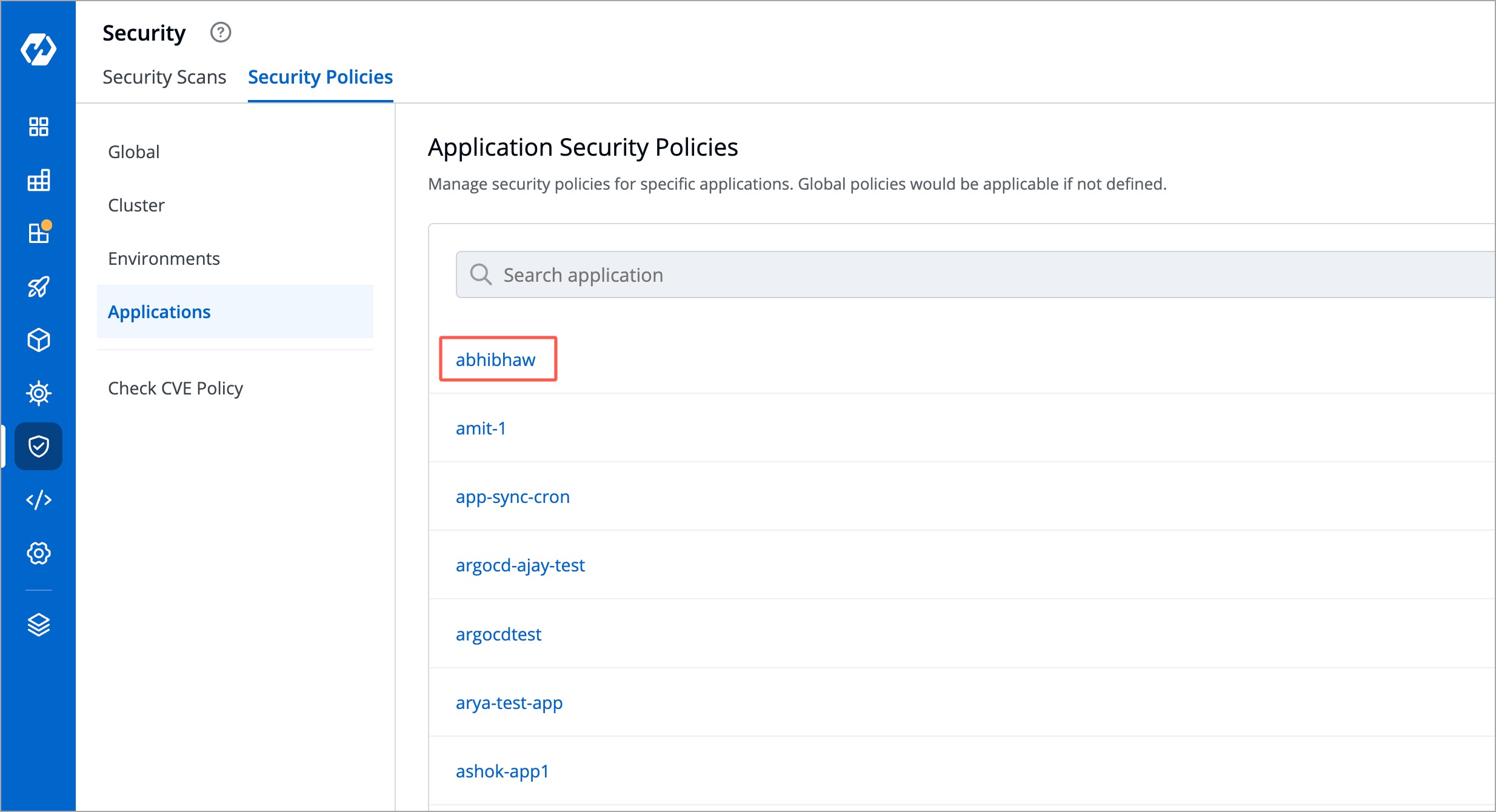
+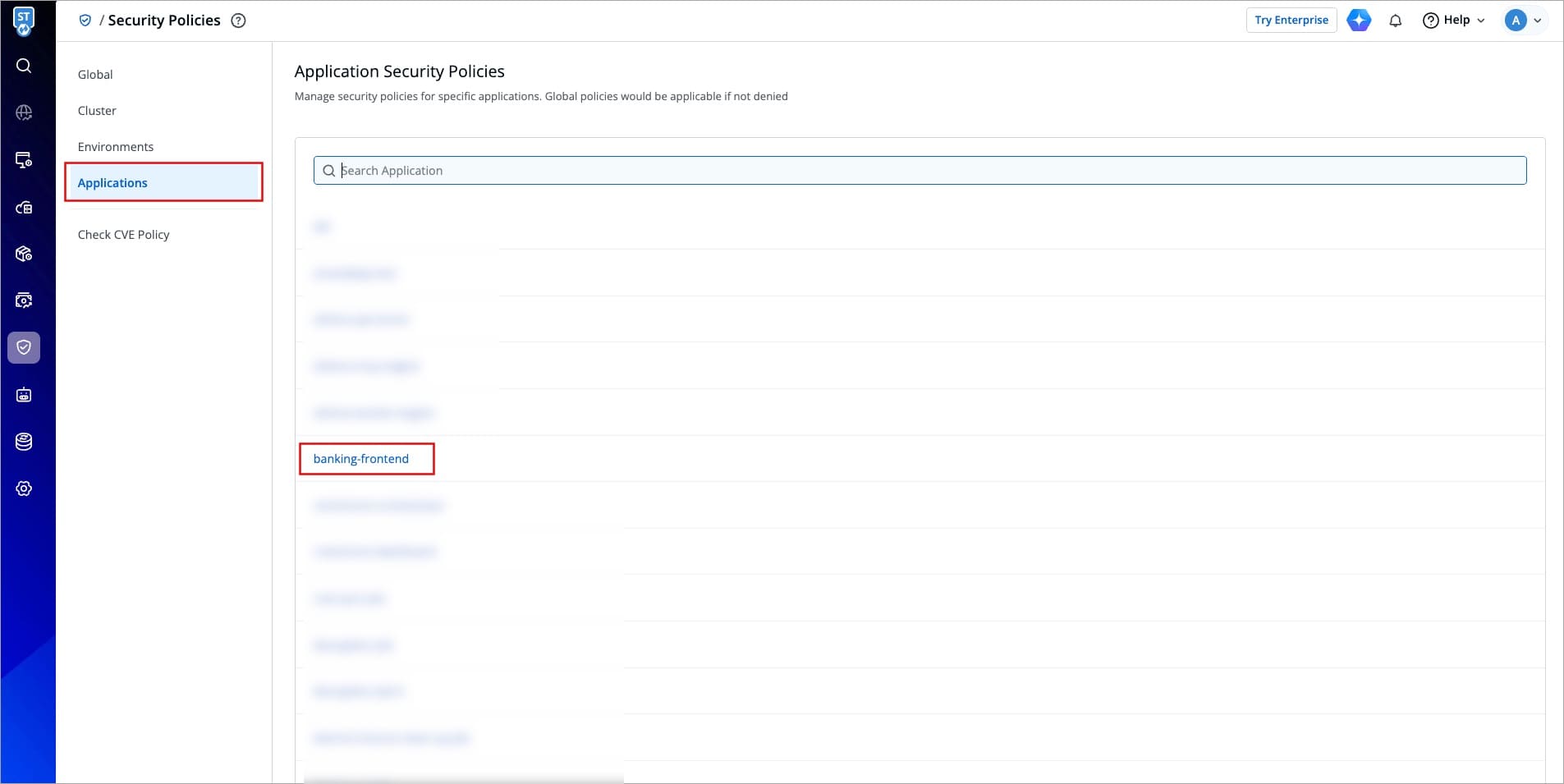
Figure 5a: Configuring Application Security Policy - Choosing an App
Next, configure a security policy for that application in the intended environment.
-
+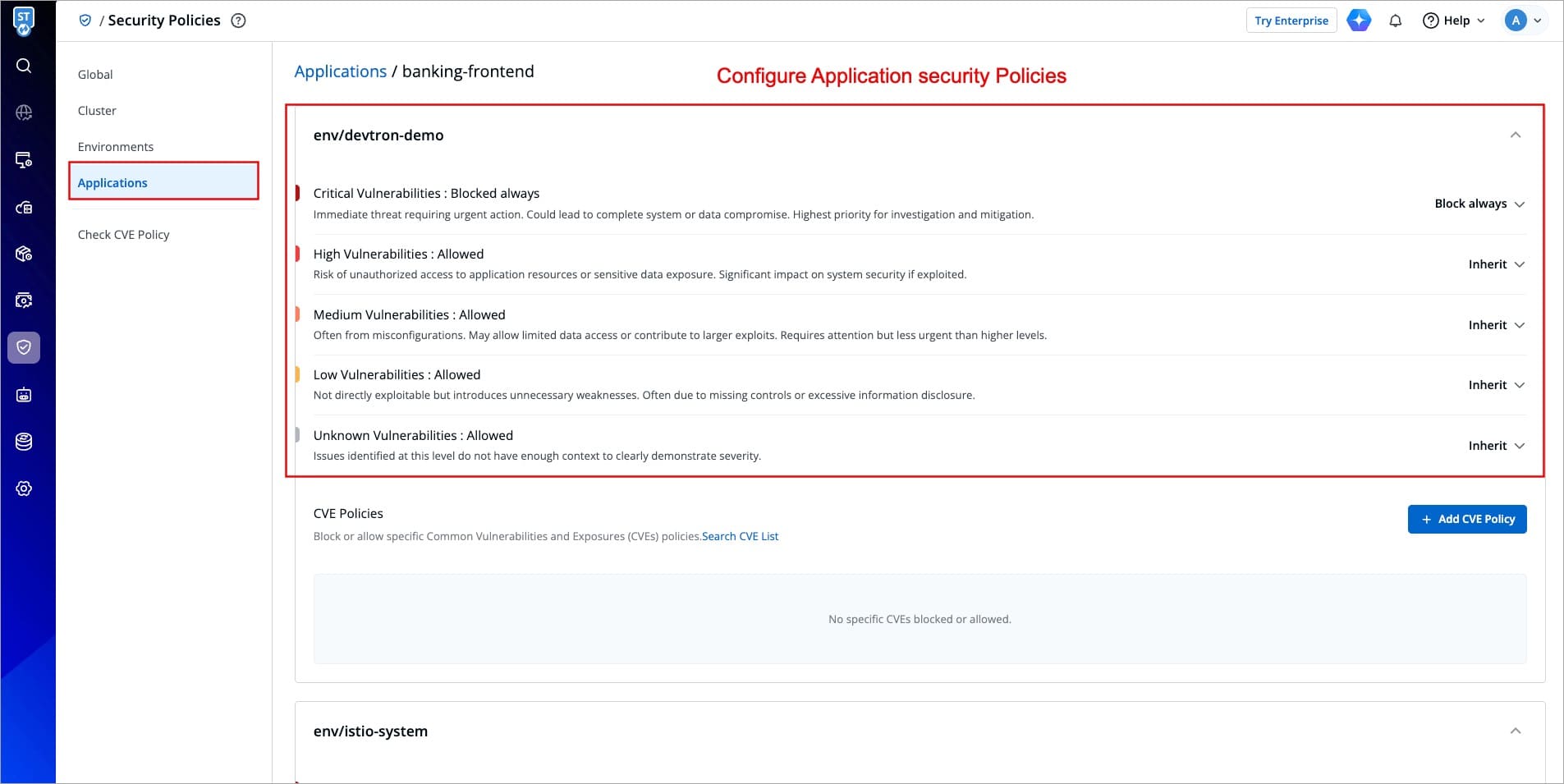
Figure 5b: Configuring Application Security Policy - Choosing an Env
---
## Example
-1. Let's say, you have defined a policy to block the deployment if critical vulnerabilities are found in a given application.
+1. Let's say, you have defined a policy to block the deployment if critical or high vulnerabilities are found in a given application.
- 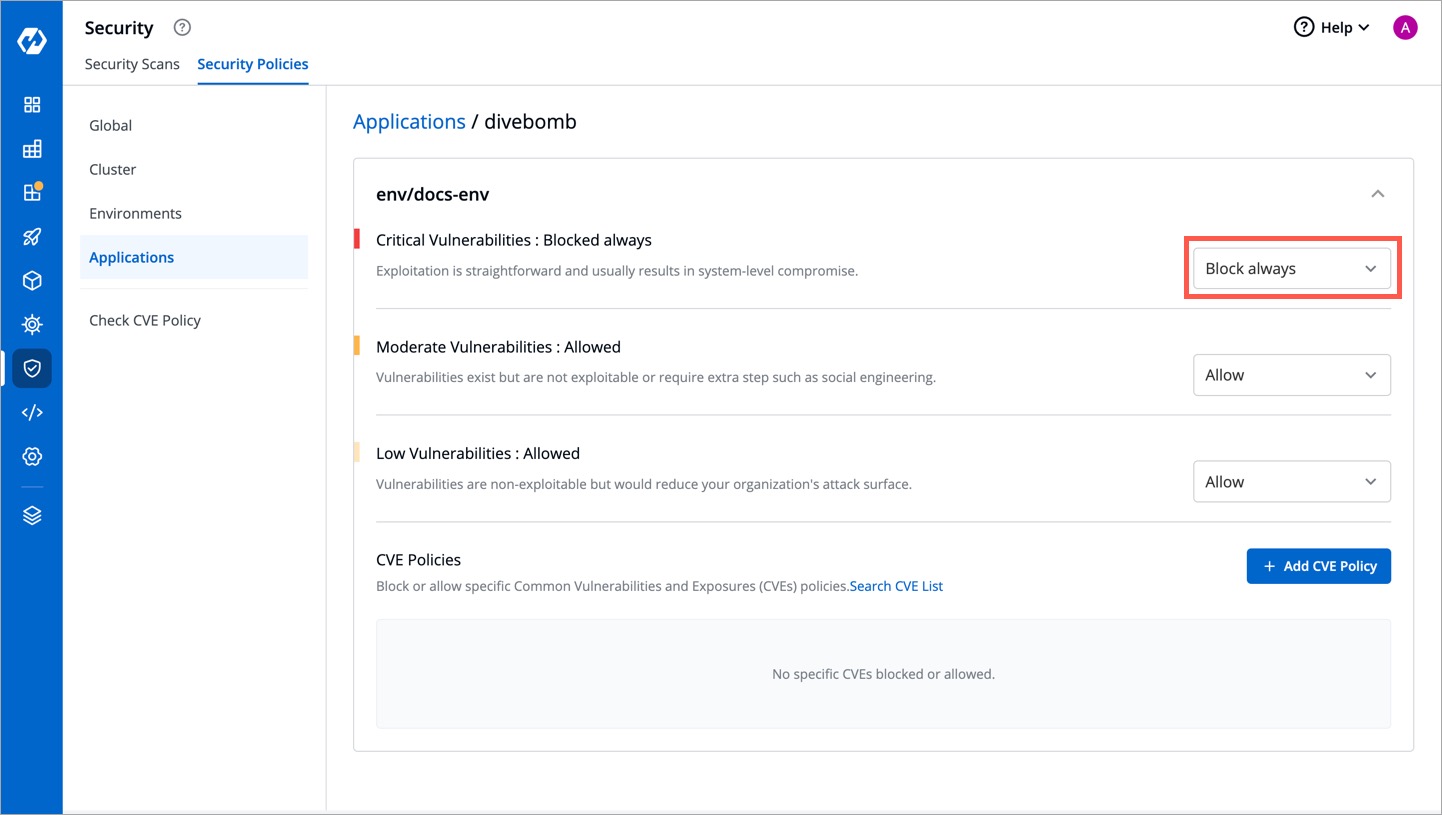
+ 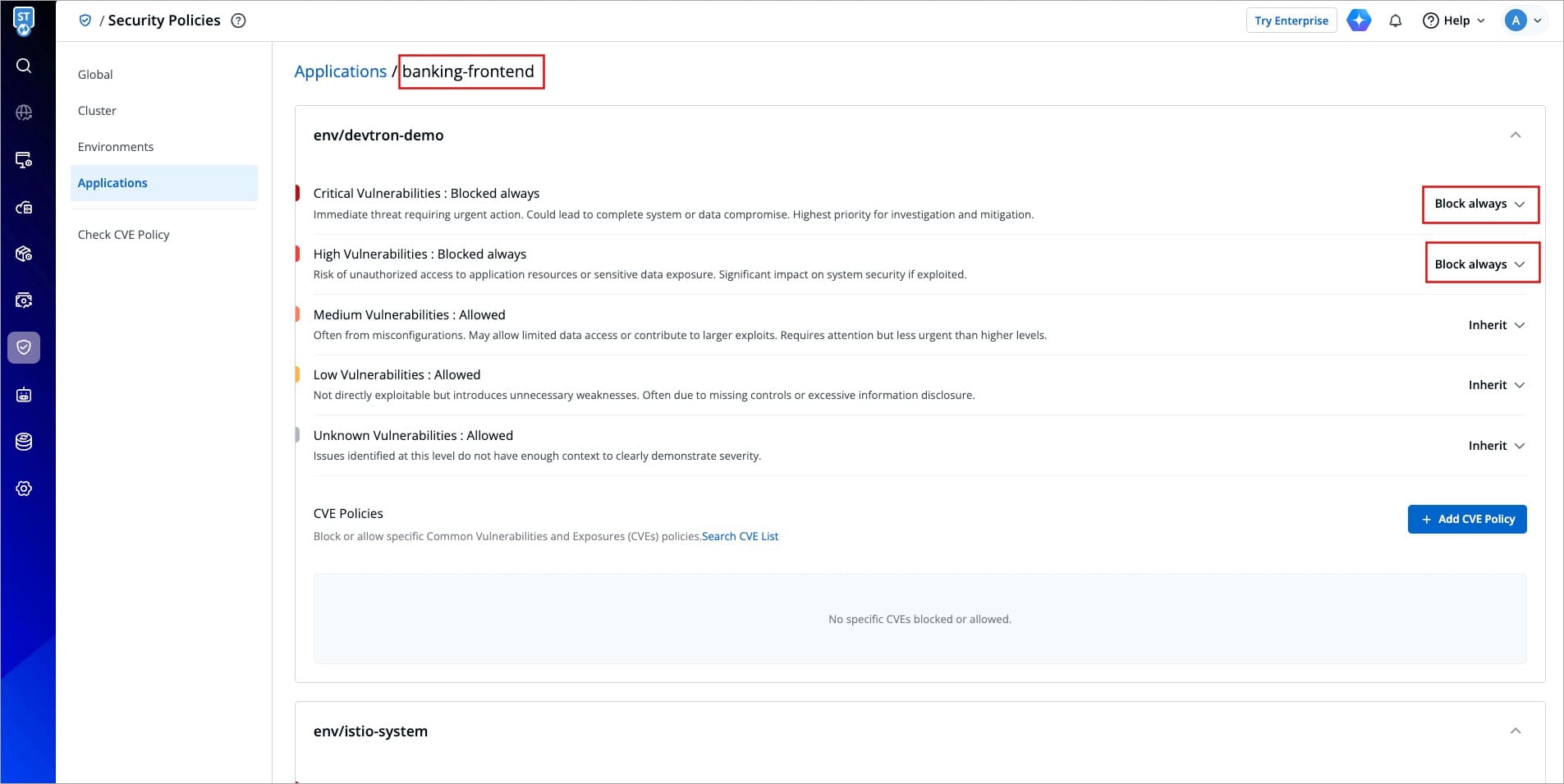
Figure 6: Defining a Block Policy
2. Now, go to the **Build & Deploy** tab of that application to select an image.
- 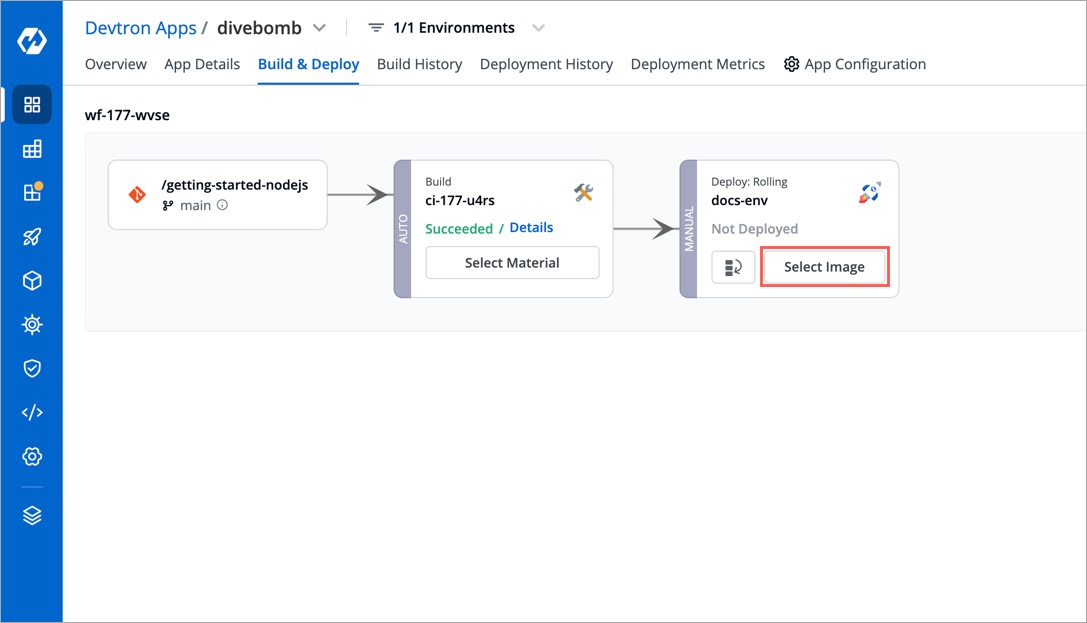
+ 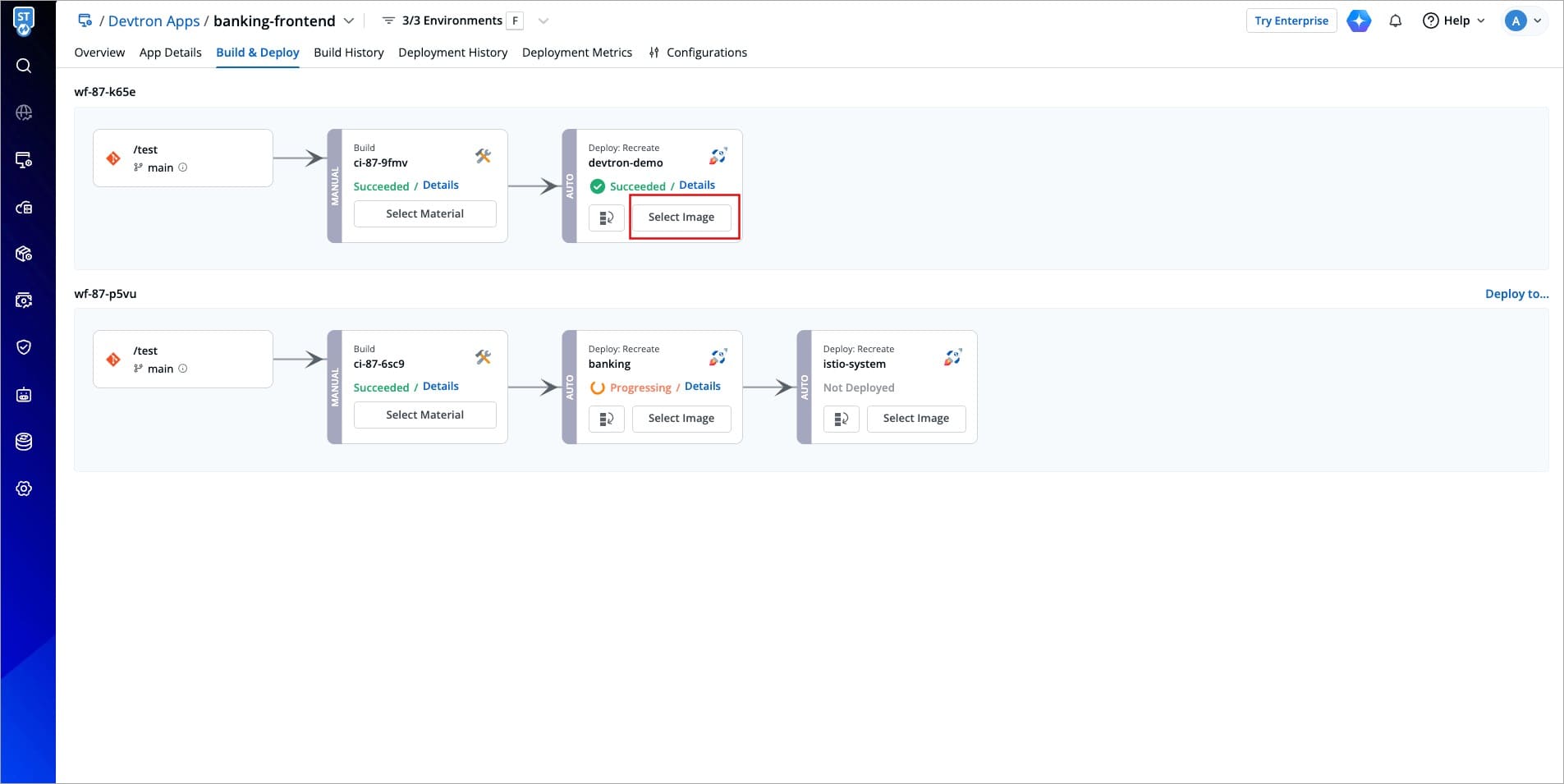
Figure 7: Selecting an Image
3. As you can see, security issues were found in the scanned image, hence it is not available for selection. Click **Show Source Info**.
- 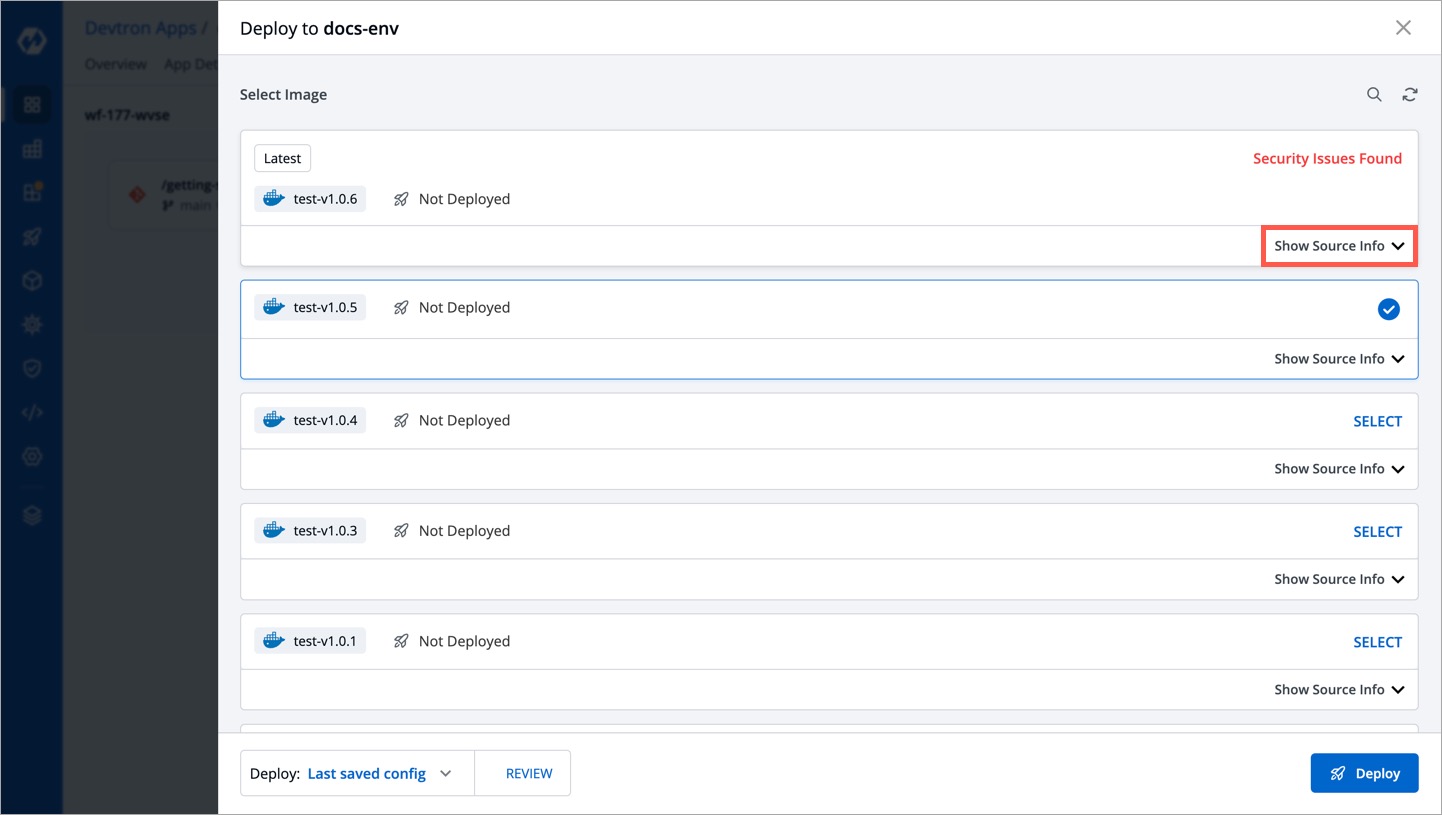
+ 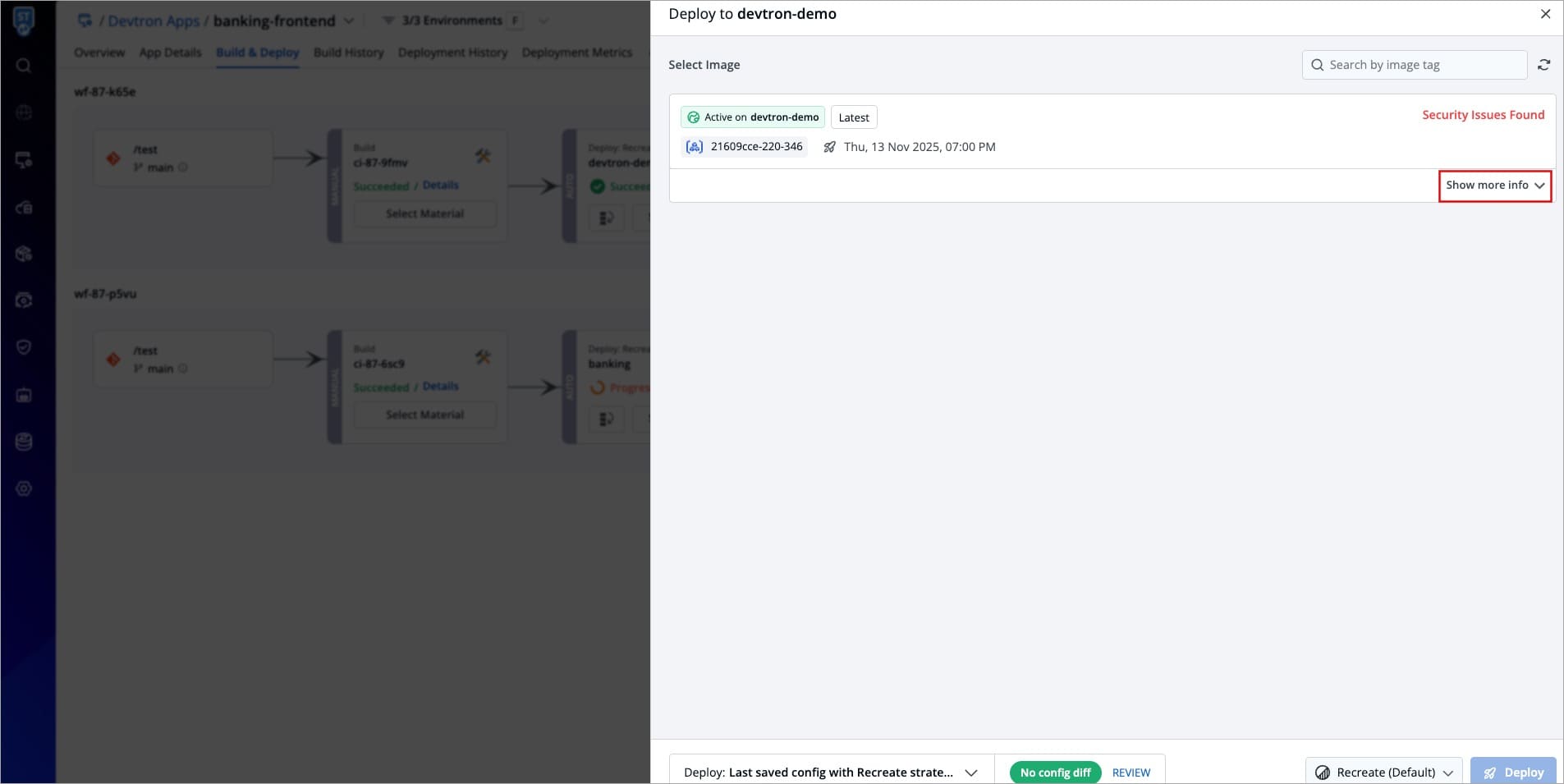
Figure 8: Blocked Deployment of Image
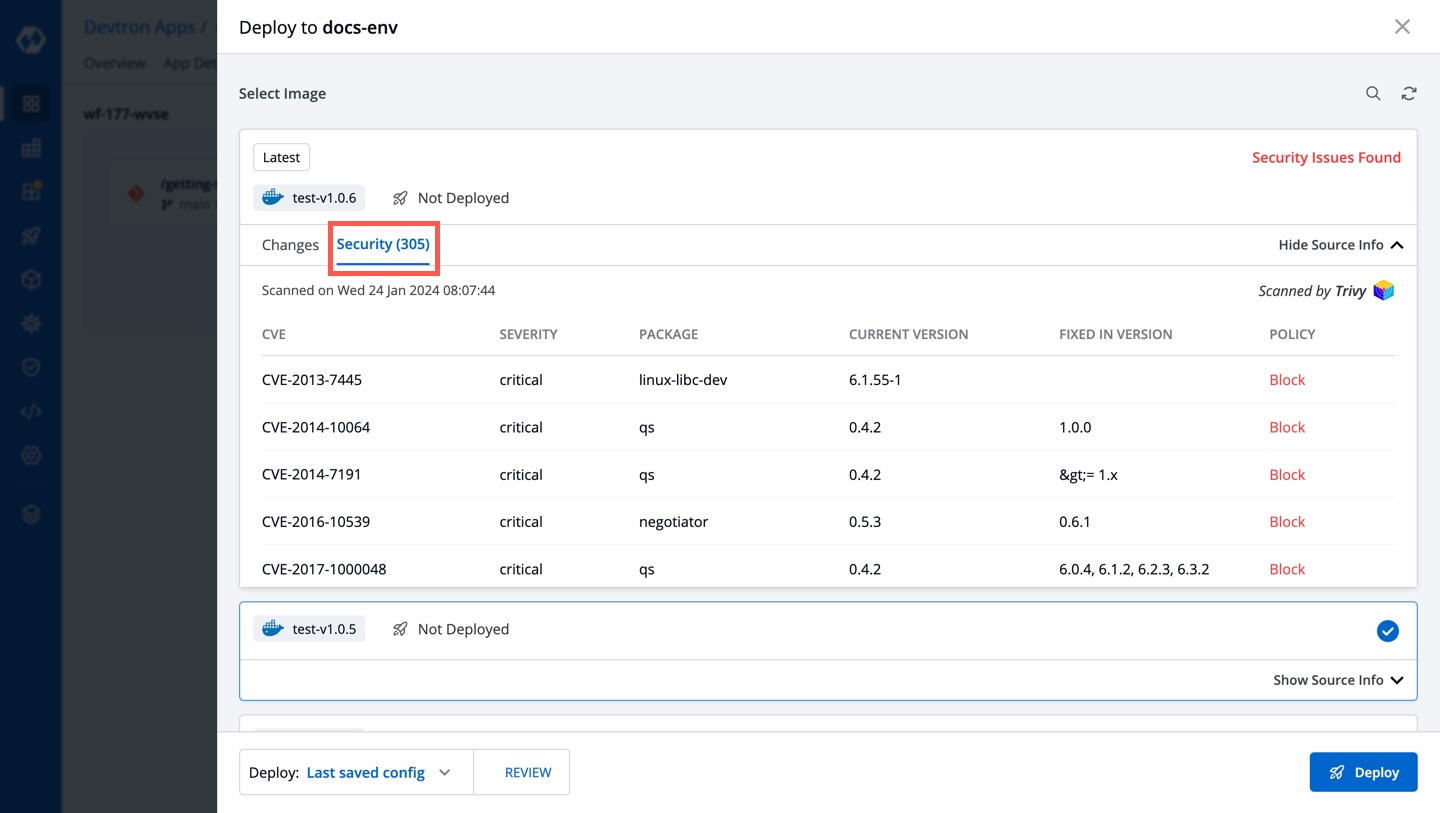
4. The `Security` tab shows the critical vulnerabilities and the policy enforced to prevent deployment.
- 
-
---
@@ -155,12 +164,12 @@ Next, configure a security policy for that application in the intended environme
To block or allow specific Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) policies, simply click **Add CVE Policy**.
-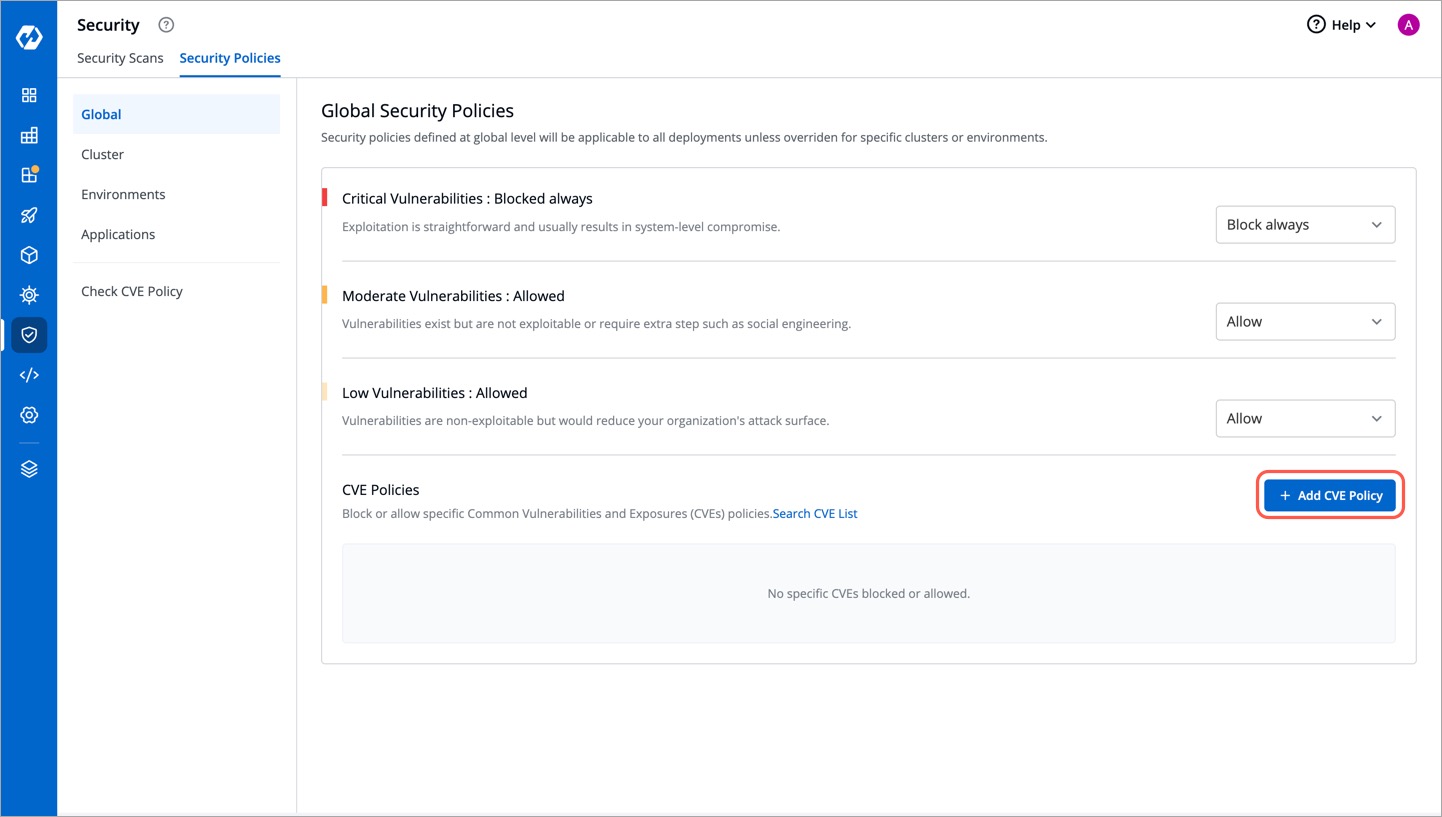
+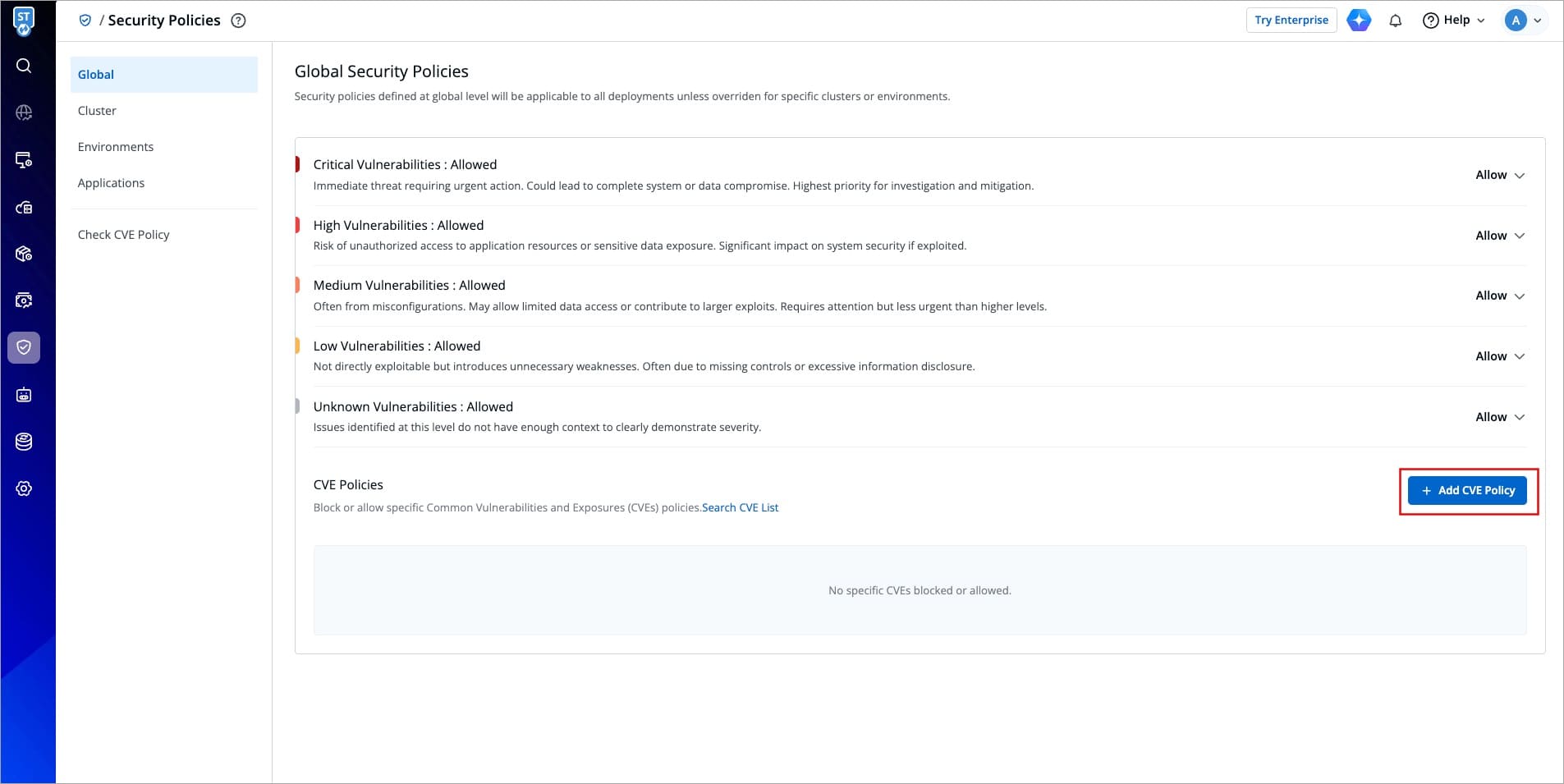
Figure 10: Adding CVE Policy
A window will appear where you can enter the CVE ID and select whether to allow or block it.
-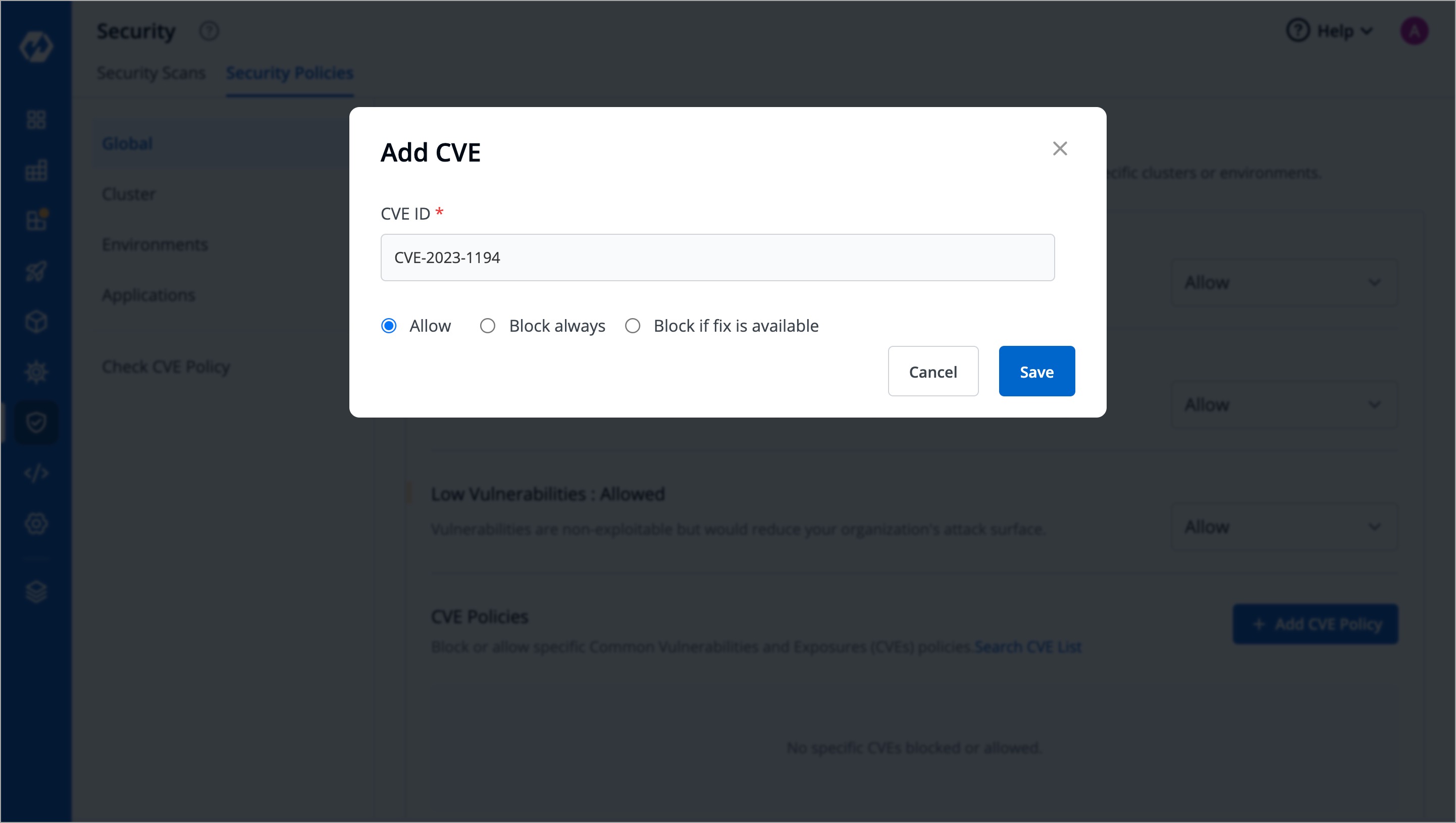
+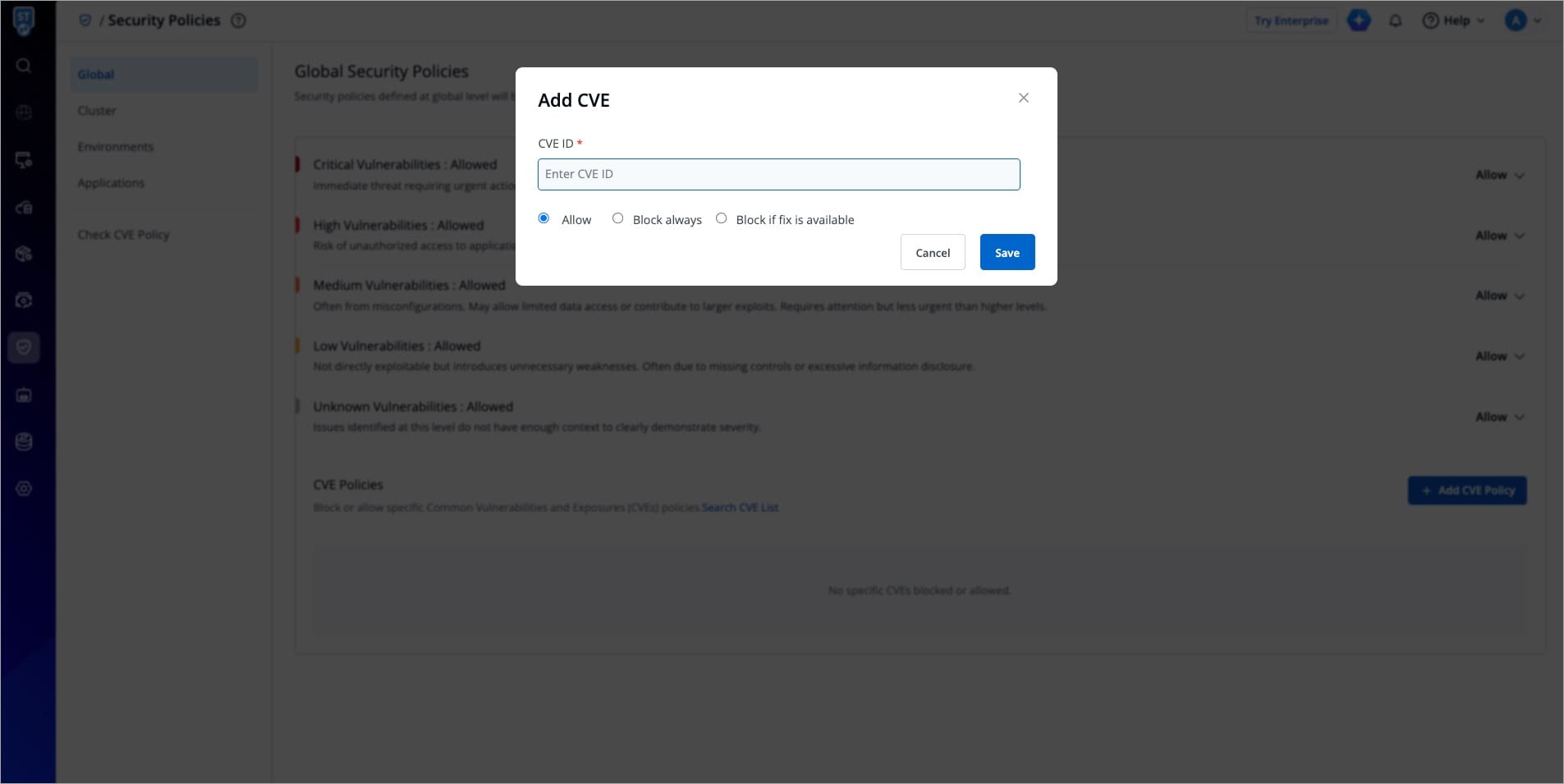
Figure 11: Allowing/Blocking a CVE ID
This action will determine whether image deployment is allowed or blocked based on the presence of vulnerabilities matching that particular CVE ID. Any other deployment decisions will be made according to the policies set previously.
diff --git a/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-scans.md b/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-scans.md
index 43c53f12c..6833a75d7 100755
--- a/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-scans.md
+++ b/docs/user-guide/security-features/security-scans.md
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ Install any one of the following integrations for scanning vulnerabilities:
Devtron's CI pipeline provides a **Scan for vulnerabilities** option as shown below. Once you enable this option, it will automatically scan the image for vulnerabilities.
-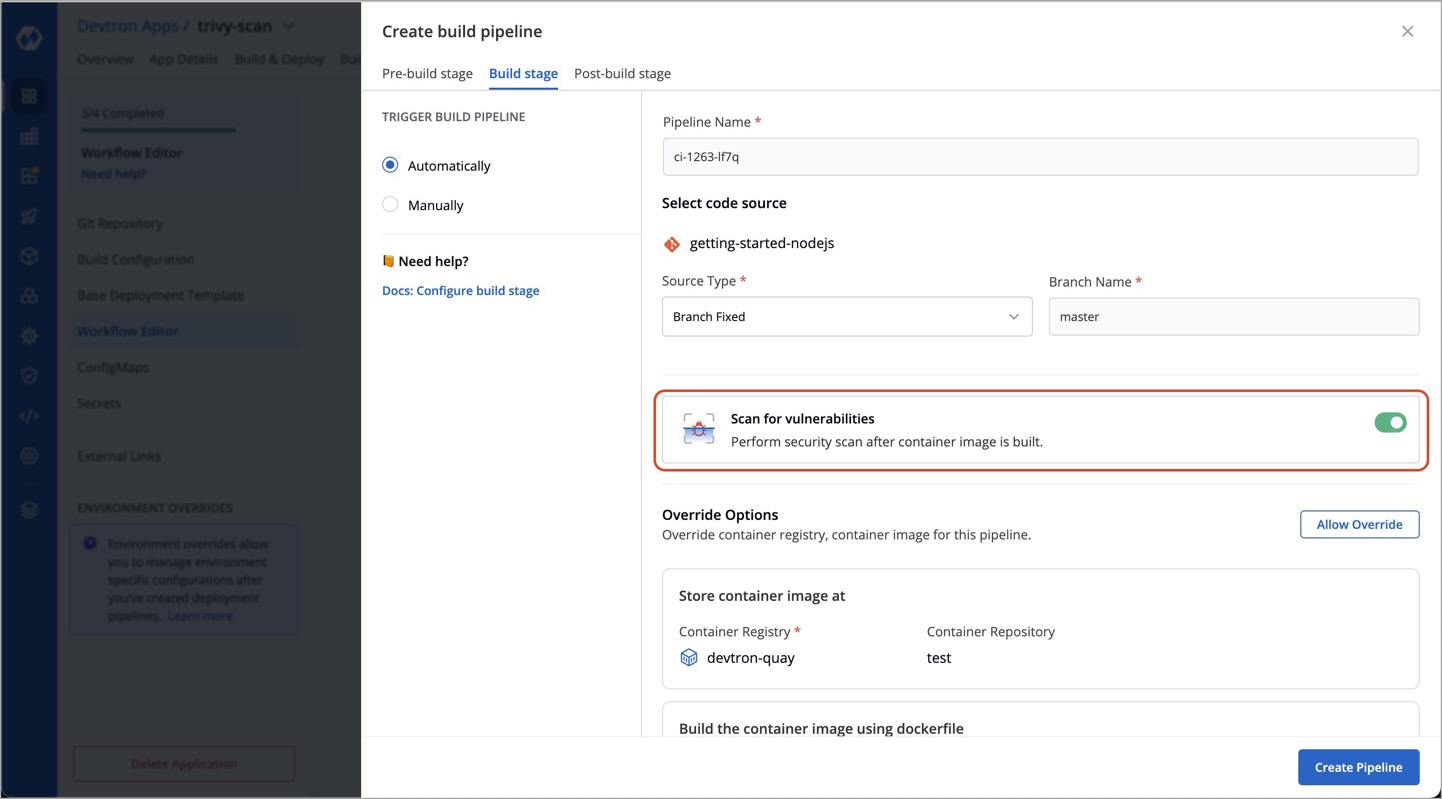
+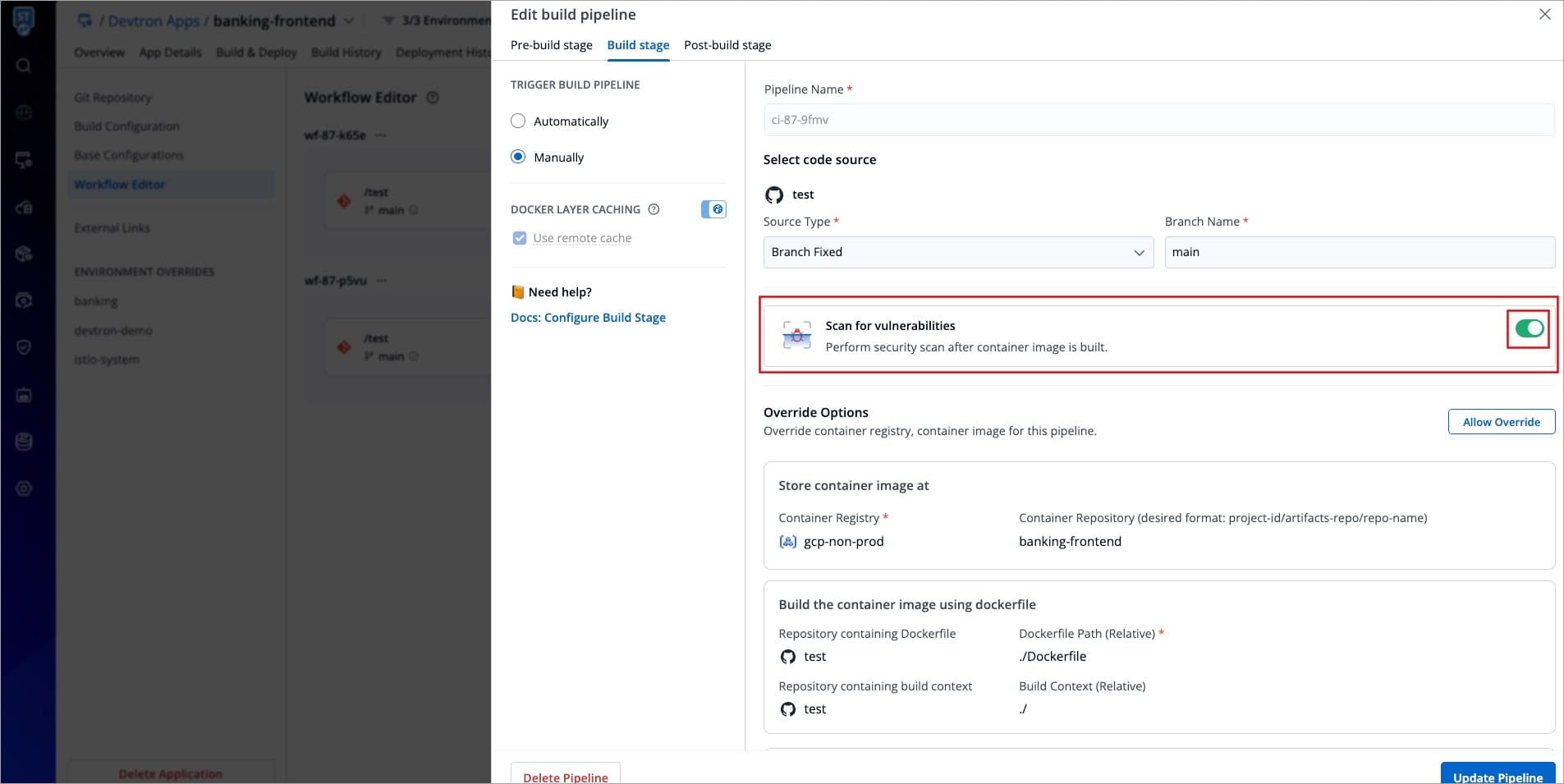
Figure 1: Scan for vulnerabilities
:::caution Who Can Perform This Action?
@@ -23,19 +23,22 @@ To access the comprehensive security scan reports, follow these steps:
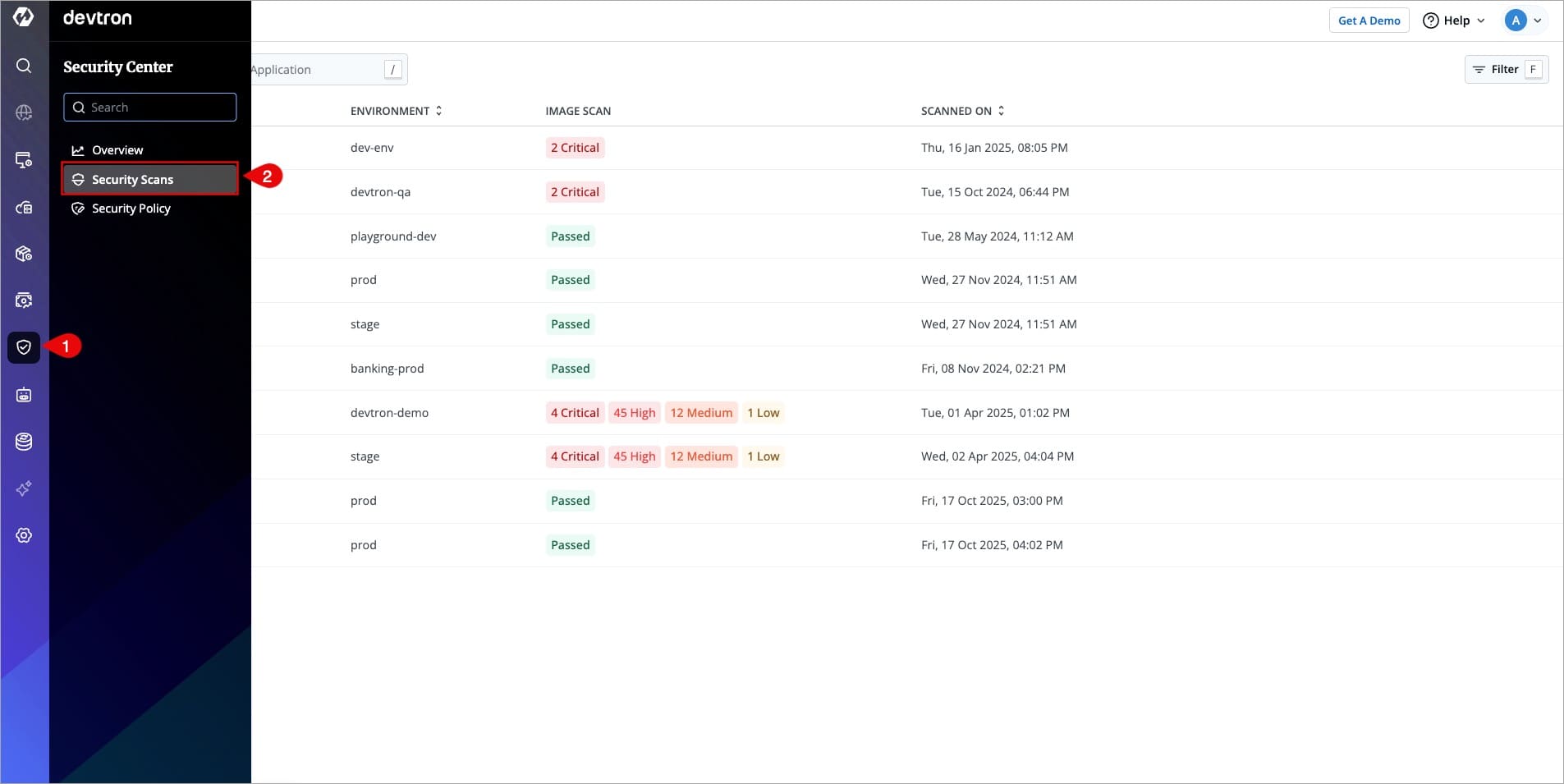
1. In the left sidebar, click **Security** and go to the `Security Scans` tab.
+ 
+
Figure 3: Navigate to Security Scans
+
:::caution Who Can Perform This Action?
Users need to have super-admin permission to view the 'Security Scans' page.
:::
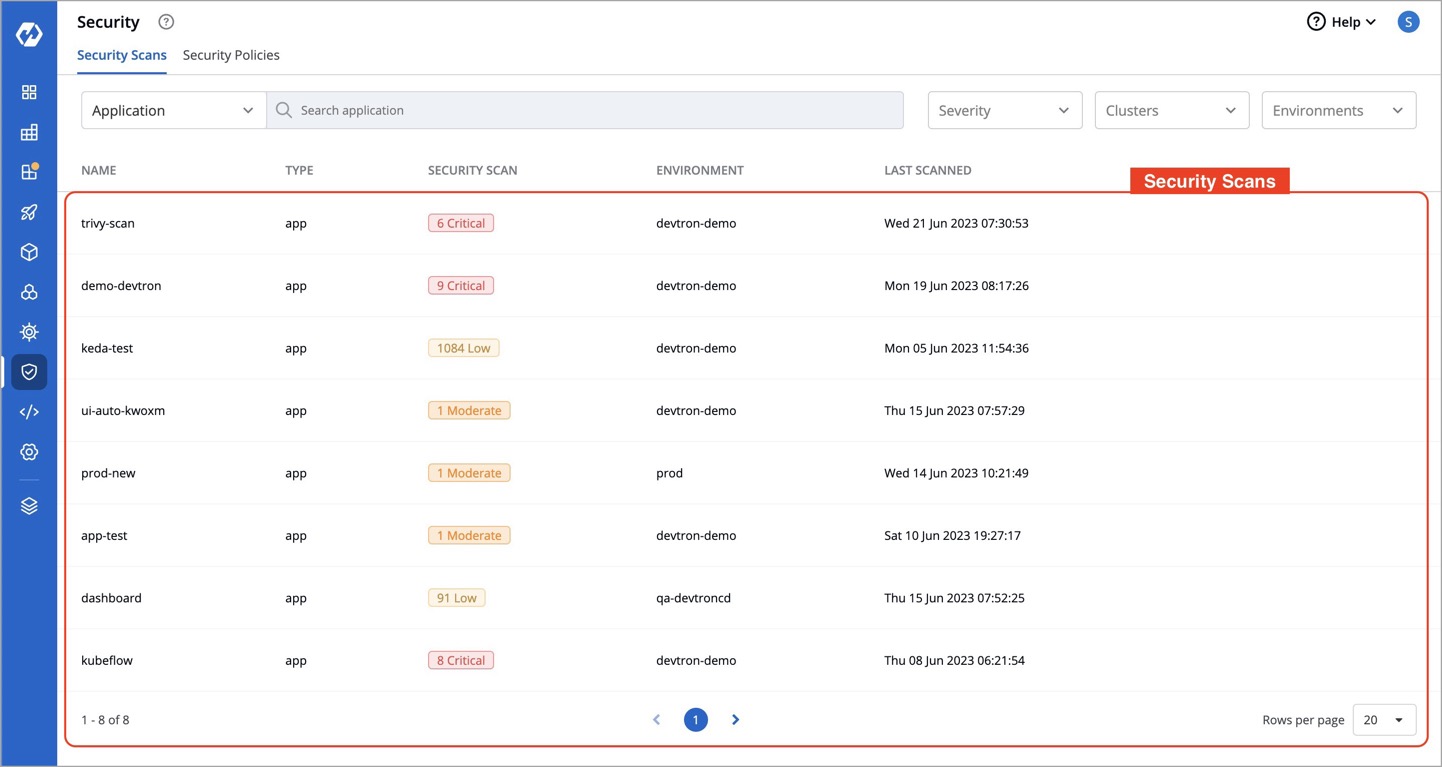
2. Select the desired application from the available list.
- 
-
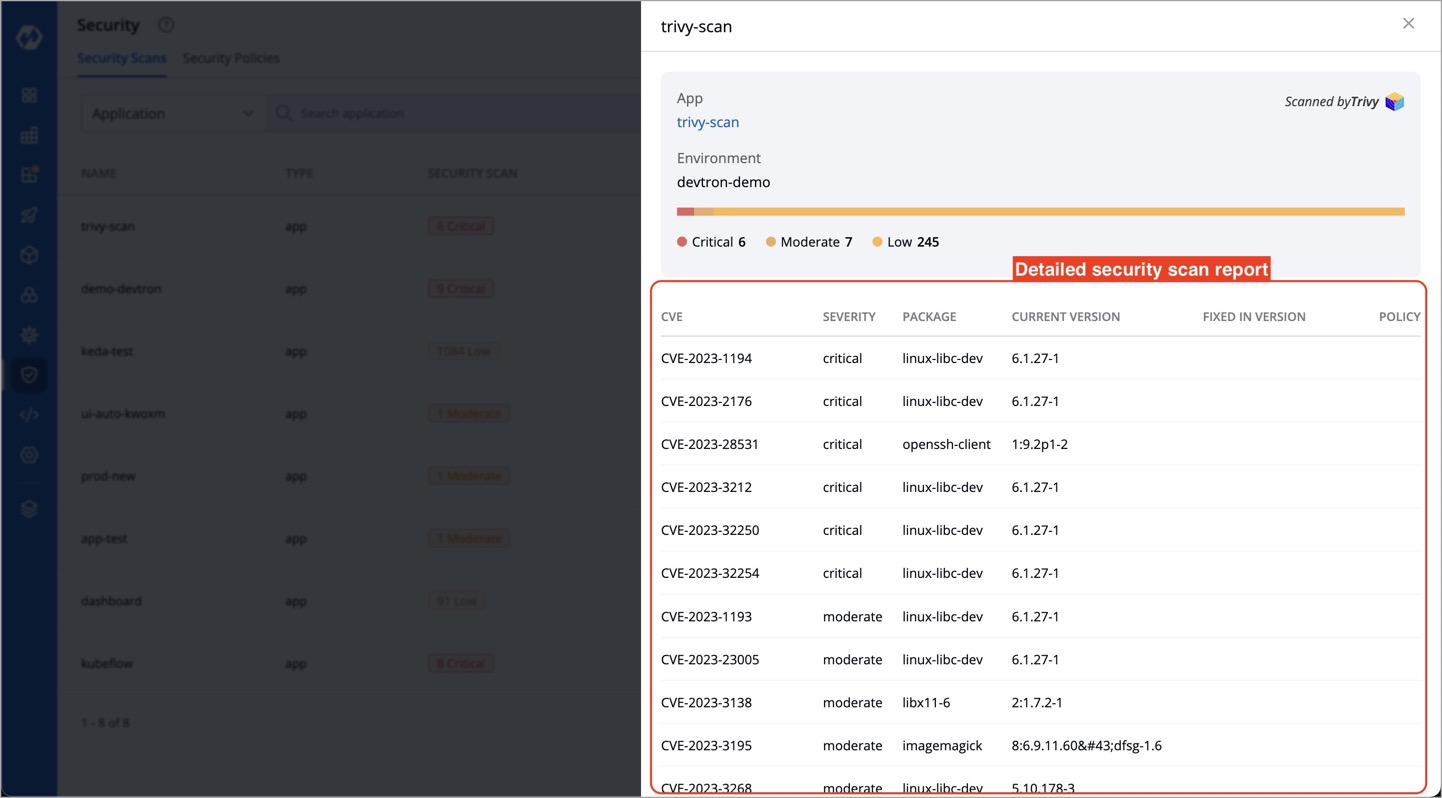
This action provides a detailed overview of the application's security scan, including CVE IDs, severity levels of vulnerabilities, and more, as shown below.
- 
-
Each vulnerability is identified by a **CVE ID** and categorized based on **Severity**, **Package**, **Current Version**, and **Fixed In Version**.
@@ -55,8 +58,8 @@ To access security vulnerability details during image deployment in Devtron, fol
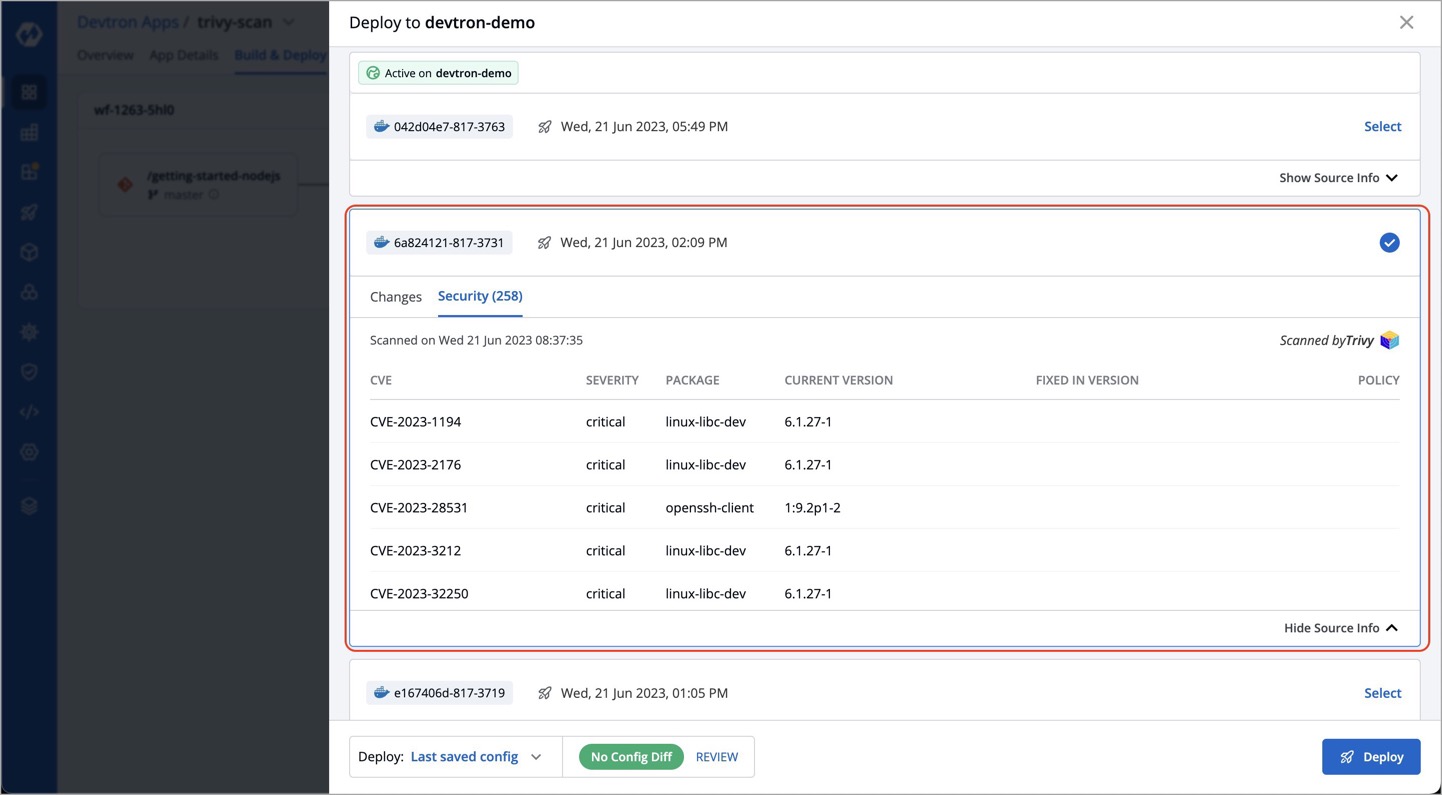
1. Click **Show Source Info** option for the desired image during the deployment process.
2. Navigate to the `Security` tab.
-
-
In the `Security` tab, you will find the security vulnerability details associated with the image.
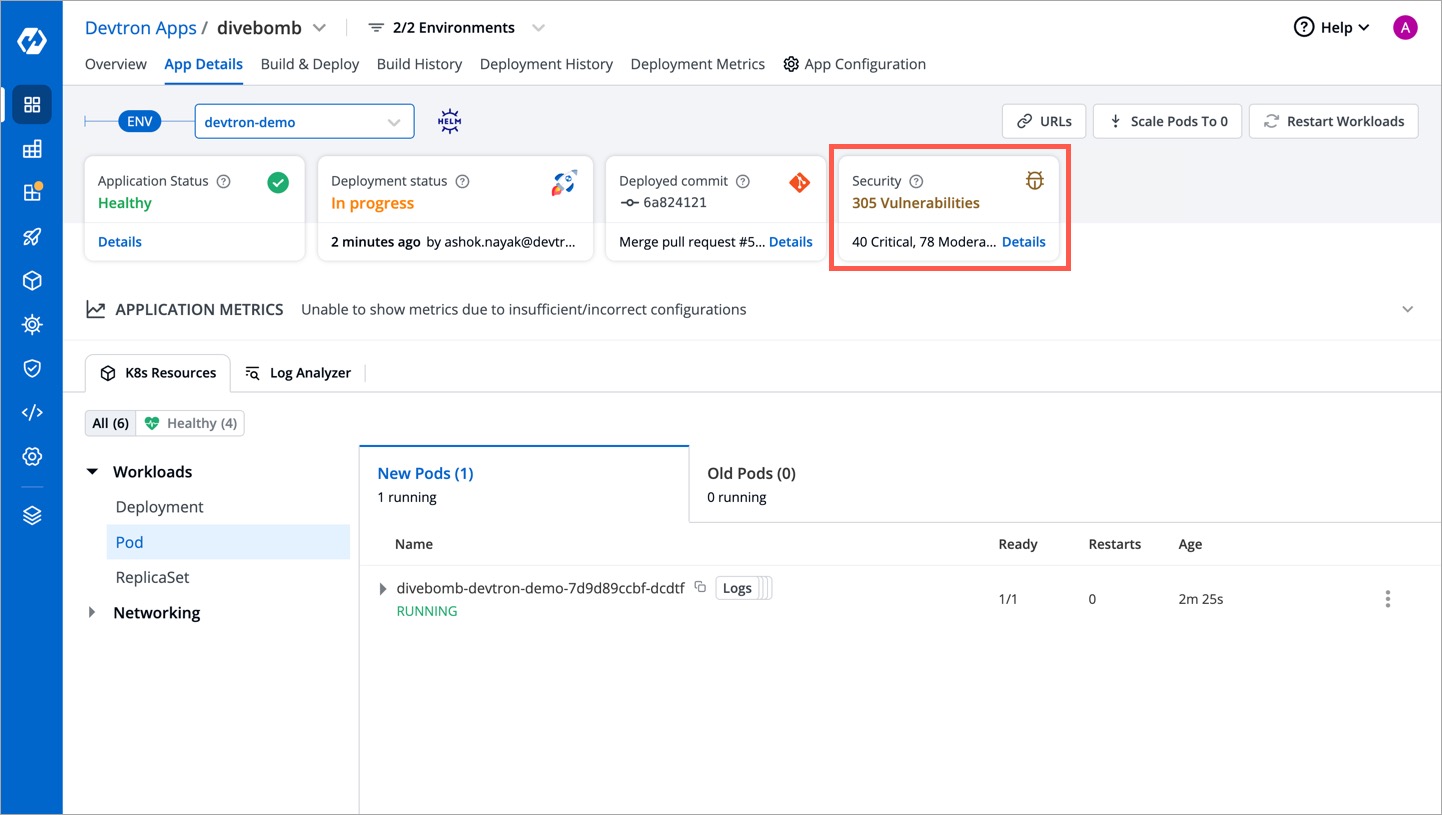
@@ -72,11 +75,11 @@ Devtron offers the capability to identify vulnerabilities even after an image ha
With this capability, Devtron empowers users to stay informed about the security vulnerabilities present in their deployed images.
-
-
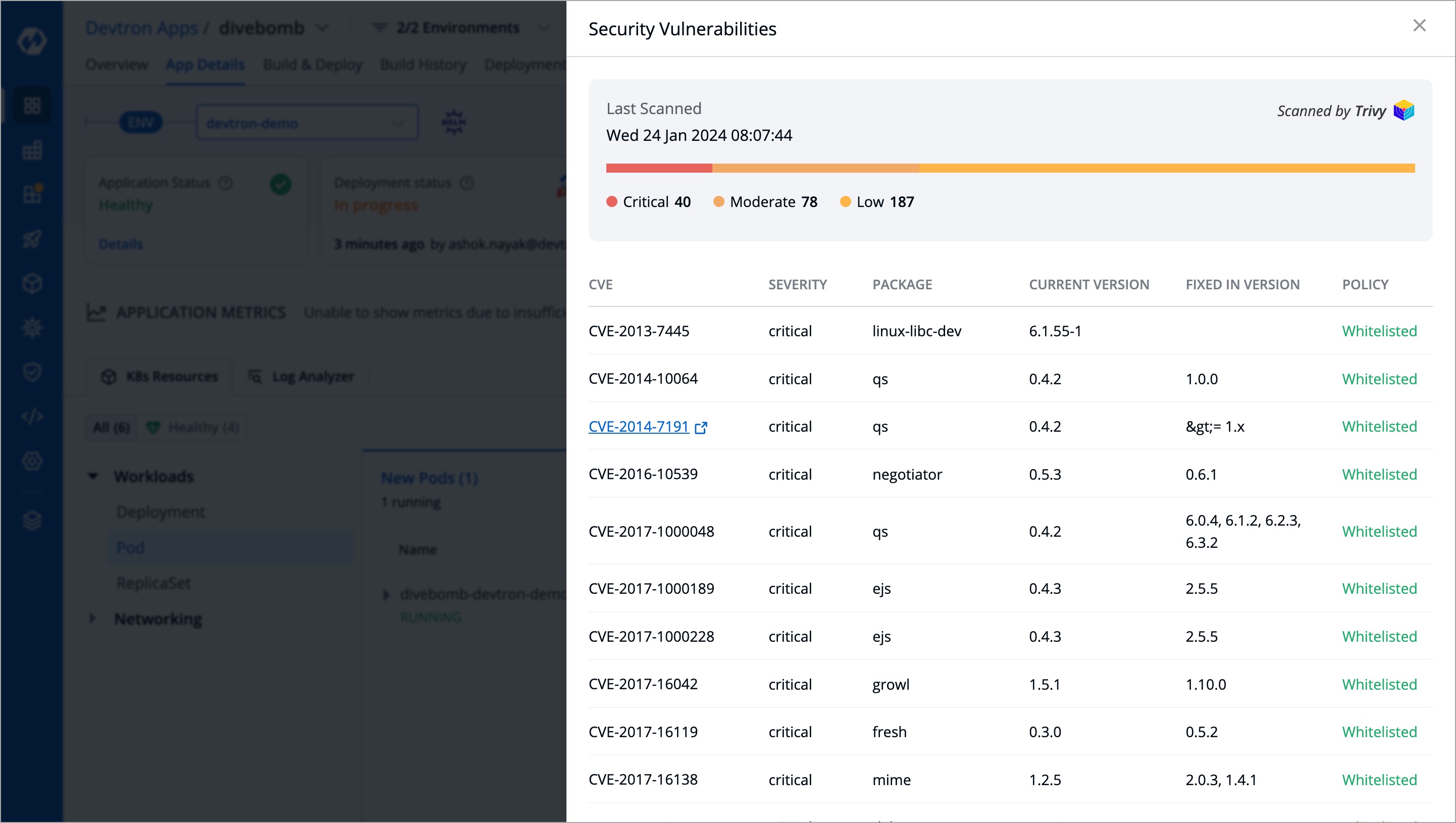
Clicking the 'Details' link in the security vulnerabilities report (shown above) reveals detailed information about those found within the deployed image.
-
-