diff --git a/README.en.md b/README.en.md
index fa2a296..0fa373b 100644
--- a/README.en.md
+++ b/README.en.md
@@ -6,16 +6,29 @@
ROS 2 examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-ROS1 examples is [here](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros_examples/blob/master/README.en.md).
-
-To run on Gazebo, click [here](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros2/README.en.md).
+For running in Gazebo (simulator), see the [rt-net/raspimouse_sim](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros2/README.md) packages.
 -## Supported ROS 2 distributions
+## Table of Contents
+
+- [raspimouse_ros2_examples](#raspimouse_ros2_examples)
+ - [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
+ - [Supported ROS distributions](#supported-ros-distributions)
+ - [Requirements](#requirements)
+ - [Installation](#installation)
+ - [Binary Installation](#binary-installation)
+ - [Source Build](#source-build)
+ - [How To Use Examples](#how-to-use-examples)
+ - [License](#license)
+ - [Contributing](#contributing)
+
+## Supported ROS distributions
-- [Humble](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
-- [Jazzy](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy) (This branch)
+### ROS 2
+
+- [Humble Hawksbill](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
+- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy)
## Requirements
@@ -25,66 +38,75 @@ To run on Gazebo, click [here](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros
- Ubuntu server 24.04
- Device Driver
- [rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse](https://github.com/rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
+
## Installation
+### Binary Installation
+
+```sh
+sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-raspimouse-ros2-examples
+```
+
+### Source Build
+
```sh
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+# Create workspace directory
+mkdir -p ~/ros2_ws/src && cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+
# Clone package
-$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
+git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
-$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
+rosdep install -r -y -i --from-paths .
# Build & Install
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws
-$ colcon build --symlink-install
-$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
+cd ~/ros2_ws
+colcon build --symlink-install
+source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
```
-## License
-
-This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see [LICENSE](./LICENSE) for details.
+## How to Use Examples
-## How To Use Examples
+Sample programs for the Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-- [joystick_control](#joystick_control)
-- [object_tracking](#object_tracking)
-- [line_follower](#line_follower)
-- [camera_line_follower](#camera_line_follower)
-- [SLAM](#slam)
-- [direction_controller](#direction_controller)
-
----
+- [Examples](#examples)
+ - [Joystick Control](#joystick-control)
+ - [Object Tracking](#object-tracking)
+ - [Line Follower](#line-follower)
+ - [Camera Line Follower](#camera-line-follower)
+ - [Direction Controller](#direction-controller)
+ - [SLAM & Navigation](#slam--navigation) (Relocated [rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2))
-### joystick_control
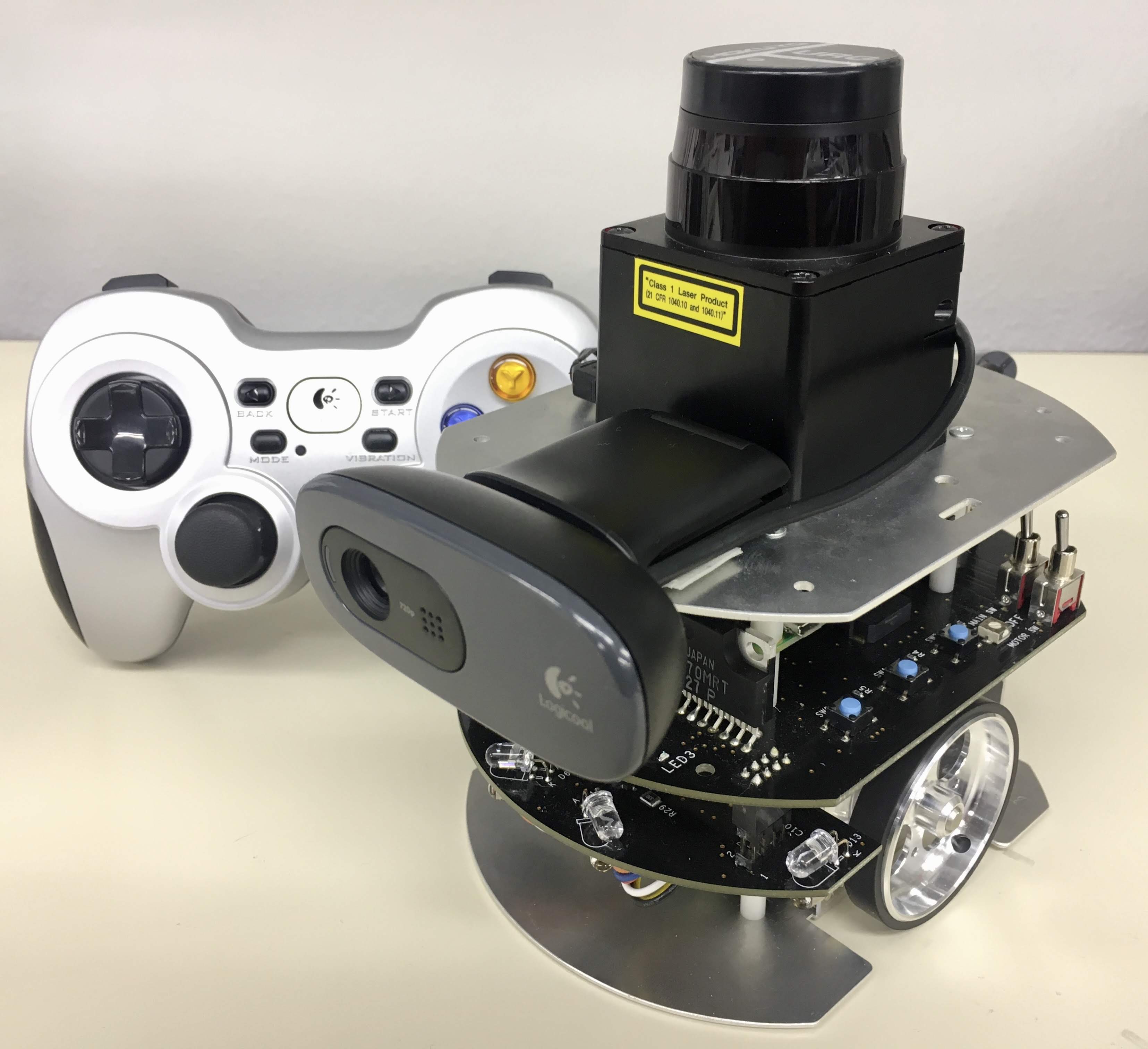
+### Joystick Control
-This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
+This is an example with a joystick controller to operate a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-#### Requirements
+
+
-## Supported ROS 2 distributions
+## Table of Contents
+
+- [raspimouse_ros2_examples](#raspimouse_ros2_examples)
+ - [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
+ - [Supported ROS distributions](#supported-ros-distributions)
+ - [Requirements](#requirements)
+ - [Installation](#installation)
+ - [Binary Installation](#binary-installation)
+ - [Source Build](#source-build)
+ - [How To Use Examples](#how-to-use-examples)
+ - [License](#license)
+ - [Contributing](#contributing)
+
+## Supported ROS distributions
-- [Humble](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
-- [Jazzy](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy) (This branch)
+### ROS 2
+
+- [Humble Hawksbill](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
+- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy)
## Requirements
@@ -25,66 +38,75 @@ To run on Gazebo, click [here](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros
- Ubuntu server 24.04
- Device Driver
- [rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse](https://github.com/rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
+
## Installation
+### Binary Installation
+
+```sh
+sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-raspimouse-ros2-examples
+```
+
+### Source Build
+
```sh
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+# Create workspace directory
+mkdir -p ~/ros2_ws/src && cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+
# Clone package
-$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
+git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
-$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
+rosdep install -r -y -i --from-paths .
# Build & Install
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws
-$ colcon build --symlink-install
-$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
+cd ~/ros2_ws
+colcon build --symlink-install
+source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
```
-## License
-
-This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see [LICENSE](./LICENSE) for details.
+## How to Use Examples
-## How To Use Examples
+Sample programs for the Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-- [joystick_control](#joystick_control)
-- [object_tracking](#object_tracking)
-- [line_follower](#line_follower)
-- [camera_line_follower](#camera_line_follower)
-- [SLAM](#slam)
-- [direction_controller](#direction_controller)
-
----
+- [Examples](#examples)
+ - [Joystick Control](#joystick-control)
+ - [Object Tracking](#object-tracking)
+ - [Line Follower](#line-follower)
+ - [Camera Line Follower](#camera-line-follower)
+ - [Direction Controller](#direction-controller)
+ - [SLAM & Navigation](#slam--navigation) (Relocated [rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2))
-### joystick_control
+### Joystick Control
-This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
+This is an example with a joystick controller to operate a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-#### Requirements
+
+  +
-- Joystick Controller
- - [Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710](https://gaming.logicool.co.jp/ja-jp/products/gamepads/f710-wireless-gamepad.html#940-0001440)
- - [SONY DUALSHOCK 3](https://www.jp.playstation.com/ps3/peripheral/cechzc2j.html)
+
+
-- Joystick Controller
- - [Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710](https://gaming.logicool.co.jp/ja-jp/products/gamepads/f710-wireless-gamepad.html#940-0001440)
- - [SONY DUALSHOCK 3](https://www.jp.playstation.com/ps3/peripheral/cechzc2j.html)
+
+Details
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
Launch nodes with the following command:
```sh
-# Use F710
+# Controlled directly on Raspberry Pi Mouse
+## Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
-
-# Use DUALSHOCK 3
+## Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
@@ -94,16 +116,15 @@ $ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
```
+#### Configure
+
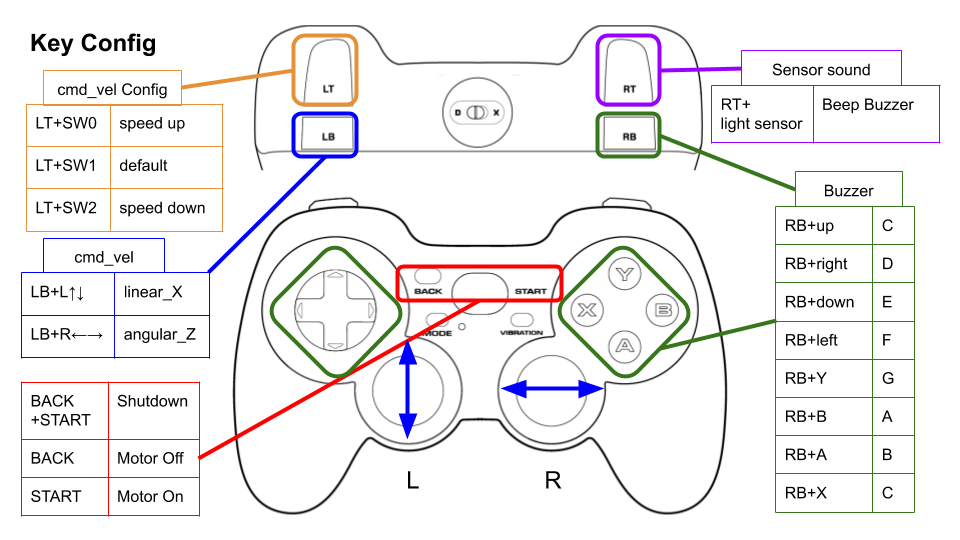
This picture shows the default key configuration.
To use Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710, set the input mode to __D__ (DirectInput Mode).
-
+ -#### Configure
-
-Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in [./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml) or
-[./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml).
+Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in [./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml) or [./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml).
```yaml
button_shutdown_1 : 8
@@ -115,19 +136,21 @@ button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/GswxdB8Ia0Y)
+
-#### Configure
-
-Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in [./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml) or
-[./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml).
+Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in [./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml) or [./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml).
```yaml
button_shutdown_1 : 8
@@ -115,19 +136,21 @@ button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/GswxdB8Ia0Y)
+
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
---
-### object_tracking
+### Object Tracking
+
+This is a code example for tracking an orange ball based on color information.
+The ball tracking is performed with a USB webcam and the OpenCV library.
- +
+ -This is an example to use RGB camera images and OpenCV library for object tracking.
+
-This is an example to use RGB camera images and OpenCV library for object tracking.
+
+Details
#### Requirements
@@ -135,19 +158,15 @@ This is an example to use RGB camera images and OpenCV library for object tracki
- [Logicool HD WEBCAM C310N](https://www.logicool.co.jp/ja-jp/product/hd-webcam-c310n)
- Camera mount
- [Raspberry Pi Mouse Option kit No.4 \[Webcam mount\]](https://www.rt-shop.jp/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1299_1395&products_id=3584&language=en)
-- Orange ball(Optional)
+- Orange ball (Optional)
- [Soft Ball (Orange)](https://www.rt-shop.jp/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1299_1307&products_id=3701&language=en)
- Software
- OpenCV
- v4l-utils
-#### Installation
-
-Install a camera mount and a web camera to Raspberry Pi Mouse, then connect the camera to the Raspberry Pi.
-
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
-Turn off automatic adjustment parameters of a camera (auto focus, auto while balance, etc.) with the following command:
+Disable the automatic camera adjustment parameters (autofocus, auto white balance, etc.) with the following command:
```sh
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src/raspimouse_ros2_examples/config
@@ -160,20 +179,20 @@ Then, launch nodes with the following command:
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples object_tracking.launch.py video_device:=/dev/video0
```
-This sample publishes two topics: `camera/color/image_raw` for the camera image and `result_image` for the object detection image.
-These images can be viewed with [RViz](https://index.ros.org/r/rviz/)
-or [rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/).
+This sample publishes two topics: `camera/color/image_raw` for the camera image and `result_image` for the object detection image.
+These images can be viewed with [RViz](https://index.ros.org/r/rviz/) or [rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/).
-**Viewing an image may cause the node to behave unstable and not publish cmd_vel or image topics.**
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> Viewing the images may cause the node to become unstable, resulting in cmd_vel or image topics not being published.
-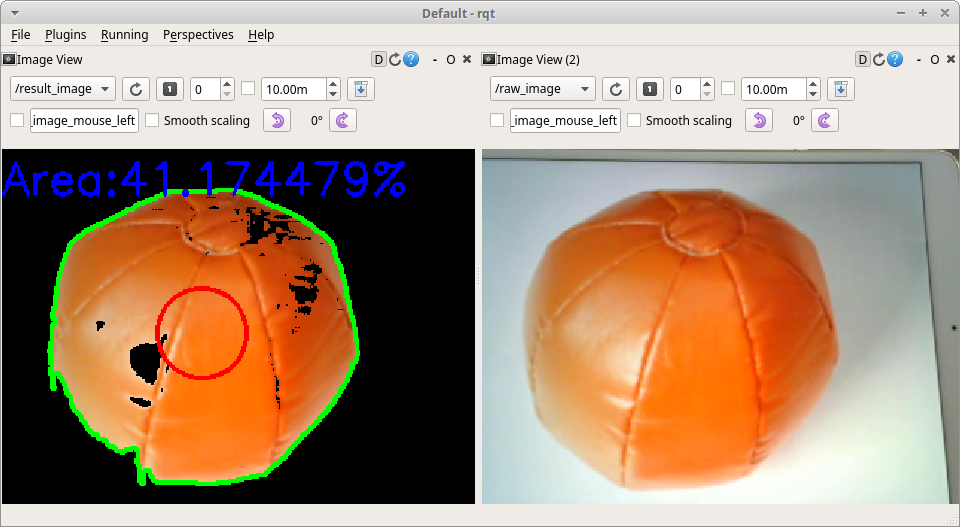 +
+ #### Configure
-Edit [`./src/object_tracking_component.cpp`](./src/object_tracking_component.cpp)
-to change a color of tracking target.
+Edit [`./src/object_tracking_component.cpp`](./src/object_tracking_component.cpp) to change the color of the tracking target.
-If the object detection accuracy is poor, adjust the camera exposure and parameters in the function
+If the object detection accuracy is poor, adjust the camera exposure and the parameters in the function.
```cpp
void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
@@ -183,31 +202,28 @@ void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(100, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(120, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Blue
```
-#### Videos
-
-[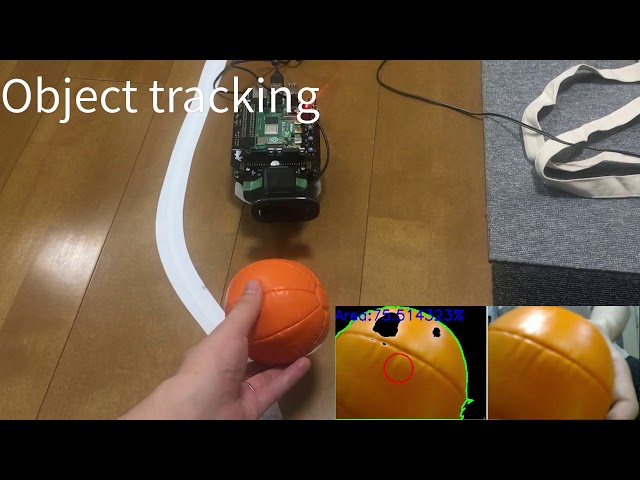](https://youtu.be/8lgmSTScP98)
+
#### Configure
-Edit [`./src/object_tracking_component.cpp`](./src/object_tracking_component.cpp)
-to change a color of tracking target.
+Edit [`./src/object_tracking_component.cpp`](./src/object_tracking_component.cpp) to change the color of the tracking target.
-If the object detection accuracy is poor, adjust the camera exposure and parameters in the function
+If the object detection accuracy is poor, adjust the camera exposure and the parameters in the function.
```cpp
void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
@@ -183,31 +202,28 @@ void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(100, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(120, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Blue
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/8lgmSTScP98)
+
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
---
-### line_follower
-
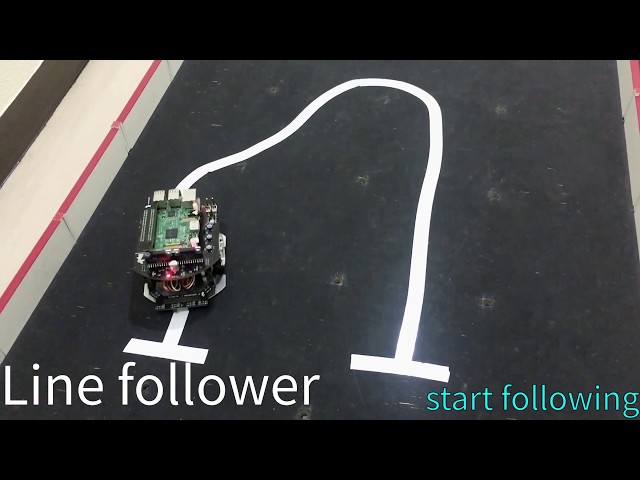
- +### Line Follower
This is an example for line following.
+
+### Line Follower
This is an example for line following.
+ +
+
+
+
+Details
+
#### Requirements
- Line following sensor
- [Raspberry Pi Mouse Option kit No.3 \[Line follower\]](https://www.rt-shop.jp/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1299_1395&products_id=3591&language=en)
- Field and lines for following (Optional)
-#### Installation
-
-Install a line following sensor unit to Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
Launch nodes with the following command:
@@ -215,46 +231,51 @@ Launch nodes with the following command:
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples line_follower.launch.py
```
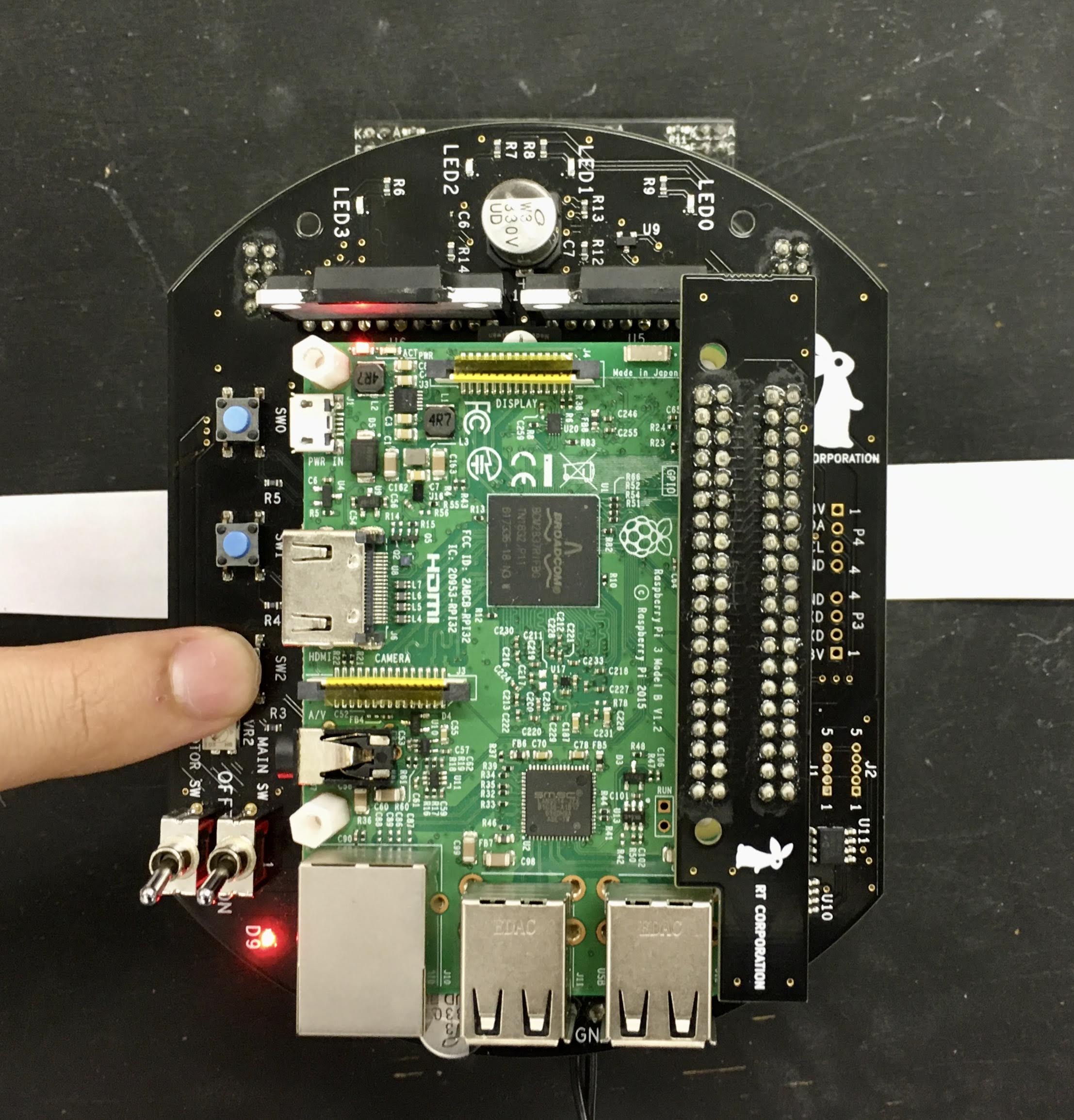
-Next, place Raspberry Pi Mouse on a field and press SW2 to sample sensor values on the field.
+Next, place the Raspberry Pi Mouse on a field and press SW2 to sample sensor values on the field.
+
+ -
- +Then, place the Raspberry Pi Mouse on the line and press SW1 to sample sensor values.
-Then, place Raspberry Pi Mouse to detect a line and press SW1 to sample sensor values on the line.
+
+Then, place the Raspberry Pi Mouse on the line and press SW1 to sample sensor values.
-Then, place Raspberry Pi Mouse to detect a line and press SW1 to sample sensor values on the line.
+ -
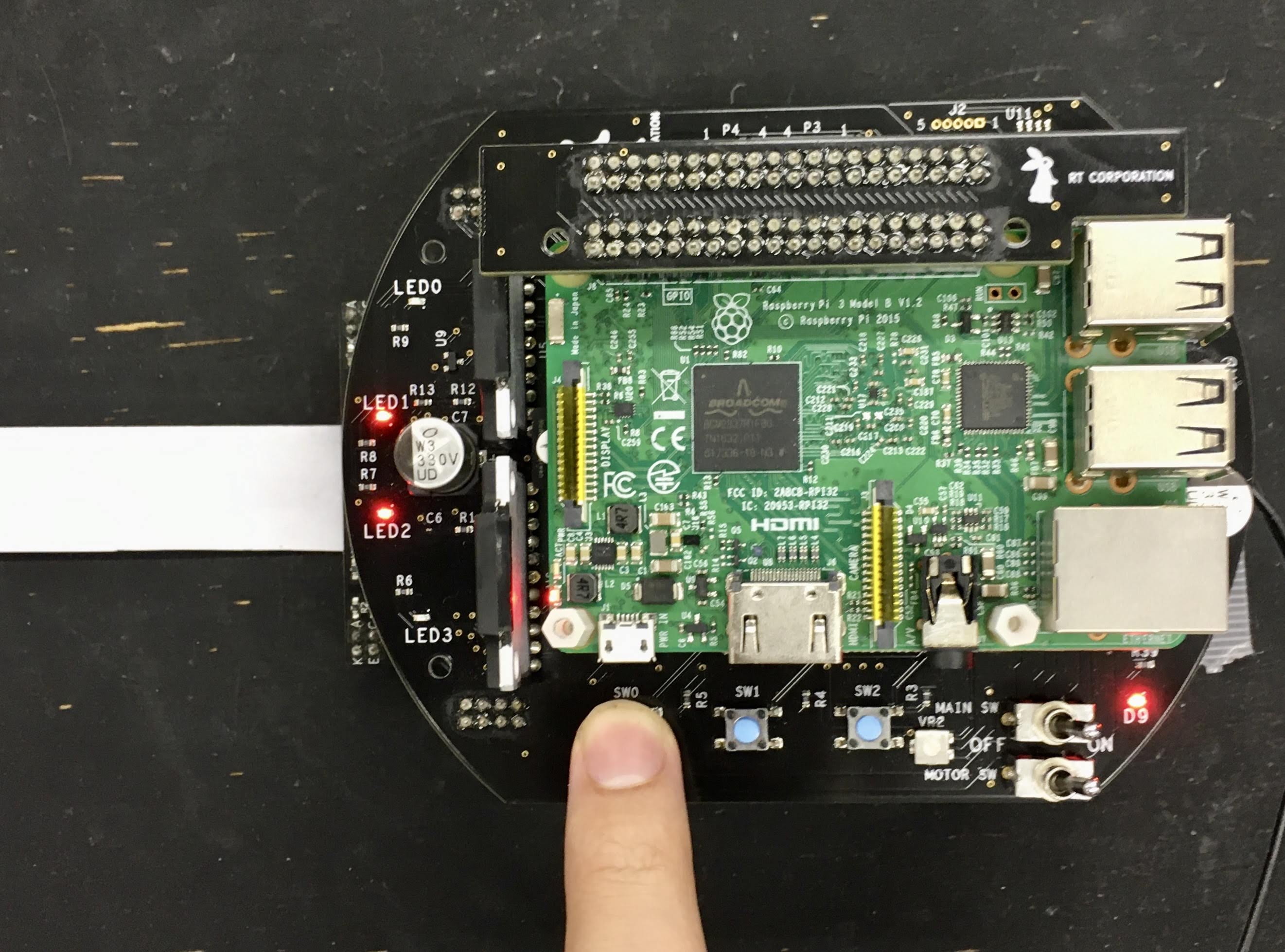
- +Finally, place the Raspberry Pi Mouse on the line and press SW0 to start line following.
-Last, place Raspberry Pi Mouse on the line and press SW0 to start line following.
+
+Finally, place the Raspberry Pi Mouse on the line and press SW0 to start line following.
-Last, place Raspberry Pi Mouse on the line and press SW0 to start line following.
+ -
- +Press SW0 again to stop the line following.
-Press SW0 again to stop the following.
+
+
+Press SW0 again to stop the line following.
-Press SW0 again to stop the following.
+
+  +
#### Configure
-Edit [`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp) to change a velocity command.
+Edit [`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp) to change the robot velocity.
```cpp
void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
{
- const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // m/s
- const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // rad/s
- const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
+ const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // [m/s]
+ const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // [rad/s]
+ const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // [rad/s]
```
-#### Videos
+
+
#### Configure
-Edit [`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp) to change a velocity command.
+Edit [`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp) to change the robot velocity.
```cpp
void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
{
- const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // m/s
- const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // rad/s
- const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
+ const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // [m/s]
+ const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // [rad/s]
+ const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // [rad/s]
```
-#### Videos
+
-[](https://youtu.be/oPm0sW2V_tY)
-
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
---
-### camera_line_follower
-
-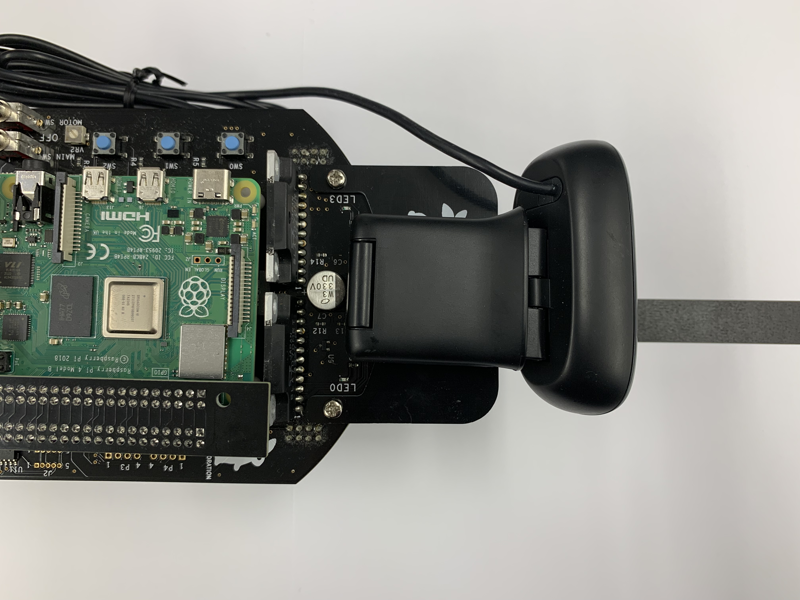 +### Camera Line Follower
This is an example for line following by RGB camera.
+
+### Camera Line Follower
This is an example for line following by RGB camera.
+ +
+
+
+
+Details
+
#### Requirements
- Web camera
@@ -262,42 +283,40 @@ This is an example for line following by RGB camera.
- Camera mount
- [Raspberry Pi Mouse Option kit No.4 \[Webcam mount\]](https://www.rt-shop.jp/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1299_1395&products_id=3584&language=en)
-#### Installation
-
-Install a camera mount and a web camera to Raspberry Pi Mouse, then connect the camera to the Raspberry Pi.
-
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
-Then, launch nodes with the following command:
+Launch nodes with the following command:
```sh
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples camera_line_follower.launch.py video_device:=/dev/video0
```
Place Raspberry Pi Mouse on the line and press SW2 to start line following.
-
-Press SW0 to stop the following.
+Press SW0 to stop the line following.
This sample publishes two topics: `camera/color/image_raw` for the camera image and `result_image` for the object detection image.
-These images can be viewed with [RViz](https://index.ros.org/r/rviz/)
-or [rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/).
+These images can be viewed in [RViz](https://index.ros.org/r/rviz/) or [rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/).
-**Viewing an image may cause the node to behave unstable and not publish cmd_vel or image topics.**
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> Viewing the images may cause the node to become unstable, resulting in cmd_vel or image topics not being published.
+
+#### Configure
-**If the line detection accuracy is poor, please adjust the camera's exposure and white balance.**
+If the line detection accuracy is poor, adjust the camera exposure and white balance.
-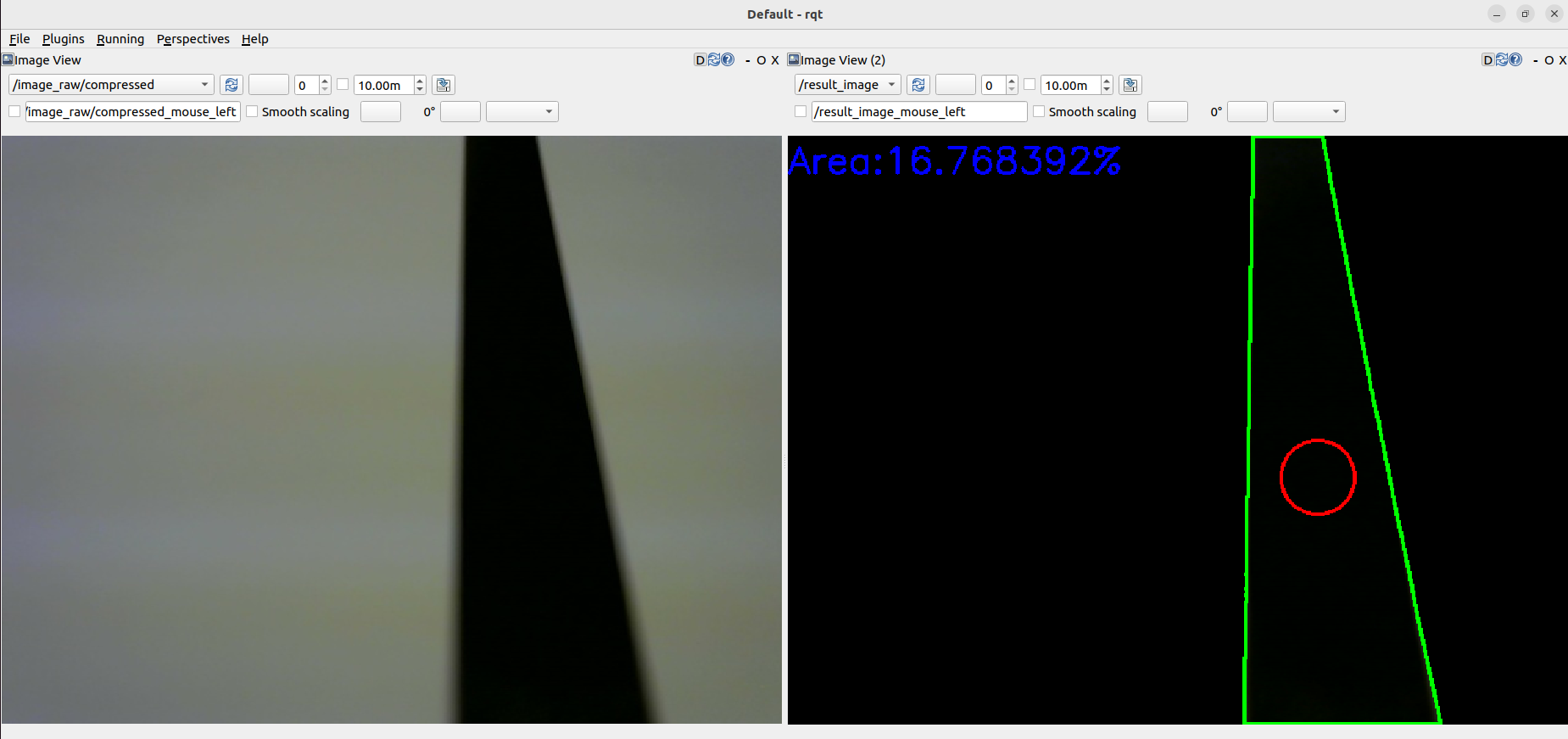 +
+ #### Parameters
- `max_brightness`
- Type: `int`
- Default: 90
- - Maximum threshold value for image binarisation.
+ - Maximum threshold value for image binarization.
- `min_brightness`
- Type: `int`
- Default: 0
- - Minimum threshold value for image binarisation.
+ - Minimum threshold value for image binarization.
- `max_linear_vel`
- Type: `double`
- Default: 0.05
@@ -306,34 +325,31 @@ or [rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/).
- Type: `double`
- Default: 0.8
- Maximum angular velocity.
-- `area_threthold`
+- `area_threshold`
- Type: `double`
- Default: 0.20
- Threshold value of the area of the line to start following.
+Run the following command to set the parameters:
+
```sh
ros2 param set /camera_follower max_brightness 80
```
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
-
----
-
-### SLAM
-
-
#### Parameters
- `max_brightness`
- Type: `int`
- Default: 90
- - Maximum threshold value for image binarisation.
+ - Maximum threshold value for image binarization.
- `min_brightness`
- Type: `int`
- Default: 0
- - Minimum threshold value for image binarisation.
+ - Minimum threshold value for image binarization.
- `max_linear_vel`
- Type: `double`
- Default: 0.05
@@ -306,34 +325,31 @@ or [rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/).
- Type: `double`
- Default: 0.8
- Maximum angular velocity.
-- `area_threthold`
+- `area_threshold`
- Type: `double`
- Default: 0.20
- Threshold value of the area of the line to start following.
+Run the following command to set the parameters:
+
```sh
ros2 param set /camera_follower max_brightness 80
```
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
-
----
-
-### SLAM
-
- +
+
-SLAM and Navigation examples for Raspberry Pi Mouse is [here](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2).
-
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
---
-### direction_controller
+### Direction Controller
+
+This is an example of using an IMU sensor for direction control.
-
 +
+
 -This is an example to use an IMU sensor for direction control.
+
-This is an example to use an IMU sensor for direction control.
+
+Details
#### Requirements
@@ -342,79 +358,87 @@ This is an example to use an IMU sensor for direction control.
- RT-USB-9axisIMU ROS Package.
- https://github.com/rt-net/rt_usb_9axisimu_driver
-#### Installation
-
-Install the IMU sensor module to the LiDAR mount.
-
- -
-Install the LiDAR mount to the Raspberry Pi Mouse.
+Attach the LiDAR mount with the IMU sensor module to the Raspberry Pi Mouse. For details, refer to the [Multi-LiDAR Mount Assembly Manual (in Japanese)](https://rt-net.jp/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/RaspberryPiMouseOptionKitManual_No08.pdf).
-
-
-Install the LiDAR mount to the Raspberry Pi Mouse.
+Attach the LiDAR mount with the IMU sensor module to the Raspberry Pi Mouse. For details, refer to the [Multi-LiDAR Mount Assembly Manual (in Japanese)](https://rt-net.jp/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/RaspberryPiMouseOptionKitManual_No08.pdf).
- +
+
 -#### How to use
+#### Usage
-Launch nodes on Raspberry Pi Mouse with the following command:
+Launch nodes on the Raspberry Pi Mouse with the following command:
```sh
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples direction_controller.launch.py
```
-Then, press SW0 ~ SW2 to change the control mode as following,
+Then, press SW0–SW2 to change the control mode as follows:
-- SW0: Calibrate the gyroscope bias and reset a heading angle of Raspberry Pi Mouse to 0 rad.
-- SW1: Start a direction control to keep the heading angle to 0 rad.
- - Press SW0 ~ SW2 or tilt the body to sideways to finish the control.
-- SW2: Start a direction control to change the heading angle to `-π ~ π rad`.
- - Press SW0 ~ SW2 or tilt the body to sideways to finish the control.
+- SW0: Calibrate the gyroscope bias and reset the Raspberry Pi Mouse's heading angle to `0`[rad].
+- SW1: Start direction control to keep the heading angle at `0`[rad].
+ - Press SW0–SW2 or tilt the body sideways to terminate the control.
+- SW2: Start direction control to change the heading angle between `-π` and `π`[rad].
+ - Press SW0–SW2 or tilt the body sideways to terminate the control.
-### Troubleshooting
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> The IMU might not be connected correctly.
+> If this happens, unplug and reconnect the USB cable, then run the above command again.
-The IMU might not be connected correctly.
-Reconnect the USB cable several times and re-execute the above command.
+#### Parameters
-#### Configure
+- `p_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
+ - Proportional gain of a PID controller for the direction control
+- `i_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
+ - Integral gain of a PID controller for the direction control
+- `d_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
+ - Derivative gain of a PID controller for the direction control
+- `target_angle`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
+ - Target angle for the SW1 (direction control mode).
+#### Published
-Set parameters to configure gains of a PID controller for the direction control.
+- `heading_angle`
+ - Type: `std_msgs/Float64`
+ - Heading angle of the robot calculated from IMU module sensor values
-```sh
-$ ros2 param set /direction_controller p_gain 10.0
-Set parameter successful
+
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
-Launch nodes on Raspberry Pi Mouse with the following command:
+Launch nodes on the Raspberry Pi Mouse with the following command:
```sh
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples direction_controller.launch.py
```
-Then, press SW0 ~ SW2 to change the control mode as following,
+Then, press SW0–SW2 to change the control mode as follows:
-- SW0: Calibrate the gyroscope bias and reset a heading angle of Raspberry Pi Mouse to 0 rad.
-- SW1: Start a direction control to keep the heading angle to 0 rad.
- - Press SW0 ~ SW2 or tilt the body to sideways to finish the control.
-- SW2: Start a direction control to change the heading angle to `-π ~ π rad`.
- - Press SW0 ~ SW2 or tilt the body to sideways to finish the control.
+- SW0: Calibrate the gyroscope bias and reset the Raspberry Pi Mouse's heading angle to `0`[rad].
+- SW1: Start direction control to keep the heading angle at `0`[rad].
+ - Press SW0–SW2 or tilt the body sideways to terminate the control.
+- SW2: Start direction control to change the heading angle between `-π` and `π`[rad].
+ - Press SW0–SW2 or tilt the body sideways to terminate the control.
-### Troubleshooting
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> The IMU might not be connected correctly.
+> If this happens, unplug and reconnect the USB cable, then run the above command again.
-The IMU might not be connected correctly.
-Reconnect the USB cable several times and re-execute the above command.
+#### Parameters
-#### Configure
+- `p_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
+ - Proportional gain of a PID controller for the direction control
+- `i_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
+ - Integral gain of a PID controller for the direction control
+- `d_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
+ - Derivative gain of a PID controller for the direction control
+- `target_angle`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
+ - Target angle for the SW1 (direction control mode).
+#### Published
-Set parameters to configure gains of a PID controller for the direction control.
+- `heading_angle`
+ - Type: `std_msgs/Float64`
+ - Heading angle of the robot calculated from IMU module sensor values
-```sh
-$ ros2 param set /direction_controller p_gain 10.0
-Set parameter successful
+
-$ ros2 param set /direction_controller i_gain 0.5
-Set parameter successful
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
-$ ros2 param set /direction_controller d_gain 0.0
-Set parameter successful
-```
-#### Parameters
+---
-- p_gain
- - Proportional gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- - type: double
-- i_gain
- - Integral gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
- - type: double
-- d_gain
- - Derivative gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- - type: double
-- target_angle
- - Target angle for the SW1 control mode.
- - default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
- - type: double
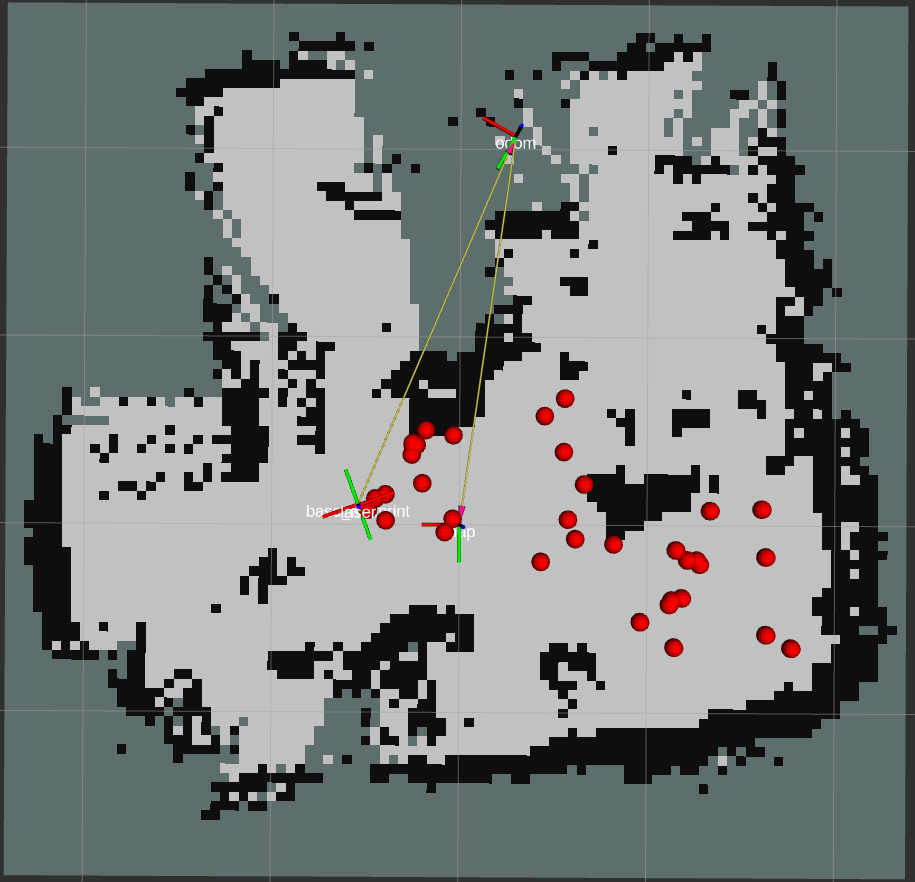
+### SLAM & Navigation
+
+This is an example of SLAM & Navigation.
+
+ +
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> The sample for SLAM and Navigation with Raspberry Pi Mouse has been moved to [rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2).
-#### Publish topics
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+
+---
+
+## License
-- heading_angle
- - Heading angle of the robot that calculated from the IMU module sensor values.
- - type: std_msgs/Float64
+(C) 2022 RT Corporation
-#### Videos
+Each file is licensed as stated in their headers.
+If no license is specified, the file is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
+The full license text is available in the [LICENSE](./LICENSE) file or at [https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0](https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
-[](https://youtu.be/ghcCYOh9_MM)
+## Contributing
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+- This software is open source, but its development is not open.
+- This software is essentially provided as open source software on an “AS IS” (in its current state) basis.
+- No free support is available for this software.
+- Requests for bug fixes and corrections of typographical errors are always accepted; however, requests for additional features will be subject to our internal guidelines. For further details, please refer to the [Contribution Guidelines](https://github.com/rt-net/.github/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 7a1924f..28aa67a 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -6,16 +6,29 @@
Raspberry Pi MouseのROS 2サンプルコード集です。
-ROS1のサンプルコード集は[こちら](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros_examples/blob/master/README.md)。
-
-Gazebo(シミュレータ)でも動作します。詳細は[こちら](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros2/README.md)。
+Gazebo(シミュレータ)で動作させる場合は、[rt-net/raspimouse_sim](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros2/README.md)パッケージを参照してください。
+
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> The sample for SLAM and Navigation with Raspberry Pi Mouse has been moved to [rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2).
-#### Publish topics
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+
+---
+
+## License
-- heading_angle
- - Heading angle of the robot that calculated from the IMU module sensor values.
- - type: std_msgs/Float64
+(C) 2022 RT Corporation
-#### Videos
+Each file is licensed as stated in their headers.
+If no license is specified, the file is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
+The full license text is available in the [LICENSE](./LICENSE) file or at [https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0](https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0).
-[](https://youtu.be/ghcCYOh9_MM)
+## Contributing
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+- This software is open source, but its development is not open.
+- This software is essentially provided as open source software on an “AS IS” (in its current state) basis.
+- No free support is available for this software.
+- Requests for bug fixes and corrections of typographical errors are always accepted; however, requests for additional features will be subject to our internal guidelines. For further details, please refer to the [Contribution Guidelines](https://github.com/rt-net/.github/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 7a1924f..28aa67a 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -6,16 +6,29 @@
Raspberry Pi MouseのROS 2サンプルコード集です。
-ROS1のサンプルコード集は[こちら](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros_examples/blob/master/README.md)。
-
-Gazebo(シミュレータ)でも動作します。詳細は[こちら](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros2/README.md)。
+Gazebo(シミュレータ)で動作させる場合は、[rt-net/raspimouse_sim](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros2/README.md)パッケージを参照してください。
 -## Supported ROS 2 distributions
+## Table of Contents
+
+- [raspimouse_ros2_examples](#raspimouse_ros2_examples)
+ - [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
+ - [Supported ROS distributions](#supported-ros-distributions)
+ - [Requirements](#requirements)
+ - [Installation](#installation)
+ - [Binary Installation](#binary-installation)
+ - [Source Build](#source-build)
+ - [How To Use Examples](#how-to-use-examples)
+ - [License](#license)
+ - [Contributing](#contributing)
+
+## Supported ROS distributions
-- [Humble](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
-- [Jazzy](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy) (This branch)
+### ROS 2
+
+- [Humble Hawksbill](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
+- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy)
## Requirements
@@ -25,67 +38,75 @@ Gazebo(シミュレータ)でも動作します。詳細は[こちら](https
- Ubuntu server 24.04
- Device Driver
- [rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse](https://github.com/rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
+
## Installation
+### Binary Installation
+
+```sh
+sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-raspimouse-ros2-examples
+```
+
+### Source Build
+
```sh
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+# Create workspace directory
+mkdir -p ~/ros2_ws/src && cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+
# Clone package
-$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
+git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
-$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
+rosdep install -r -y -i --from-paths .
# Build & Install
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws
-$ colcon build --symlink-install
-$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
+cd ~/ros2_ws
+colcon build --symlink-install
+source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
```
-## License
-
-このリポジトリはApache 2.0ライセンスの元、公開されています。
-ライセンスについては[LICENSE](./LICENSE)を参照ください。
+## How to Use Examples
-## How To Use Examples
+Raspberry Pi Mouseを動作させるサンプル集です。
-- [joystick_control](#joystick_control)
-- [object_tracking](#object_tracking)
-- [line_follower](#line_follower)
-- [camera_line_follower](#camera_line_follower)
-- [SLAM](#slam)
-- [direction_controller](#direction_controller)
-
----
+- Examples
+ - [Joystick Control](#joystick-control)
+ - [Object Tracking](#object-tracking)
+ - [Line Follower](#line-follower)
+ - [Camera Line Follower](#camera-line-follower)
+ - [Direction Controller](#direction-controller)
+ - [SLAM & Navigation](#slam--navigation) ([rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2)に移動しました)
-### joystick_control
+### Joystick Control
ジョイスティックコントローラでRaspberryPiMouseを動かすコード例です。
-#### Requirements
+
+
-## Supported ROS 2 distributions
+## Table of Contents
+
+- [raspimouse_ros2_examples](#raspimouse_ros2_examples)
+ - [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
+ - [Supported ROS distributions](#supported-ros-distributions)
+ - [Requirements](#requirements)
+ - [Installation](#installation)
+ - [Binary Installation](#binary-installation)
+ - [Source Build](#source-build)
+ - [How To Use Examples](#how-to-use-examples)
+ - [License](#license)
+ - [Contributing](#contributing)
+
+## Supported ROS distributions
-- [Humble](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
-- [Jazzy](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy) (This branch)
+### ROS 2
+
+- [Humble Hawksbill](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
+- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy)
## Requirements
@@ -25,67 +38,75 @@ Gazebo(シミュレータ)でも動作します。詳細は[こちら](https
- Ubuntu server 24.04
- Device Driver
- [rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse](https://github.com/rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
+
## Installation
+### Binary Installation
+
+```sh
+sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-raspimouse-ros2-examples
+```
+
+### Source Build
+
```sh
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+# Create workspace directory
+mkdir -p ~/ros2_ws/src && cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+
# Clone package
-$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
+git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
-$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
+rosdep install -r -y -i --from-paths .
# Build & Install
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws
-$ colcon build --symlink-install
-$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
+cd ~/ros2_ws
+colcon build --symlink-install
+source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
```
-## License
-
-このリポジトリはApache 2.0ライセンスの元、公開されています。
-ライセンスについては[LICENSE](./LICENSE)を参照ください。
+## How to Use Examples
-## How To Use Examples
+Raspberry Pi Mouseを動作させるサンプル集です。
-- [joystick_control](#joystick_control)
-- [object_tracking](#object_tracking)
-- [line_follower](#line_follower)
-- [camera_line_follower](#camera_line_follower)
-- [SLAM](#slam)
-- [direction_controller](#direction_controller)
-
----
+- Examples
+ - [Joystick Control](#joystick-control)
+ - [Object Tracking](#object-tracking)
+ - [Line Follower](#line-follower)
+ - [Camera Line Follower](#camera-line-follower)
+ - [Direction Controller](#direction-controller)
+ - [SLAM & Navigation](#slam--navigation) ([rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2)に移動しました)
-### joystick_control
+### Joystick Control
ジョイスティックコントローラでRaspberryPiMouseを動かすコード例です。
-#### Requirements
+
+  +
-- Joystick Controller
- - [Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710](https://gaming.logicool.co.jp/ja-jp/products/gamepads/f710-wireless-gamepad.html#940-0001440)
- - [SONY DUALSHOCK 3](https://www.jp.playstation.com/ps3/peripheral/cechzc2j.html)
+
+
-- Joystick Controller
- - [Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710](https://gaming.logicool.co.jp/ja-jp/products/gamepads/f710-wireless-gamepad.html#940-0001440)
- - [SONY DUALSHOCK 3](https://www.jp.playstation.com/ps3/peripheral/cechzc2j.html)
+
+Details
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
```sh
-# Use F710
+# Controlled directly on Raspberry Pi Mouse
+## Use F710
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=f710 mouse:=true
-
-# Use DUALSHOCK 3
+## Use DUALSHOCK 3
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py joydev:="/dev/input/js0" joyconfig:=dualshock3 mouse:=true
# Control from remote computer
@@ -95,16 +116,15 @@ $ ros2 run raspimouse raspimouse
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples teleop_joy.launch.py mouse:=false
```
+#### Configure
+
デフォルトのキー割り当てはこちらです。
Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710を使う場合はモード切替スイッチを __D__ (DirectInput Mode)に設定します。
-
+ -#### Configure
-
-[./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml)、[./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml)
-のキー番号を編集することで、キー割り当てを変更できます。
+[./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml)、[./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml)のキー番号を編集することで、キー割り当てを変更できます。
```yaml
button_shutdown_1 : 8
@@ -116,21 +136,22 @@ button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/GswxdB8Ia0Y)
+
-#### Configure
-
-[./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml)、[./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml)
-のキー番号を編集することで、キー割り当てを変更できます。
+[./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml)、[./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml)のキー番号を編集することで、キー割り当てを変更できます。
```yaml
button_shutdown_1 : 8
@@ -116,21 +136,22 @@ button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/GswxdB8Ia0Y)
+
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
---
-### object_tracking
-
- +### Object Tracking
色情報をもとにオレンジ色のボールの追跡を行うコード例です。
USB接続のWebカメラとOpenCVを使ってボール追跡をします。
+
+### Object Tracking
色情報をもとにオレンジ色のボールの追跡を行うコード例です。
USB接続のWebカメラとOpenCVを使ってボール追跡をします。
+ +
+
+
+
+Details
+
#### Requirements
- Webカメラ
@@ -143,13 +164,9 @@ USB接続のWebカメラとOpenCVを使ってボール追跡をします。
- OpenCV
- v4l-utils
-#### Installation
-
-Raspberry Pi Mouseにカメラマウントを取り付け、WebカメラをRaspberry Piに接続します。
-
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
-次のスクリプトを実行して、カメラの自動調節機能(自動露光,オートホワイトバランス等)を切ります。
+次のスクリプトを実行して、カメラの自動調節機能(自動露光、オートホワイトバランス等)を切ります。
```sh
$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src/raspimouse_ros2_examples/config
@@ -163,13 +180,13 @@ $ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples object_tracking.launch.py video_device:=/
```
カメラ画像は`camera/color/image_raw`、物体検出画像は`result_image`というトピックとして発行されます。
-これらの画像は[RViz](https://index.ros.org/r/rviz/)
-や[rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/)
-で表示できます。
+これらの画像は[RViz](https://index.ros.org/r/rviz/)や[rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/)で表示できます。
-**画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。**
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> 画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。
- +
+ #### Configure
@@ -187,31 +204,28 @@ void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(100, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(120, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Blue
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/8lgmSTScP98)
+
#### Configure
@@ -187,31 +204,28 @@ void Tracker::tracking(const cv::Mat & input_frame, cv::Mat & result_frame)
// cv::inRange(hsv, cv::Scalar(100, 100, 100), cv::Scalar(120, 255, 255), extracted_bin); // Blue
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/8lgmSTScP98)
+
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
---
-### line_follower
-
- +### Line Follower
ライントレースのコード例です。
+
+### Line Follower
ライントレースのコード例です。
+ +
+
+
+
+Details
+
#### Requirements
- ライントレースセンサ
- [Raspberry Pi Mouse オプションキット No.3 \[ライントレース\]](https://www.rt-shop.jp/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1299_1395&products_id=3591)
- フィールドとライン (Optional)
-#### Installation
-
-Raspberry Pi Mouseにライントレースセンサを取り付けます。
-
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
@@ -221,18 +235,22 @@ $ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples line_follower.launch.py
Raspberry Pi Mouseをフィールドに置き、SW2を押してフィールド上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
- +
+ 次に、センサとラインが重なるようにRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW1を押してライン上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
-
次に、センサとラインが重なるようにRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW1を押してライン上のセンサ値をサンプリングします。
- +
+ 最後に、ライン上にRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW0を押してライントレースを開始します。
-
最後に、ライン上にRaspberry Pi Mouseを置き、SW0を押してライントレースを開始します。
- +
+ もう一度SW0を押すとライントレースを停止します。
+
+
もう一度SW0を押すとライントレースを停止します。
+
+  +
+
#### Configure
走行速度を変更するには[`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp)を編集します。
@@ -245,20 +263,21 @@ void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/oPm0sW2V_tY)
+
+
+
#### Configure
走行速度を変更するには[`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp)を編集します。
@@ -245,20 +263,21 @@ void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/oPm0sW2V_tY)
+
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
---
-### camera_line_follower
-
- +### Camera Line Follower
RGBカメラによるライントレースのコード例です。
+
+### Camera Line Follower
RGBカメラによるライントレースのコード例です。
+ +
+
+
+
+Details
+
#### Requirements
- Webカメラ
@@ -266,11 +285,7 @@ RGBカメラによるライントレースのコード例です。
- カメラマウント
- [Raspberry Pi Mouse オプションキット No.4 \[Webカメラマウント\]](https://www.rt-shop.jp/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1299_1395&products_id=3584)
-#### Installation
-
-Raspberry Pi Mouseにカメラマウントを取り付け、WebカメラをRaspberry Piに接続します。
-
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
@@ -282,15 +297,18 @@ $ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples camera_line_follower.launch.py video_devi
停止させる場合はSW0を押します。
カメラ画像は`camera/color/image_raw`、物体検出画像は`result_image`というトピックとして発行されます。
-これらの画像は[RViz](https://index.ros.org/r/rviz/)
-や[rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/)
+これらの画像は[RViz](https://index.ros.org/r/rviz/)や[rqt_image_view](https://index.ros.org/p/rqt_image_view/)
で表示できます。
-**画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。**
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> 画像を表示するとノードの動作が不安定になり、cmd_velや画像トピックが発行されないことがあります。
+
+#### Configure
-**ラインの検出精度が悪い場合はカメラの露光やホワイトバランスの調整を行ってください。**
+ラインの検出精度が悪い場合はカメラの露光やホワイトバランスの調整を行ってください。
- +
+ #### Parameters
@@ -315,30 +333,27 @@ $ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples camera_line_follower.launch.py video_devi
- Default: 0.20
- 走行を開始するためのライン面積のしきい値
+各種パラメータを設定する際は、以下のコマンドを実行します。
+
```sh
ros2 param set /camera_follower max_brightness 80
```
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
-
----
-
-### SLAM
-
-
#### Parameters
@@ -315,30 +333,27 @@ $ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples camera_line_follower.launch.py video_devi
- Default: 0.20
- 走行を開始するためのライン面積のしきい値
+各種パラメータを設定する際は、以下のコマンドを実行します。
+
```sh
ros2 param set /camera_follower max_brightness 80
```
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
-
----
-
-### SLAM
-
- +
+
-Raspberry Pi MouseでSLAMとNavigationを行うサンプルは[rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2)へ移行しました。
-
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
---
-### direction_controller
-
-
 +### Direction Controller
IMUセンサを使用した角度制御のコード例です。
+
+### Direction Controller
IMUセンサを使用した角度制御のコード例です。
+
 +
+
+
+
+Details
+
#### Requirements
- [USB出力9軸IMUセンサモジュール](https://www.rt-shop.jp/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=1348_1&products_id=3416&language=ja)
@@ -346,17 +361,11 @@ IMUセンサを使用した角度制御のコード例です。
- RT-USB-9axisIMU ROS Package
- https://github.com/rt-net/rt_usb_9axisimu_driver
-#### Installation
-
-LiDAR MountにIMUセンサモジュールを取り付けます。
+IMUセンサモジュールを取り付けたLiDAR MountをRaspberry Pi Mouseに取り付けます。詳細は、[マルチLiDARマウント組み立てマニュアル](https://rt-net.jp/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/RaspberryPiMouseOptionKitManual_No08.pdf)を参照してください。
- +
+
 -Raspberry Pi Mouse にLiDAR Mountを取り付けます。
-
-
-Raspberry Pi Mouse にLiDAR Mountを取り付けます。
-
- -
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
@@ -364,61 +373,76 @@ Raspberry Pi Mouse にLiDAR Mountを取り付けます。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples direction_controller.launch.py
```
-SW0 ~ SW2を押して動作モードを切り替えます。
+SW0-SW2を押して動作モードを切り替えます。
-- SW0: ジャイロセンサのバイアスをキャリブレーションし、ラズパイマウスの方位角を`0 rad`にリセットします
-- SW1: 方位角を`0 rad`に維持する角度制御を開始します
- - SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
-- SW2: 方位角を`-π ~ π rad`に変化させる角度制御を開始します
- - SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
+- SW0: ジャイロセンサのバイアスをキャリブレーションし、ラズパイマウスの方位角を`0`[rad]にリセットします
+- SW1: 方位角を`0`[rad]に維持する角度制御を開始します
+ - SW0–SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
+- SW2: 方位角を`-π ~ π`[rad]に変化させる角度制御を開始します
+ - SW0–SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
-### Troubleshooting
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> IMUの接続が正常に行われない場合があります。
+> その際は、IMUのUSBケーブルを抜き差しした後、コマンドを再度実行してください。
-IMUの接続が正常に行われない場合があります。
-その時は、IMUのUSBケーブルを抜き差ししてください。
-抜き差し実施後は、コマンドを再度実行してください。
+#### Parameters
-#### Configure
+- `p_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
+ - 角度制御用PIDコントローラの比例ゲイン
+- `i_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
+ - 角度制御用PIDコントローラの積分ゲイン
+- `d_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
+ - 角度制御用PIDコントローラの微分ゲイン
+- `target_angle`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
+ - SW1(角度制御モード)の目標角度
-パラメータで角度制御に使うPIDゲインを変更できます。
+#### Published
+- `heading_angle`
+ - Type: `std_msgs/Float64`
+ - IMUモジュールのセンサ値をもとに計算されたロボットの向き(進行方向の角度)
-```sh
-$ ros2 param set /direction_controller p_gain 10.0
-Set parameter successful
+
-
-#### How to use
+#### Usage
次のコマンドでノードを起動します。
@@ -364,61 +373,76 @@ Raspberry Pi Mouse にLiDAR Mountを取り付けます。
$ ros2 launch raspimouse_ros2_examples direction_controller.launch.py
```
-SW0 ~ SW2を押して動作モードを切り替えます。
+SW0-SW2を押して動作モードを切り替えます。
-- SW0: ジャイロセンサのバイアスをキャリブレーションし、ラズパイマウスの方位角を`0 rad`にリセットします
-- SW1: 方位角を`0 rad`に維持する角度制御を開始します
- - SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
-- SW2: 方位角を`-π ~ π rad`に変化させる角度制御を開始します
- - SW0 ~ SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
+- SW0: ジャイロセンサのバイアスをキャリブレーションし、ラズパイマウスの方位角を`0`[rad]にリセットします
+- SW1: 方位角を`0`[rad]に維持する角度制御を開始します
+ - SW0–SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
+- SW2: 方位角を`-π ~ π`[rad]に変化させる角度制御を開始します
+ - SW0–SW2を押すか、ラズパイマウス本体を横に傾けると終了します
-### Troubleshooting
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> IMUの接続が正常に行われない場合があります。
+> その際は、IMUのUSBケーブルを抜き差しした後、コマンドを再度実行してください。
-IMUの接続が正常に行われない場合があります。
-その時は、IMUのUSBケーブルを抜き差ししてください。
-抜き差し実施後は、コマンドを再度実行してください。
+#### Parameters
-#### Configure
+- `p_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
+ - 角度制御用PIDコントローラの比例ゲイン
+- `i_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
+ - 角度制御用PIDコントローラの積分ゲイン
+- `d_gain`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
+ - 角度制御用PIDコントローラの微分ゲイン
+- `target_angle`
+ - Type: `double`
+ - Default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
+ - SW1(角度制御モード)の目標角度
-パラメータで角度制御に使うPIDゲインを変更できます。
+#### Published
+- `heading_angle`
+ - Type: `std_msgs/Float64`
+ - IMUモジュールのセンサ値をもとに計算されたロボットの向き(進行方向の角度)
-```sh
-$ ros2 param set /direction_controller p_gain 10.0
-Set parameter successful
+
-$ ros2 param set /direction_controller i_gain 0.5
-Set parameter successful
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
-$ ros2 param set /direction_controller d_gain 0.0
-Set parameter successful
-```
+---
-#### Parameters
+### SLAM & Navigation
+
+SLAMとNavigationを行います。
+
+ +
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> Raspberry Pi MouseでSLAMとNavigationを行うサンプルは[rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2)へ移行しました。
+
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+
+---
+
+## License
+
+(C) 2022 RT Corporation
+
+各ファイルはライセンスがファイル中に明記されている場合、そのライセンスに従います。
+特に明記されていない場合は、Apache License, Version 2.0に基づき公開されています。
+ライセンスの全文はLICENSEまたはhttps://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0から確認できます。
+
+## Contributing
-- p_gain
- - Proportional gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- - type: double
-- i_gain
- - Integral gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
- - type: double
-- d_gain
- - Derivative gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- - type: double
-- target_angle
- - Target angle for the SW1 control mode.
- - default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
- - type: double
-
-#### Publish topics
-- heading_angle
- - Heading angle of the robot that calculated from the IMU module sensor values.
- - type: std_msgs/Float64
-
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/ghcCYOh9_MM)
-
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+- 本ソフトウェアはオープンソースですが、開発はオープンではありません。
+- 本ソフトウェアは基本的にオープンソースソフトウェアとして「AS IS」(現状有姿のまま)で提供しています。
+- 本ソフトウェアに関する無償サポートはありません。
+- バグの修正や誤字脱字の修正に関するリクエストは常に受け付けていますが、
+それ以外の機能追加等のリクエストについては社内のガイドラインを優先します。
+詳しくは[コントリビューションガイドライン](https://github.com/rt-net/.github/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)に従ってください。
+
+> :warning: Note
+>
+> Raspberry Pi MouseでSLAMとNavigationを行うサンプルは[rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2)へ移行しました。
+
+[Back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+
+---
+
+## License
+
+(C) 2022 RT Corporation
+
+各ファイルはライセンスがファイル中に明記されている場合、そのライセンスに従います。
+特に明記されていない場合は、Apache License, Version 2.0に基づき公開されています。
+ライセンスの全文はLICENSEまたはhttps://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0から確認できます。
+
+## Contributing
-- p_gain
- - Proportional gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 10.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- - type: double
-- i_gain
- - Integral gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 0.0, min:0.0, max:5.0
- - type: double
-- d_gain
- - Derivative gain of a PID controller for the direction control
- - default: 20.0, min:0.0, max:30.0
- - type: double
-- target_angle
- - Target angle for the SW1 control mode.
- - default: 0.0, min:-π, max:+π
- - type: double
-
-#### Publish topics
-- heading_angle
- - Heading angle of the robot that calculated from the IMU module sensor values.
- - type: std_msgs/Float64
-
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/ghcCYOh9_MM)
-
-[back to example list](#how-to-use-examples)
+- 本ソフトウェアはオープンソースですが、開発はオープンではありません。
+- 本ソフトウェアは基本的にオープンソースソフトウェアとして「AS IS」(現状有姿のまま)で提供しています。
+- 本ソフトウェアに関する無償サポートはありません。
+- バグの修正や誤字脱字の修正に関するリクエストは常に受け付けていますが、
+それ以外の機能追加等のリクエストについては社内のガイドラインを優先します。
+詳しくは[コントリビューションガイドライン](https://github.com/rt-net/.github/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)に従ってください。
 -#### Configure
-
-Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in [./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml) or
-[./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml).
+Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in [./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml) or [./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml).
```yaml
button_shutdown_1 : 8
@@ -115,19 +136,21 @@ button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/GswxdB8Ia0Y)
+
-#### Configure
-
-Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in [./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml) or
-[./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml).
+Key assignments can be edited with key numbers in [./config/joy_f710.yml](./config/joy_f710.yml) or [./config/joy_dualshock3.yml](./config/joy_dualshock3.yml).
```yaml
button_shutdown_1 : 8
@@ -115,19 +136,21 @@ button_motor_on : 9
button_cmd_enable : 4
```
-#### Videos
-
-[](https://youtu.be/GswxdB8Ia0Y)
+ -## Supported ROS 2 distributions
+## Table of Contents
+
+- [raspimouse_ros2_examples](#raspimouse_ros2_examples)
+ - [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
+ - [Supported ROS distributions](#supported-ros-distributions)
+ - [Requirements](#requirements)
+ - [Installation](#installation)
+ - [Binary Installation](#binary-installation)
+ - [Source Build](#source-build)
+ - [How To Use Examples](#how-to-use-examples)
+ - [License](#license)
+ - [Contributing](#contributing)
+
+## Supported ROS distributions
-- [Humble](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
-- [Jazzy](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy) (This branch)
+### ROS 2
+
+- [Humble Hawksbill](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
+- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy)
## Requirements
@@ -25,66 +38,75 @@ To run on Gazebo, click [here](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros
- Ubuntu server 24.04
- Device Driver
- [rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse](https://github.com/rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
+
## Installation
+### Binary Installation
+
+```sh
+sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-raspimouse-ros2-examples
+```
+
+### Source Build
+
```sh
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+# Create workspace directory
+mkdir -p ~/ros2_ws/src && cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+
# Clone package
-$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
+git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
-$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
+rosdep install -r -y -i --from-paths .
# Build & Install
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws
-$ colcon build --symlink-install
-$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
+cd ~/ros2_ws
+colcon build --symlink-install
+source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
```
-## License
-
-This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see [LICENSE](./LICENSE) for details.
+## How to Use Examples
-## How To Use Examples
+Sample programs for the Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-- [joystick_control](#joystick_control)
-- [object_tracking](#object_tracking)
-- [line_follower](#line_follower)
-- [camera_line_follower](#camera_line_follower)
-- [SLAM](#slam)
-- [direction_controller](#direction_controller)
-
----
+- [Examples](#examples)
+ - [Joystick Control](#joystick-control)
+ - [Object Tracking](#object-tracking)
+ - [Line Follower](#line-follower)
+ - [Camera Line Follower](#camera-line-follower)
+ - [Direction Controller](#direction-controller)
+ - [SLAM & Navigation](#slam--navigation) (Relocated [rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2))
-### joystick_control
+### Joystick Control
-This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
+This is an example with a joystick controller to operate a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-#### Requirements
+
+
-## Supported ROS 2 distributions
+## Table of Contents
+
+- [raspimouse_ros2_examples](#raspimouse_ros2_examples)
+ - [Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)
+ - [Supported ROS distributions](#supported-ros-distributions)
+ - [Requirements](#requirements)
+ - [Installation](#installation)
+ - [Binary Installation](#binary-installation)
+ - [Source Build](#source-build)
+ - [How To Use Examples](#how-to-use-examples)
+ - [License](#license)
+ - [Contributing](#contributing)
+
+## Supported ROS distributions
-- [Humble](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
-- [Jazzy](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy) (This branch)
+### ROS 2
+
+- [Humble Hawksbill](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/humble)
+- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples/tree/jazzy)
## Requirements
@@ -25,66 +38,75 @@ To run on Gazebo, click [here](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_sim/blob/ros
- Ubuntu server 24.04
- Device Driver
- [rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse](https://github.com/rt-net/RaspberryPiMouse)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
- Remote Computer (Optional)
- - ROS
+ - ROS 2
- [Jazzy Jalisco](https://docs.ros.org/en/jazzy/index.html)
- Raspberry Pi Mouse ROS 2 package
- https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse2
+
## Installation
+### Binary Installation
+
+```sh
+sudo apt install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-raspimouse-ros2-examples
+```
+
+### Source Build
+
```sh
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+# Create workspace directory
+mkdir -p ~/ros2_ws/src && cd ~/ros2_ws/src
+
# Clone package
-$ git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
+git clone -b $ROS_DISTRO https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_ros2_examples.git
# Install dependencies
-$ rosdep install -r -y --from-paths . --ignore-src
+rosdep install -r -y -i --from-paths .
# Build & Install
-$ cd ~/ros2_ws
-$ colcon build --symlink-install
-$ source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
+cd ~/ros2_ws
+colcon build --symlink-install
+source ~/ros2_ws/install/setup.bash
```
-## License
-
-This repository is licensed under the Apache 2.0, see [LICENSE](./LICENSE) for details.
+## How to Use Examples
-## How To Use Examples
+Sample programs for the Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-- [joystick_control](#joystick_control)
-- [object_tracking](#object_tracking)
-- [line_follower](#line_follower)
-- [camera_line_follower](#camera_line_follower)
-- [SLAM](#slam)
-- [direction_controller](#direction_controller)
-
----
+- [Examples](#examples)
+ - [Joystick Control](#joystick-control)
+ - [Object Tracking](#object-tracking)
+ - [Line Follower](#line-follower)
+ - [Camera Line Follower](#camera-line-follower)
+ - [Direction Controller](#direction-controller)
+ - [SLAM & Navigation](#slam--navigation) (Relocated [rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2](https://github.com/rt-net/raspimouse_slam_navigation_ros2))
-### joystick_control
+### Joystick Control
-This is an example to use joystick controller to control a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
+This is an example with a joystick controller to operate a Raspberry Pi Mouse.
-#### Requirements
+
+  +
-- Joystick Controller
- - [Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710](https://gaming.logicool.co.jp/ja-jp/products/gamepads/f710-wireless-gamepad.html#940-0001440)
- - [SONY DUALSHOCK 3](https://www.jp.playstation.com/ps3/peripheral/cechzc2j.html)
+
+
-- Joystick Controller
- - [Logicool Wireless Gamepad F710](https://gaming.logicool.co.jp/ja-jp/products/gamepads/f710-wireless-gamepad.html#940-0001440)
- - [SONY DUALSHOCK 3](https://www.jp.playstation.com/ps3/peripheral/cechzc2j.html)
+ +### Line Follower
This is an example for line following.
+
+### Line Follower
This is an example for line following.
+ -
- -
- -
- +
#### Configure
-Edit [`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp) to change a velocity command.
+Edit [`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp) to change the robot velocity.
```cpp
void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
{
- const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // m/s
- const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // rad/s
- const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
+ const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // [m/s]
+ const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // [rad/s]
+ const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // [rad/s]
```
-#### Videos
+
+
#### Configure
-Edit [`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp) to change a velocity command.
+Edit [`./src/line_follower_component.cpp`](./src/line_follower_component.cpp) to change the robot velocity.
```cpp
void Follower::publish_cmdvel_for_line_following(void)
{
- const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // m/s
- const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // rad/s
- const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // rad/s
+ const double VEL_LINEAR_X = 0.08; // [m/s]
+ const double VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.8; // [rad/s]
+ const double LOW_VEL_ANGULAR_Z = 0.5; // [rad/s]
```
-#### Videos
+ +### Camera Line Follower
This is an example for line following by RGB camera.
+
+### Camera Line Follower
This is an example for line following by RGB camera.
+ +
+ +
+
 +
+ -
-Install the LiDAR mount to the Raspberry Pi Mouse.
+Attach the LiDAR mount with the IMU sensor module to the Raspberry Pi Mouse. For details, refer to the [Multi-LiDAR Mount Assembly Manual (in Japanese)](https://rt-net.jp/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/RaspberryPiMouseOptionKitManual_No08.pdf).
-
-
-Install the LiDAR mount to the Raspberry Pi Mouse.
+Attach the LiDAR mount with the IMU sensor module to the Raspberry Pi Mouse. For details, refer to the [Multi-LiDAR Mount Assembly Manual (in Japanese)](https://rt-net.jp/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/RaspberryPiMouseOptionKitManual_No08.pdf).
- +
+